IT change management is a structured approach that enables organizations to handle changes within their IT infrastructure. When there is an internal or external requirement to make a change to an IT environment, change management ensures that these enhancements are managed effectively. The goal is to ensure changes can be made to the IT environment while minimizing disruptions and maintaining continuity.
IT change management involves various activities, including planning, testing, implementing, and reviewing changes. It’s about managing risks and ensuring that changes lead to actual improvements rather than causing disruptions or problems. It also involves communication between all stakeholders to ensure everyone understands the changes and their impacts.
Table of Contents
Toggle- IT Change Management vs. Release Management
- Benefits of IT Change Management
- Consequences of Not Using IT Change Management
- What is a Change Advisory Board (CAB)?
- Types of IT Change Management
- Tips from the Expert
- The ITIL IT Change Management Model
- IT Change Management Challenges
- IT Change Management Best Practices
- Faddom: Supporting Change Management with Application Dependency Mapping
- See Additional Guides on Key Information Security Topics
This is part of an extensive series of guides about information security
IT Change Management vs. Release Management
IT Change Management focuses on the process of managing changes in your IT services. It involves identifying the need for change, evaluating the impact, planning, testing, and implementing the change.
Release management is the process of planning, scheduling, and controlling the movement of releases to test and live environments. It ensures that the correct versions of all IT services are available when and where they are needed.
In other words, while change management is about controlling and managing changes to individual IT services, Release management is about managing and coordinating the release of new or updated services into the live environment. Both are crucial elements in guaranteeing the reliability and availability of your IT services. Release management is often the final step in the change management process.
Benefits of IT Change Management
A well-defined change management process accounts for the management of common issues that result from planned and uncontrolled change events. Benefits of developing a change management process include:
- IT services become better aligned with business requirements
- Greater visibility and communication of Change team members
- A more comprehensive approach to risk assessment
- Lower impact on operations
- Improved cost assessment for proposed changes before they are applied
- Back-out changes are reduced or are streamlined
- Problem and Availability Management is enhanced due to documented change history
- User experience, less disruption and greater productivity
- Greater agility and ability to complete more changes
Learn more in our detailed guide to IT Change Management Best Practices
Consequences of Not Using IT Change Management
There is much to be gained from a structured approach to managing changes in an IT environment, however, there’s even more that can be lost without one. Consequences of not using IT Change Management include:
- Unplanned spending caused by poorly planned changes
- Operational downtime caused by critical system failures
- Lack of productivity as staff cannot meet performance goals
- Customer attrition due to poor or non-existent service delivery
- Revenue loss
- Regulatory non-compliance that can lead to fines
What is a Change Advisory Board (CAB)?
A Change Advisory Board consists of a group of stakeholders who evaluate and endorse changes based on their potential impact, costs, and benefits.
The CAB is a governing body that oversees the Change Management process. It is responsible for evaluating proposed changes, assessing their impact, and deciding whether they should be approved or not. The members of the CAB can include representatives from various departments such as IT, business, finance, and operations.
The purpose of the CAB is to ensure that all changes align with the business objectives and do not disrupt the current IT services. By having a diverse group of stakeholders, the CAB can better assess the potential impact and benefits of each change. This ensures a balanced decision-making process that takes into account a broad range of perspectives and considerations.
In modern IT organizations, the CAB system is becoming less practical due to the fast paced nature of DevOps processes and cloud environments. Many organizations are creating more flexible and streamlined processes for change governance, which still enable oversight and feedback from relevant stakeholders.
Types of IT Change Management
Major
Major changes are high impact and high-risk items that may change or affect production systems. Major changes require CAB approval and business approval due to the financial impact they have on ongoing business. An example of a major change could be the replacement of enterprise resource planning software or migrating.
Standard
Standard changes are typically low-impact and low-risk, and also typically pre-approved. They take place periodically. Given their low-pact and risk profile, these types of changes do not follow the conventional process flow and it can be saved as a standard change template for reuse. As a result, CAB approval is not required for each standard change as they are evaluated and approved once initially.
Standard change examples include operating systems upgrades, deploying a patch, or creating a user account.
Minor
Minor changes are less risky to execute. They are typical changes that do not occur frequently but must follow each stage of the change lifecycle including CAB approval. Minor changes can also be converted to a standard change in the future. Examples include application performance improvements or website changes.
Emergency
Emergency changes are unexpected interruptions that need to be fixed as quickly as possible These can be major incidents. As emergencies, RFCs are produced in retrospect (after implementation) and approvals can be managed through Emergency CAB (ECAB). It’s a best practice to review these changes later to avoid potential infrastructure risks. Documentation is completed after the change has been executed. Examples include addressing security breaches or managing a server outage.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better manage IT change management:
-
Automate routine changes
Use automation tools for low-risk, routine changes such as patch management or user account creation. This reduces manual effort and ensures consistency, speeding up change implementation.
-
Implement real-time monitoring for change impact
Use real-time monitoring tools to immediately assess the impact of changes. This enables rapid rollback if issues arise and minimizes downtime in critical systems.
-
Integrate change management with incident management
Ensure your change management process is tightly linked with incident management to quickly assess if a change caused a new issue, allowing for faster root cause analysis. -
Conduct post-change reviews for continuous improvement
After every major change, conduct detailed reviews to identify areas of improvement. This feedback loop helps refine your change processes and reduces risk in future changes. -
Leverage AI and machine learning
Leverage tools like Faddom to map application dependencies before implementing changes. This helps identify potential downstream impacts, ensuring smoother change implementation with fewer disruptions.
The ITIL IT Change Management Model
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL), is a commonly used set of IT best practices which helps organizations effectively deliver IT services. ITIL provides a structured process for change management, which can be useful even for organizations not strictly practicing ITIL:
1. Request for Change
For a change to be initiated, it must be considered valid and there are four reasons that are acceptable:
- An incident causes a new change
- Change is created as a result of a known problem
- End-user requests a new change
- Change manager creates a change as a result of an ongoing maintenance
A Request for Change proposal is created and must contain the following information:
- Reason for change: Why it must be created, who the affected parties are, and a desired outcome
- Impact & risk assessment: Impact and risk of implementing the change are calculated and documented including configuration items
- Cost-benefit analysis: An estimated resource utilization and cost incurred with potential benefits.
- Implementation planning: Steps for implementing change along with project management members, timelines and the methodology to be applied
2. Change Evaluation and planning
With a completed proposal, the change assessment committee evaluates the submitted RFC and suggests changes. Change planning is then initiated, including the following procedures:
- Prioritizing a change after analyzing the reasons and RFC and determining the change type depending on the risk/impact
- Scheduling a change according to priority. Low priority changes are often postponed to a later date or development window. Scheduling also includes:
- Establishing a start date and end date
- Ensuring there aren’t any clashes with other planned major activities
- Creating plan details for the implementation steps and approach
- Identifying stakeholders responsible for implementing and approving the change
3. Change approvals
Communicating the change and its details to relevant stakeholders is essential. To streamline approvals, aim to automate the approval process to reduce manual effort. The approval process flow is decided depending on the type of change. Major changes require approval from the Change Advisory Board (CAB), a group of stakeholders tasked with assessing changes to an IT environment.
4. Change implementation & review
Once approved, implementation is executed with the assistance of the release management team. The release team manages the planning and testing and change review occurs once implementation is completed to determine whether it’s a success or failure. Reviews are also instrumental when revisiting and modifying existing change management processes if necessary.
Related content: Read our guide to ITIL Change Management Types
IT Change Management Challenges
Change is inevitable, but it is also challenging, especially when it comes to managing IT infrastructure. Here are several common challenges that can arise:
Prohibitive Costs
Implementing IT change management often requires significant resources, both in terms of time and money. There may be costs associated with training staff, acquiring new technology, or hiring external consultants. And these costs can quickly escalate if the changes aren’t managed effectively.
Furthermore, there can also be hidden costs that are not immediately apparent. For instance, if changes are not implemented properly, they can lead to technical debt that will require additional maintenance or development work at a later date.
Slowing Down Innovation
The rigidity of IT change management processes can inadvertently slow down innovation within an organization. While these processes are designed to minimize risk and ensure stability, they can also create bureaucratic hurdles that delay the implementation of new technologies or updates.
This can be particularly challenging in fast-paced industries where the ability to rapidly adapt and innovate is critical to staying competitive. Companies may find themselves stuck in lengthy approval and review cycles, hindering their agility and responsiveness to market changes or technological advancements. Thus, while IT change management is crucial for mitigating risks, it must be balanced with the need for flexibility and speed in innovation.
Unauthorized Changes
Unauthorized changes are changes that are made without going through the proper change management procedures. Unauthorized changes can cause significant issues, as they can lead to system instability or even system failures.
Unauthorized changes can happen for a variety of reasons. Sometimes, they are the result of employees not understanding change management procedures. Other times, they occur because the change management procedures are too cumbersome or time-consuming, and employees seek a shortcut to get things done quickly.
IT Change Management Best Practices
Make Change Management as Simple as Possible
Simplifying change management procedures helps in reducing the complexity and time required to approve and implement changes. This involves automating routine tasks, establishing clear guidelines for different types of changes, and minimizing bureaucratic hurdles.
Simplification ensures that changes can be implemented more swiftly and with less effort, thereby reducing the likelihood of unauthorized changes and increasing compliance with the change management policies. It also makes the process more accessible to all stakeholders, encouraging adherence and understanding across the organization.
Deploy Smaller Releases to Ensure Changes Succeed
Implementing smaller, incremental releases rather than large, infrequent updates can significantly improve the success rate of changes. This approach allows for more manageable testing and easier rollback in case of issues, reducing the impact on the IT infrastructure and operations.
Smaller releases facilitate quicker adaptation to feedback and changes, enabling a more agile and responsive IT environment. It also helps in identifying potential problems early in the process, thereby reducing risks and increasing the overall quality of IT services.
Measure Progress and Effectiveness of Change Implementations
Monitoring and evaluating the progress and outcomes of change implementations are essential for continuous improvement. This involves tracking the implementation process, assessing whether changes meet their objectives, and identifying any issues or areas for improvement.
By measuring the effectiveness of change implementations, organizations can learn from each change and apply those lessons to future changes. This feedback loop is vital for refining change management processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring that changes contribute positively to the IT environment and business goals.
Establish and Measure Key Metrics and KPIs
Key metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be established to gauge the effectiveness of the IT change management process. These metrics can include the success rate of changes, the impact of changes on IT services, the time taken to implement changes, and the frequency of unauthorized changes.
By measuring these KPIs, organizations can gain insights into the performance of their change management practices, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve the process. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these metrics ensures that the change management process remains aligned with organizational goals and adapts to changes in the IT landscape.
Faddom: Supporting Change Management with Application Dependency Mapping
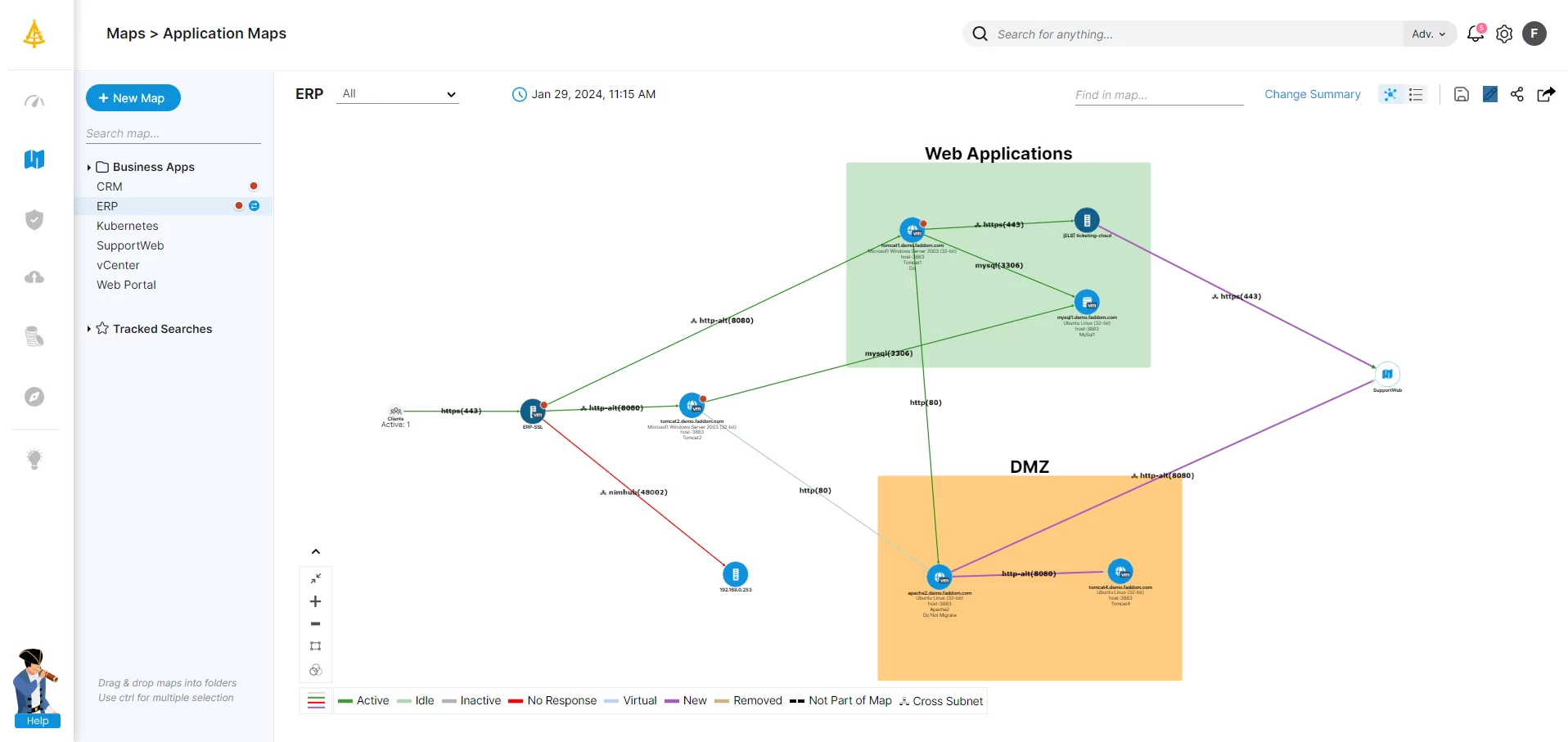
If you are managing IT changes, there is a safe and effective way to control an IT environment, ensuring that changes are less stressful and less complex and that touching one application won’t break another.
Faddom’s application dependency mapping tool discovers and maps business application dependencies in only 60 minutes. It is a 100% non-intrusive solution. It’s also agentless and credentialless, and there is no need to reconfigure firewalls – we work passively using existing network traffic protocols (IP address-based) and the map automatically 24/7 and in real-time, so our maps are always up-to-date.
Schedule a demo to learn how to discover all applications and their dependencies, plan for micro-segmentation, and more.
See Additional Guides on Key Information Security Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of information security.
IT Documentation
Authored by Faddom
- [Guide] IT Documentation: 9 Standards and Best Practices
- [Guide] Network Documentation: What to Document & 4 Best Practices
- [Product] Faddom | Instant Application Dependency Mapping Tool
IT Mapping
Authored by Faddom
- [Guide] IT Mapping: Why You Need It & 4 Ways to Map Your Environment
- [Guide] IT Service Mapping: Capabilities, Process, and Tools
- [Product] Compliance and IT Audit With Faddom
Data Security
Authored by Cloudian