Table of Contents
Toggle- What is IT Service Mapping?
- How Does Service Mapping Work?
- Key Capabilities of Service Mapping
- Benefits and Use Cases of Service Mapping
- Service Map Lifecycle Process
- Choosing IT Mapping Software
- How is Service Mapping Different from Application Mapping?
- Faddom: Application Dependency Mapping that Solves IT Mapping Challenges
What is IT Service Mapping?
IT service mapping provides organizations with a complete understanding of how applications and systems deliver internal and external business services. This includes a detailed view of the infrastructure that governs IT, OT, and the services they deliver, plus how they may overlap. Organizations must be able to see how data flows to and through applications/systems while also showing how people use them for business process fulfillment via service mapping.
The goal is to define business services across the enterprise via a map that provides a visual or graphical model of all system/process connections and how they drive business services for:
- Greater visibility across the enterprise
- Resilience through business continuity and regulatory compliance
- Detection and correction of anomalies
- Development of KPIs and metrics like average transaction duration, requests per minute, and errors per minute
(For more background, see The Complete Guide to Application Mapping and IT documentation examples and best practices.)
How Does Service Mapping Work?
Service mapping works through a series of steps that involve discovering, organizing, and visualizing the various components and relationships within an organization’s IT infrastructure. Here’s a high-level overview of the process:
- Discovery: The first step is to gather data on all the components within the IT environment, such as servers, databases, applications, and network devices. This can be done using automated discovery tools, manual inventory, or a combination of both.
- Identification: Once the components are discovered, they need to be accurately identified and classified based on their functions and roles within the IT infrastructure.
- Relationship mapping: In this step, the relationships and dependencies between the identified components are established. This includes both direct connections, such as a server hosting a specific application, and indirect connections, such as a database supporting multiple applications.
- Service definition: Next, the various IT services that the organization provides are defined. These services can be customer-facing, like an e-commerce website, or internal, like an HR management system. The components supporting each service are then mapped to their respective services.
- Visualization: The mapped relationships and services are then visualized in a graphical format, often using specialized software. This visual representation is called a service map or a dependency map. It provides a clear view of the IT infrastructure and its interdependencies, making it easier to understand the overall IT landscape.
- Maintenance and updates: To ensure the service map remains accurate and up-to-date, it should be regularly maintained and updated as changes occur within the IT infrastructure, such as the addition or removal of components or the reconfiguration of services.
Key Capabilities of Service Mapping
Service mapping provides several key features that can greatly benefit organizations in managing their IT infrastructure. Here, we discuss four essential features: visibility, accuracy, efficiency, and multi-cloud support.
Related content: Read our guide to network topology mapping
Visibility
Service mapping offers a clear and comprehensive view of the IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, applications, and services. By visually representing the relationships and dependencies between various components, it enables IT teams to better understand the entire IT ecosystem. This improved visibility is crucial for making informed decisions, identifying potential issues, and optimizing service delivery.
Accuracy
A well-maintained service map ensures that the information it contains is accurate and up-to-date. This is crucial for IT teams to effectively manage and troubleshoot issues within the infrastructure. Accurate service maps also help organizations identify redundancies, optimize resource allocation, and plan for future capacity needs.
Efficiency
By providing a clear view of the IT infrastructure and its interdependencies, service mapping enables IT teams to more efficiently troubleshoot and resolve issues. When an incident occurs, the service map can help pinpoint the root cause and affected components, reducing the time spent on diagnosing problems and minimizing downtime. Additionally, service maps can be used to identify areas for improvement, streamlining processes, and optimizing resource utilization.
Multi-cloud support
With the growing adoption of cloud-based services and multi-cloud environments, it is essential for service mapping tools to support these architectures. A multi-cloud service map provides a unified view of an organization’s entire IT landscape, including on-premises, private, and public cloud infrastructure. (Learn more about IT mapping and network mapping tools.)
Benefits and Use Cases of Service Mapping
Service mapping can only be useful if it’s based on a commonly accepted definition of a service. Services are anything that delivers value to end users or customers without the burden of costs and risks. In an organization, that can be anything from email to complex services that span product management, marketing, sales, finance/back office, operations, and customer support.
Business services go far beyond applications to the delivery chain. That includes bare metal/VM servers, database configuration, storage, and networks along with on-premises and cloud environments that support them. Providing the service without flaws requires organizations (and IT in particular) to have a holistic view of how these components integrate to deliver the service. Having this complete graphical map delivers many benefits, including a complete understanding of how an organization’s business services are delivered.
Related content: Read our guide to network microsegmentation
Organizations also gain improved operations management through inventory and infrastructure relationship knowledge across hybrid environments (on-premises and cloud) to deliver more reliable services and innovate more frequently by:
- Meeting SLAs and uptime
- Improving mean time to resolution (MTTR)
Service mapping additionally delivers improved risk management by automating processes to proactively detect, track, and eliminate security and audit compliance failures while delivering better backup and disaster recovery. The visibility gain can be used to optimize asset performance to pinpoint areas of service underperformance, such as system inefficiencies or manual processes that keep humans from doing higher-order work like improving or adding new services.
A graphical service map enables business-capability mapping (business-process mapping) to improve understanding of what the organization does best and the possibilities for expanding those capabilities. Organizations can also manage their portfolio to ensure the right mix of services to match their business strategy with budget constraints.
There is also the benefit of relationship management to enforce communication across all levels of the enterprise for a common understanding of:
- Service needs, expectations, and experiences
- Value planning
- Service quality
- Customer experiences
Business analysis brings a common understanding of organizational and customer improvement options to all stakeholders as well. Plus, improved product and service architecture management allows for an organization to maximize resource activities and flow for lower costs, top- and bottom-line growth, and efficiency.
Lastly, a graphical service map ensures that service configuration information is available at the right times and places through visualization and documentation to enable improved analysis of the service’s impact, triggers and outcomes, risks, and throughput capacity and availability.
Successful service mapping does more than discover and identify critical components and map them into services. The resulting visual graphic document creates service, source, entity, and attribute relationships that have a major impact on efficiency, security, the bottom line, and market growth.
Service Map Lifecycle Process
The service mapping process can be complex or simple depending on the organization and its needs. But every service mapping process has the following seven steps that should be followed:
1. Create a cross-functional team consisting of people who manage and depend on different components of the service along with IT admin knowledgeable about the systems connected to delivering the service.
2. Define the mapping template, which should include:
– Map orientation
– Mapping structure (hierarchical maps, mind maps, or other preferred structures)
– Naming conventions
– Additional standards for each service
3. Determine the level of detail to be captured by the service map to support service management practices while avoiding unnecessary management and communication complexity.
4. Select specific services for mapping based on:
– Top customer-facing and revenue-generation services
– Those services needing major near-term changes
5. Choose the right service mapping software.
6. Ensure the map is easily understood across IT and business leaders via techniques like dependency structure matrix (DSM) and hyperlink documentation.
7. Implement service map maintenance to make sure the map (which is a living document) is updated across its lifecycle so that it always:
- Aligns to the changing service structure/environment
- Delivers service-management value to the organization
Choosing IT Mapping Software
Typically, IT mapping tools are either agent-based or agentless asset discovery tools. Agent-based software installs a software agent for discovery across each system while agentless discovery tools forgo installing software agents at the endpoints. There are many benefits of agentless versus agent scanning, including cost efficiency, simplicity, performance, and scalability.
The criteria for choosing the right discovery tool depends on many factors from the business structure, size, intent, and budget to the software’s ability to discover and visualize services across:
- Hybrid cloud environments/architectures (on-premises and cloud)
- Network architectures
- Multi-cloud environments
- Bare metal servers
- VMs
- Containers
- Microservices
- APIs
- IoT devices, and more
Another important aspect is the service mapping software’s ability to integrate with application mapping tools, which is critical to a complete view.
How is Service Mapping Different from Application Mapping?
SMB and enterprise environments are full of complexity in the digital age where interaction and dependencies to deliver the needed functionality and services can span:
- IT/OT environments and workloads
- Applications and their dependencies
- Network architectures and devices
- Virtual and cloud systems, platforms, applications, and devices
Discovering and mapping these dependencies is critical for every organization, but that can mean the use of both service maps and application dependency mapping. It is the differences between these two processes, how they overlap, and their integration that defines how they bring greater strength to an organization.
Application mapping, also known as application dependency mapping (ADM), discovers and identifies how applications and their dependencies interact. This process is critical to:
- Incident management, to ensure high availability of applications
- Proper resource allocation
- Cloud cost optimization
- Maintaining optimum uptime
- Intelligent cloud migration and data center transformation
- Effective IT documentation and asset management as well as regulatory compliance
- Microsegmentation
Faddom: Application Dependency Mapping that Solves IT Mapping Challenges
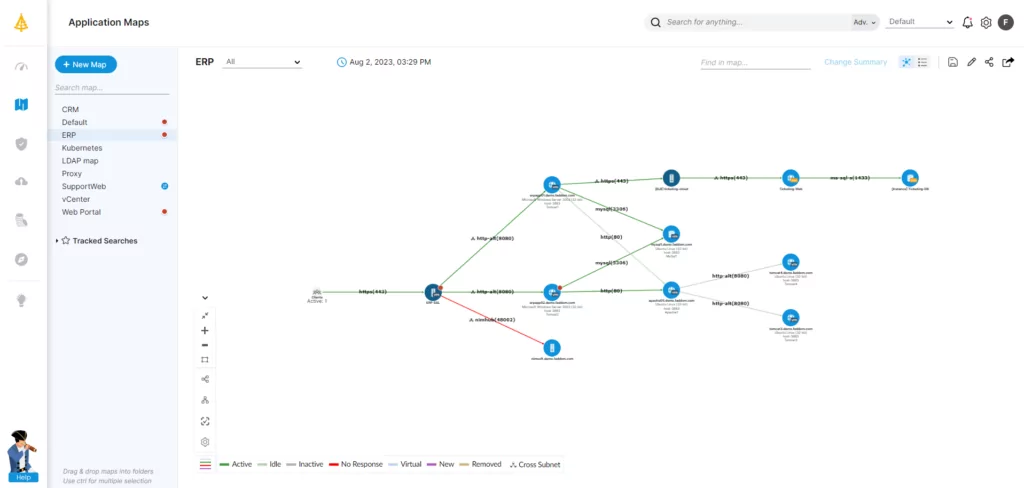
Faddom helps organizations worldwide by mapping their entire hybrid IT environments — both in the cloud and on premise — in as little as one hour with application dependency mapping. Start a free trial today!





