What is a data center migration?
Data center migration is the process of moving an organization’s data and processes from one data center to another or a cloud environment. It can also refer to moving data from one room or floor to another within the same data center. Data center migrations can be complex and time-consuming, taking months or years to complete.
Organizations may migrate their data center for a number of reasons, including:
- Reducing costs
- Moving to a colocation facility to reduce management overhead and costs
- Improving the time to market
- Migrating to a cloud environment
- Organizational expansion
- A company merger or other organizational expansion
- Regulatory requirements
Some best practices for a successful migration include:
- Planning: Ensure the new facility meets or exceeds future requirements, and that it’s compatible with current applications
- Testing: Conduct a test migration to ensure a smooth relocation
- Backup and recovery: Develop a comprehensive backup and recovery plan, including the 3-2-1 backup rule
- Inventory: Have a complete inventory of hardware components to identify dependencies and ensure compatibility
- Staff: Plan how to relocate and manage staff schedules and workflows
(For more information, see our guide to Cloud Migration.)
Table of Contents
Toggle- What is a data center migration?
- Types of data center migrations
- What are the main reasons for migrating a data center?
- What are the benefits of a data center migration?
- Tips from the Expert
- Data center migration challenges
- 10 steps to a successful data center migration
- Data center migration best practices
- Data center migration tools
- Streamline your data center migration with Faddom
Types of data center migrations
There are several types of data center migrations, each dependent on the enterprise’s objectives. Migration options include:
Consolidation migration
Consolidation migrations are a means of reducing the number of physical data centers or servers. Often, consolidation migrations are due to acquisitions, mergers, the need to cut costs or leverage virtualization solutions.
Colocation or relocation migration
Relocation or colocation migrations are a move of infrastructure from one data center to another. There are two data centers involved; the source and target location. Migration options include physical to physical, physical to virtual, virtual to virtual, physical to cloud, and virtual to cloud.
Cloud migration
Cloud migrations involve transitioning applications, infrastructure, systems, and workloads into the cloud. Cloud migrations can also involve migrating from one cloud solutions provider to another.
Learn more in our detailed guide to cloud migration strategy
Hybrid migration
Hybrid migrations are a combination of the above migration types. These take place in cases where organizations use both on-premise and off-premise infrastructure and software. Hybrid migrations are typically executed to improve resilience and business continuity.
What are the main reasons for migrating a data center?
- Reducing costs: Organizations may seek to lower operational expenses by reducing energy consumption, optimizing hardware utilization, or adopting newer, more efficient technologies. Cost reductions can also be achieved by consolidating multiple data centers into a single facility or transitioning to providers offering economies of scale.
- Moving to a colocation facility to reduce management overhead and costs: Migrating to a colocation facility allows organizations to lease space within a professionally managed data center. This reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure and eliminates the costs of maintaining physical facilities, power, cooling, and security. Organizations can focus their resources on core business functions instead of infrastructure management.
- Improving time to market: Data center migrations aimed at improving time to market often involve upgrading infrastructure to speed up deployment cycles. Migrating to modern facilities or cloud environments with advanced automation capabilities enables organizations to roll out applications, services, and updates faster.
- Migrating to a cloud environment: Cloud migrations provide scalability, flexibility, and access to advanced services like machine learning and data analytics. This migration type reduces dependence on physical hardware, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to changing workloads and pay only for the resources they use.
- Organizational expansion: As businesses grow, their IT requirements also increase. Expanding to larger or more strategically located facilities supports higher capacity, enhanced connectivity, and proximity to customers or partners. Migration may also be necessary to accommodate new systems or technology.
- A company merger or other organizational expansion: Mergers and acquisitions often result in duplicate IT infrastructure. A data center migration can consolidate resources, improve efficiency, and standardize technology across the merged organization, leading to cost savings and smoother operations.
- Regulatory requirements: Compliance with industry regulations or data sovereignty laws may require a migration to a data center in a specific geographic location or with specific certifications. Migration ensures that systems meet legal and operational standards, reducing risks of non-compliance.
What are the benefits of a data center migration?
While data center migrations occur for various reasons, there are several benefits that can be realized. These include:
Lower operational costs
As the cloud becomes a viable option, more organizations are transitioning to cloud-enabled networks. The cost of hosted applications and infrastructure proves more affordable than the larger CAPEX cost organizations must absorb every three to five years.
Modern hardware and software
Migrations often present the chance to upgrade infrastructure and modernize software. With access to modernized equipment and applications, businesses can realize productivity gains.
Learn more in our detailed guide to cloud migration checklist
A faster Network
Enterprises have the opportunity to leverage edge computing, helping reduce latency for application users.
Improved security threat posture
With cloud-based solutions becoming the backbone of many enterprises, security becomes less of a concern. Large security and threat management R&D investments by hyperscalers ensure the best threat detection and prevention solutions, improving cybersecurity for enterprises.
Regulatory compliance is easily achieved
Hyperscale cloud solutions are backed by heavy investment to meet compliance requirements, easing the investment required to meet regulatory compliance as an enterprise.
Greater scalability
Scalability is a key concern for organizations. As the need for more computing power, storage, and network bandwidth increase, the costs of keeping up with these demands can be exorbitant. Migrating to cloud ecosystems presents enterprises with access to state-of-the-art infrastructure and services that can be scaled alongside operational requirements, without the large investment.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you ensure a successful data center migration:
-
Create a detailed migration roadmap
Outline each phase, including timelines, dependencies, and resource allocation, to prevent delays and manage risks.
-
Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment
Identify potential pitfalls and develop contingency plans to address them proactively.
-
Implement robust data backup and recovery plans
Ensure all data is backed up and recovery processes are tested before migration to avoid data loss.
-
Utilize automated migration tools
Leverage automation to handle repetitive tasks and reduce manual errors.
-
Perform thorough post-migration testing
Validate that all systems, applications, and data are functioning as expected in the new environment.
Data center migration challenges
While data center migrations can be very beneficial, they are a complex and risky undertaking. Here are some of the key challenges:
Inadequate planning
Some organizations neglect planning and underestimate risks when migrating between data centers because they may not fully understand the complexity and potential impact of the process. This can lead to unexpected downtime, data loss, or other serious issues that can have a negative impact on business operations.
Having a sufficiently detailed migration plan is essential to minimize risks and ensure a smooth transition. The plan should include a detailed inventory of all IT assets, a comprehensive timeline, and contingency plans for potential issues. It should also include testing and verification procedures to ensure that all systems are functioning correctly after the migration is complete.
Gaps in the hardware inventory
It is important to have a complete inventory of hardware components when implementing a data center migration because it allows organizations to identify dependencies between systems and ensure compatibility. Organizations often focus on machines like CPUs and motherboards while ignoring devices like routers, cables, PSUs, and fuses, which can be problematic.
These components are critical to the overall functioning of the data center infrastructure, and failure to identify them can result in unexpected downtime or compatibility issues during the migration process. Listing dependencies between system components is crucial because it allows organizations to understand how different components interact with each other and ensure that they are migrated in the correct order.
Inaccurate planning for performance and capacity
Incorrectly estimating the performance level and storage capacity of the new data center’s hardware can cause several problems for an organization. If the hardware is underestimated, the organization may experience performance issues, such as slow application response times, which can lead to decreased productivity and user dissatisfaction.
Additionally, if storage capacity is underestimated, the organization may run out of space quickly, which can result in data loss or downtime while new storage solutions are implemented. Overestimating hardware can also be a waste of resources, resulting in unnecessary expenses for the organization.
Data loss
Critical data loss is the worst outcome for a data center migration because it can have severe consequences for an organization’s operations and reputation. Causes of data loss during a migration can include provider networking issues, unexpected power outages, breaks in communication during data transfer, security vulnerabilities, errors in data retention policies, human error, and natural disasters. Ensuring data backup and recovery plans are in place and tested before the migration can help minimize the risk of data loss.
10 steps to a successful data center migration
To ensure a smooth transition from your existing computing environment to a new one, it’s recommended that you use the following guidelines:
- Create a viable business case. A data center migration business case outlines a clear case for making the transition. It includes a risk assessment and discovery phase, cost analysis, implementation plan, and identifies who will run the project.
- Get buy-in from all stakeholders. Migrations should benefit all staff, however, without buy-in can cause frustration and hurt productivity. Establish clear and open communications with all stakeholders and provide regular updates on the migration project. Ensure that the benefits of the migration are communicated, especially in the context of how it will serve each stakeholder and division.
- Establish roles and responsibilities. Identify and recruit team members to assist with the migration. Include core team members that provide track project status and manage the budget, technical experts to develop the migration strategy, and business stakeholders who identify risks and issues associated with the migration.
- Review contractual obligations. Migrations can require leaving one physical address for another. Ensure that any lease agreements have been reviewed and contracts terminated in advance and according to lease agreement obligations to avoid unnecessary costs.
- Create an inventory of all assets. Before migrating establish what assets must be moved and identify all application dependencies along with technical requirements. Ensure that hardware is accounted for and determine which infrastructure (including communications equipment) will be moved or replaced during the migration.
- Determine the architecture and design specifications. Establish how data will be moved, where data will be stored, and how it will be tested.
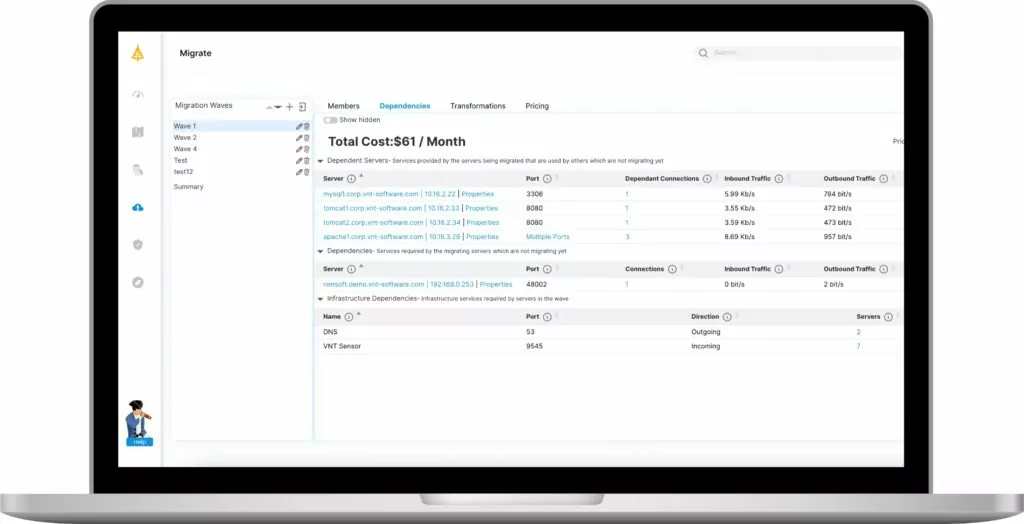
- Migrate in batches and systematically. As infrastructure is machinery and failure is possible, segment data into batches or categories. Smaller or categorized data subsets are easier to migrate and test for integrity than large data volumes. It is important to map the networks’ dependencies and to have full visibility of the infrastructure before, during and after the migration waves occurred.
- Develop efficient staff schedules. Data center migrations impact entire organizations. Ensure that workflow planning has been accounted for to limit or completely remove any impact to business operations during the migration.
- Review audit trails and logs. With a migration completed, it’s essential to confirm that all data has been correctly migrated to avoid applications with dependencies from failing to operate efficiently or causing productivity bottlenecks.
- Optimize the new environment. Post-migration, examine the new environment for improvement. Optimization also includes identifying opportunities to cut costs even further by identifying which services are not required, and by leveraging features like automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to free up human capital to focus on higher-level tasks.
Data center migration best practices
Organizations can ensure a successful data center migration by implementing the following practices.
Plan the Migration
Effective planning is the foundation for a successful data center migration. Begin by creating a detailed roadmap that outlines each phase of the migration, including specific timelines, resource allocation, and dependencies between tasks. Ensure that all stakeholders are aligned on the plan and aware of their responsibilities to prevent miscommunication and delays.
Another critical aspect of planning is risk assessment. Identify potential issues that could arise during the migration, such as compatibility challenges, downtime, or regulatory requirements. Develop contingency plans to address these risks proactively, ensuring that business continuity is maintained throughout the process.
Implement Thorough Testing
Testing should be conducted at multiple stages to validate the migration process and minimize errors. Start with a pilot migration involving non-critical systems or data. This allows teams to identify and resolve any technical issues in a controlled environment before scaling to full migration.
After the migration is complete, perform rigorous testing of all applications, systems, and network configurations in the new environment. Test for performance, data integrity, and functionality to confirm that everything operates as expected and meets the organization’s requirements.
Prepare Backup and Recovery
Having a reliable backup and recovery strategy is essential to mitigate the risk of data loss. Implement the 3-2-1 backup rule: maintain three copies of data, stored on two different media, with one copy offsite. Test backups regularly to ensure they are functional and can be restored if needed.
Ensure that recovery procedures are documented and tested before the migration. Simulate disaster scenarios to verify that backups can be restored within acceptable timeframes, minimizing the impact of unexpected failures during the migration.
Establish an Inventory
A comprehensive inventory of IT assets is critical to identifying dependencies and ensuring compatibility in the new environment. Document all hardware, including servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and smaller components like cables and power supplies. Include details about each component’s specifications, age, and condition.
In addition to hardware, inventory software applications and their interdependencies. This will help ensure that all necessary components are migrated in the correct sequence, avoiding compatibility or performance issues in the target environment.
Coordinate with Staff
Data center migrations require careful coordination among IT staff, business units, and external vendors. Assign clear roles and responsibilities to each team member to prevent confusion and ensure accountability. Include subject matter experts who can address technical challenges during the migration.
Plan staff schedules to minimize disruptions to business operations. If the migration requires work during off-hours or weekends, ensure that team members are informed well in advance and have the resources they need to execute their tasks.
Data center migration tools
There are various tools available to assist with data migration projects. These tools can be broadly categorized into the following categories:
-
- Data migration tools: These tools facilitate the actual transfer of data from the source to the target environment. These tools include extract, transform, load (ETL) tools, replication tools, and backup and recovery tools.
-
- Testing and validation tools: These tools help in verifying the migrated data and ensuring that it is functioning correctly in the new environment. Testing and validation tools include data profiling and quality tools, migration simulation tools, and performance testing tools.
-
- Monitoring and management tools: These tools help in monitoring the migrated environment, identifying issues, and managing the ongoing operation of the infrastructure. These tools include monitoring and analytics tools, configuration management tools, and security and compliance tools.
-
- Planning and assessment tools: These tools help in assessing the existing infrastructure, identifying dependencies, and planning for the migration. Some of the tools in this category include discovery and inventory tools, application dependency mapping tools, and migration readiness assessment tools.
One specific tool worth mentioning in the planning and assessment category is application dependency mapping tools. These tools help identify the dependencies between applications and infrastructure components in the existing environment. This information is critical for planning the migration and ensuring that all dependencies are accounted for in the new environment.
Application dependency mapping tools can also help in identifying potential issues and risks associated with the migration, which can be addressed proactively to minimize disruption to the business.
Streamline your data center migration with Faddom
Planning is the most crucial aspect of any data center migration, and Faddom is the ideal platform to ensure that nothing is overlooked. With Faddom’s advanced application dependency mapping, you gain unparalleled visibility into your IT environment, facilitating a seamless and well-informed migration process..
- Comprehensive Discovery: Faddom maps all your application dependencies in under 60 minutes, providing real-time insights and ensuring nothing is left behind.
- Non-Intrusive Solution: 100% agentless, credential-free, and no need to reconfigure firewalls. Faddom works passively with network traffic for accurate results without disruption.
- Plan with Confidence: With Faddom, you eliminate guesswork, reduce risks, and accelerate the planning phase, which often consumes 80% of migration efforts.
- Migration Optimization: Identify underused resources to improve efficiency and lower costs in your new environment.
Learn more about how Faddom simplifies even the most complex migrations so you can execute them precisely and achieve lasting success.
Schedule a call with our experts, and let us show you how Faddom can support your migration projects!