Today’s cyber threats have convinced most business and IT leaders that ransomware, with its potential for business downtime and loss, is a primary reason for disaster recovery (DR) planning. However, a ransomware DR plan is only as effective as an organization’s deep understanding of its data, IT infrastructure, and application dependencies. Gaining that understanding as the foundation of a ransomware discovery plan can be a complex process in a hybrid and distributed enterprise world.
Fully grasping the nature and meaning behind disaster recovery and malware is an ongoing process. Phishing attacks are the primary ingress for ransomware, which have increased by 13% since 2021 alone, dwarfing the total of several previous years. (For more information, see our Guide to Disaster Recovery.)
The driving force behind this statistic is the growth in ransomware vulnerabilities, strains, and incidents spurred by human error. Once in the network, ransomware takes its time to find files, access permissions, and find other vulnerabilities in a growing enterprise data landscape.
This all makes the goal of building a solid DR plan that mitigates the risk of ransomware attacks and data loss even more complex. It’s simultaneously true that organizations must meet the need for uninterrupted access to data, applications, workloads, infrastructure, and endpoints beyond the network’s edge.
Disasters can be equally varied, unpredictable, and often regionally impactful, but ransomware attacks are an equal opportunity disaster that arguably poses the hardest recovery. That’s why it’s best to build a disaster recovery plan on the foundation of understanding ransomware and its impact on organizations across the globe.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe State of Ransomware
What makes ransomware more insidious than other forms of malware is its ability to encrypt files and data? There is no guarantee that an organization can access the files and data with the decryption key obtained via payment to the attackers. Ransomware strains also continually grow with fresh approaches like ransomware as a service (RaaS). This makes it possible for any bad actor to gain access to ransomware strains and use them with no coding knowledge, which exponentially increases the potential victim count.
The Sophos ransomware report for 2022 reveals that 66% of surveyed organizations experienced a ransomware attack last year—this figure stood at 37% in 2020. The survey polled 5,600 IT professionals from all sizes of organizations, with over 950 detailing ransom payments forced upon them.
2022 Ransomware Attacks and Costs
Major attacks across the globe in 2022 alone included the first attack on an entire country (Costa Rica). Actors demanded $20 million and halted finance, government services, and trade. Another attack targeting Costa Rica’s healthcare and social security system followed.
The victims of ransomware include both public and private sectors and range from the smallest business to the largest global enterprise.
The Sophos report additionally showed that 1 in 10 organizations are paying $1 million or more in ransoms, with the highest average being $2.04 million (manufacturing) and the lowest $197,000 (healthcare). Extortion for the release of data is only one major impact to an organization affected by a ransomware attack. Since there is no guarantee that the decryption key provided on payment will work, irreversible data loss and business downtime are long-term repercussions that can cost millions to remedy.
These costs accrue through ransom payments, remediation of the damage/IT environment, and possible regulatory violation fines. There is also reputational damage to consider. An Arcserve report found that 28% of customers would switch to a competitor if they learned of a ransomware attack; it also shows that this percentage increases as downtime goes beyond 24 hours.
Brand Loyalty, Market Share, and Customer Loss
There are countless stories about businesses losing money, customers, and brand loyalty because of downtime from ransomware or other disasters. The Veeam 2022 Ransomware Trends Report estimates $1,467 per minute in downtime costs for the average enterprise.
Coupling these actual costs with customer attrition and decreased brand loyalty/market share can add up to massive losses. These ongoing costs can affect an organization for years with some never fully recovering.
Data loss from a ransomware attack can vary depending on its critical nature and the amount of data lost. One recent study reports a loss of over 34 TB of personal and other sensitive data in both May and June of 2022 across the EU, U.K., and the U.S.
Whether it’s phishing to gain access to a network or security vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit, there are only two options for organizations that fall victim: to pay or not to pay the ransom once the attacker has access and control of data and files. That’s a major reason why many organizations, CIOs, CTOs, CISOs, and cybersecurity experts regard disaster recovery as the best defense against ransomware.
Disaster Recovery as the Best Ransomware Defense
While there is no way for a business to avoid disaster forever, a DR plan is the best defense for a fast and full recovery. This plan will minimize disruption, limit damages from a ransomware attack or other disaster, and provide the business with a coherent plan for pre- and post-recovery.
A ransomware DR plan provides recovery from disaster with a focus on data and access encryption. Organizations, however, must first achieve a basic understanding of business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR).
What Is BCDR?
Business continuity and disaster recovery provides a way for organizations to create processes that support recovery from a disaster like a ransomware attack and continue business operations without interruption. Business continuity focuses on policies and procedures that keep business operations going. Disaster recovery focuses on the technology of backups, including restoring servers and networks, data backup copies, and backups of an enterprise’s entire system setup.
Backup Standards and Approaches
The most resilient and effective backup plan for disaster recovery uses off-site backups to mitigate downtime risks. The ongoing standard for backup has been the 3-2-1 strategy. This is where the business creates three backup copies of the data and places them on two different media types with off-site storage of one copy.
The 3-2-1-1-0 backup strategy has changed this in recent years where the additional “1” stands for an additional offline copy for immutability (unchangeable). The “0” represents the storage of all copies without errors via regular testing and monitoring.
Different backups that are commonly used include tape backups, cloud backups, and hybrid cloud backups that combine onsite and cloud backups. Many businesses are turning to a disaster-recovery-as-a-service (DRaaS) model where a third-party cloud provider handles the DR cloud orchestration and backup via a SaaS solution interface. It’s only logical that organizations start by determining DR goals for an effective cloud-backup strategy before choosing a backup approach.
Steps in a Disaster Recovery Plan
Each organization starts with an understanding of the likely disasters based on their region and sector. For example, earthquakes and tornadoes may be unlikely in some regions while cyberattacks such as ransomware can be high and nondiscriminatory based on region, business size, or sector. They can then look at the impact and costs of such a disaster.
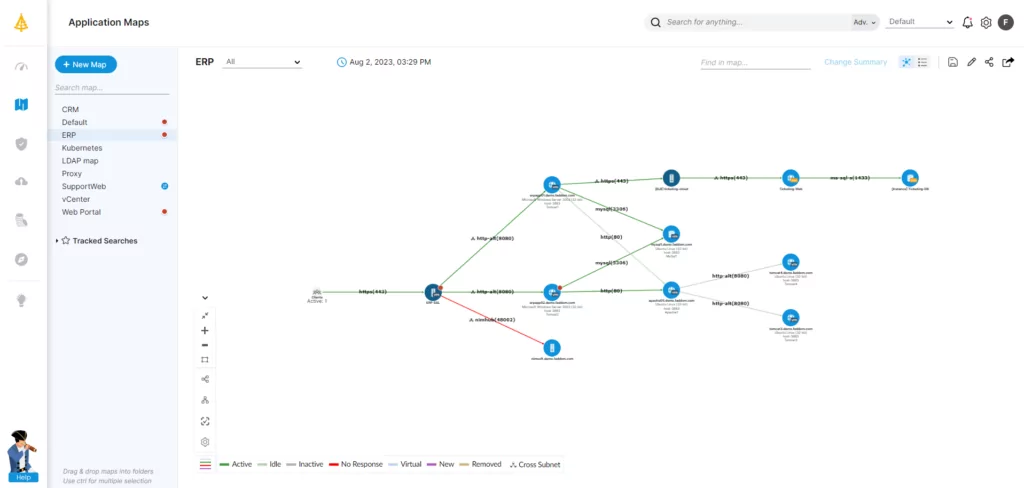
The next step is to determine the organization’s critical assets to be protected including applications, data sets, and systems. Discovering IT infrastructure (e.g., networking and switches), applications/dependencies, workloads, databases, and devices is just a start.
The comprehensive view must include on-premises data centers and cloud environments, which are crucial to creating a comprehensive ransomware disaster recovery plan. This requires detailed discovery and mapping of IT infrastructure, along with applications and their compute, storage, and network security aspects in order to determine:
- Frequency of backups
- Data types to be protected (physical or virtual)
- Amount of data that needs to be copied and for how long
Regulatory compliance (HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, PPA) is a major part of ransomware discovery since data such as personally identifiable information (PII), personal health information (PHI), and payment card information (PCI) for personal financial data may come into play.
Organizations must also protect intellectual property data, which can be wide-ranging across every business. This all requires ensuring the protection of data at rest (on servers and within databases connected to applications) and, in transit (moving across the network and from on-premises to the cloud and beyond).
Assets/devices can include PCs, tablets, applications, servers, network components, IoT devices, APIs, and more. Once discovered and mapped, organizations can then group them into critical, important, and non-critical asset categories.
This is where the organization must define its recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO). RTO is the amount of time a business can go without access to critical data or systems, while RPO refers to how old the recovered files from backup storage can be and still get the business back to normal operations. RPO also informs backup frequency.
A disaster recovery plan must constantly change to meet changing recovery needs. This requires constant testing of each step in the plan to ensure it works and is always relevant via updates, modifications, and new training where needed. The plan must also include regular discovery and mapping of IT assets as a part of the foundation to track changes for ongoing adjustments.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips to strengthen your ransomware-focused disaster recovery (DR) plan:
-
Use immutable backups
Implement backups that cannot be altered or deleted, such as those in a 3-2-1-1-0 strategy, to safeguard against ransomware encrypting your backup files.
-
Prioritize RTO and RPO alignment
Clearly define recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) based on business-critical systems to minimize downtime and data loss.
-
Automate IT asset discovery
Regularly map applications, dependencies, and infrastructure using automated tools to ensure your DR plan covers all evolving assets and systems.
-
Test recovery frequently
Conduct regular, realistic recovery tests to verify that backups are functional and that RTO/RPO targets can be met under ransomware scenarios.
-
Segment and monitor networks
Use network segmentation and advanced monitoring to contain ransomware spread and ensure that critical assets are isolated for faster recovery.
IT Discovery and Mapping for DR Plan Development
The modern SME or global enterprise has thousands of IT assets, devices, and workflows with untold data stores that have hundreds of interdependencies. This organizational landscape is constantly changing as each business develops new processes, applications, and endpoints. Having a continually updated and single-pane-of-glass view of everything requires a comprehensive discovery and mapping approach.
Organizations can only do this via an automated solution that is agentless so it doesn’t affect normal operations as it maps their IT asset landscape. Organizations also need to have a comprehensive record of services via IT service mapping to see how these assets connect to business services.
Having a unified approach to discovering and mapping the entire IT infrastructure environment is a tall order. This would include applications, workloads, devices, dependencies, and services across on-premises and cloud environments. That doesn’t change the fact that without this singular approach, BCDR plans, and ransomware disaster recovery plans in particular, may fail a business.
DR testing and the chosen RPO and RTO are all dependent on regular asset discovery and mapping since assets like applications and workloads are constantly changing. This mapping ensures that the organization places all updated assets, dependencies, databases, and services within the DR plan for future testing.
In Conclusion
Organizations around the globe understand that ransomware is the beginning of a complex set of challenges that can spell disaster for a business. These challenges come into play at any point from loss of access to business recovery. The costs can be insurmountable and ongoing, but this blog provides an understanding of the best roadmap to minimizing risk by:
- Implementing a BCDR plan to avoid downtime and loss from a ransomware attack with an RTO and RPO based on business needs
- Ensuring the DR plan covers discovery and mapping, disaster recovery procedure development, testing procedures, testing analysis, and lifecycle management of the recovery process
- Having the right IT infrastructure and application discovery and mapping to understand business processes and services as the foundation of developing a comprehensive ransomware DR plan
- Implementing ongoing discovery and mapping to improve continuous DR testing and recovery preparedness
- Using this approach to reach the goal of minimizing or eliminating the risks of business downtime, loss of revenue and brand loyalty, ransomware payments, and regulatory violation fines that can all cost a business competitive positioning
Every organization’s IT and business process environment is constantly changing, just like ransomware threats. Disasters for every business are a matter of when not if.
Organizations should view a ransomware attack and subsequent data, application, and infrastructure access loss as being among the worst-case scenarios. There are countless security tools and technologies available today to stop an attack. However, BCDR is the only way to guarantee a recovery that is fast, affordable, and complete—with minimal loss.
Every successful DR plan relies on visibility into the IT infrastructure, application, and services environment across on-premises, the cloud, and beyond the network edge. Having a comprehensive, automated solution for mapping and discovery is the starting point to achieving an accurate view of ongoing environment changes and an effective BCDR strategy.
Meet Faddom
Faddom’s agentless application dependency mapping platform provides a complete, real-time view of your hybrid IT infrastructure—on-premises and in the cloud—in under an hour.
- Visualize Critical Dependencies: Map applications, servers, and networks for seamless recovery.
- Strengthen Ransomware Resilience: Identify vulnerabilities and enhance recovery strategies.
- Keep Your DR Plan Accurate: Continuously update your IT mapping for faster, smarter disaster recovery.
Get the clarity you need to minimize downtime and safeguard your operations.
Start your free trial today by filling out the form in the sidebar!