Before the COVID-19 pandemic, cloud computing was something that organizations slowly explored and adopted. In a post-pandemic world, digital transformation has become essential to business operations worldwide. As such, companies across industries continue to invest heavily in technology and security.
According to Gartner, enterprise spending on public cloud services is expected to grow by 20.4% to $494.7 billion this year. By 2023, that number is forecasted to rise to almost $600 billion.
However, not having an in-depth understanding of an organization’s security and technology needs can quickly lead to budget deficiencies and waste. To mitigate risk, it’s always best to formulate an information technology audit (or IT audit) to better understand the company’s current technology infrastructure and security posture in order to determine the best way forward. (This is part of an extensive series of guides about compliance management.)
Table of Contents
Toggle- What is an IT Audit?
- What is the Goal of an IT Audit?
- What Are the Different Types of IT Audits?
- Tips from the Expert
- How Do You Prepare for an IT Audit?
- How Do You Conduct an IT Audit?
- How Do Companies Use IT Audits?
- What Are the Potential Challenges of IT Audits?
- How Faddom Can Help with IT Audits
- Learn More About IT Audits
- See Our Additional Guides on Key Compliance Management Topics
What is an IT Audit?
Enterprises engage in IT audits to examine and evaluate an organization’s IT infrastructure, policies, and procedures as well as do IT documentation. For example, companies analyze the company’s network, applications, security protocols, and data use and management.
This approach also assesses the organization’s policies, procedures, and operational processes against established internal policies and recognized industry standards. Whenever there is a presence of adequate security and compliance protocols, businesses still require a line of action to ensure proper preparation for an unlikely event like a data breach or ransomware attack.
What is the Goal of an IT Audit?
An organization’s IT audit goals can vary depending on the specific business and industry vertical. However, for the most part, the majority of enterprises share the following objectives:
- Accelerate the data collection process
- Align IT assessment and IT strategy
- Do IT asset management
- Eliminate potential bottlenecks in data flow
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Ensure verifiability and reliability
- Improve operational workflows
- Identify potential vulnerabilities, threats, and risks and set up controls to mitigate them
- Reduce IT-related costs
- Systematize, enhance, and integrate business processes
What Are the Different Types of IT Audits?
There is a wide variety of IT audits, but they can be loosely divided into two categories:
- Application control: A security measure to restrict unauthorized applications from putting data and systems at risk. The primary objective is to verify that records are accurate and complete and that their entries are valid.
- General controls: Ensure data availability, confidentiality, and integrity. IT departments can apply these basic IT system controls to applications, databases, operating systems, and support. General controls also examine the logical and physical security of all data centers and resources.
Client/Server, Telecommunication, Intranet, and Extranet Audit
As the name suggests, this audit concentrates on telecommunication controls on the client and server side to ensure efficiency and timeliness. This approach helps ensure that proper measures are in place to govern client, server, and network connections.
Information Processing Facilities Audit
Comprehensive IT audits also evaluate all data processing facilities, including third-party external data centers. The audit examines the entire IT infrastructure, hardware, operating systems, and applications.
The goal of the information processing facilities audit is to verify that data is processed accurately and in a timely manner, even under significantly disruptive conditions. It is also beneficial to leverage this approach to complement your cloud migration checklist.
Management of IT and Enterprise Architecture Audit
It is critical to audit IT and enterprise architecture management protocols to ensure the structured management and efficient control of the data processing environment. This approach also assesses the frameworks and tools used to follow best practices.
Security Audit
Information security audits analyze how effective an organization’s established security protocols are. It is also ideal at this stage to test the effectiveness of the organization’s IT disaster and recovery plan.
However, unlike other types of IT audits, an external partner always conducts security audits by examining all activities, system records, and related documents. This approach helps identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities in-house security teams may have missed.
Systems and Applications Audit
A systems and applications audit concentrates on the applications and systems in an organization. This type of audit helps verify security across every level of enterprise activity. For example, it checks if all systems and applications on the network are appropriate, efficient, reliable, and up to date.
Systems Development Audit
As better systems emerge, cloud infrastructures will evolve at an accelerated pace. As such, enterprises operating in fast-paced cloud environments must ensure that all systems under development meet their goals and established standards.
Technological Position Audit
Technology position audits evaluate the organization’s current technologies and the value they add to business goals. This audit also examines the business’ future technological needs and categorizes them as:
- Base: A description of the past or “yesterday’s” technology and industry situation and competitive advantage.
- Key: A description of the present or “today’s” technology and industry situation and competitive advantage.
- Pacing: A description of the future or “tomorrow’s” source of competitive advantages based on potential business opportunities created by current developments.
- Emerging: A description of technology opportunities that could evolve into business opportunities and longer-term challenges. Businesses will consider high-risk emerging technologies and opportunities, but many will never be realized.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better conduct and leverage IT audits effectively:
-
Use continuous auditing tools
Implement real-time monitoring to detect and address compliance or security issues as they arise, minimizing potential risks and disruptions.
-
Align audits with business risk management
Integrate IT audits into your overall business risk management framework to ensure that technology risks are considered alongside business priorities, enabling more strategic decision-making.
-
Automate routine audit processes
Utilize automation for repetitive tasks like data gathering and compliance validation. This increases efficiency, reduces human error, and allows auditors to focus on more complex issues.
-
Adopt a zero-trust security model
During IT audits, assess your adherence to zero-trust principles, ensuring every user and device is authenticated and authorized before accessing resources, even within your internal network.
-
Map application and data dependencies
Focus on understanding the interdependencies between applications and data flows. This knowledge is crucial for effective risk management, especially during cloud migrations or when integrating new technologies.
How Do You Prepare for an IT Audit?
Preparing for an IT audit will ensure that you don’t run into potential hurdles down the road. To avoid potential disruptions later, inform all stakeholders about the IT audit as soon as possible.
From management to support verticals, everyone within the organization must be ready to provide details or documents during the audit. These documents include organization charts, internal and external policies, procedure documents, and descriptions of master data listings.
Before the audit, it will help to do the following:
- Create an IT asset inventory
- Create a list of current controls and safeguards
- Get a document checklist
- Get your IT policies and procedures ready
- Prepare for the unknown
You can also conduct surveys about technology related to issues and their severity to help the auditor prioritize the tasks.
How Do You Conduct an IT Audit?
Organizations that want to conduct the IT audit internally can start by performing a high-level overview of the entire technology ecosystem and procedures.
IT audits usually take place in four phases:
1. Planning
Thorough planning often leads to smooth and successful technology audits. Whenever businesses don’t have a good grasp of internal IT processes and procedures, it can result in unexpected delays, costs, and even false conclusions.
Successful IT audits follow these principles:
- Risk management
- Due diligence
- Confidentiality (integrity, objectivity)
- Documentation (comprehensive)
- Internal controls
- Audit reporting (clear and transparent)
- Knowing your enterprise architecture frameworks
Before initiating an IT audit, it is best to get as much help as possible. Organizations can work with external IT partners, consultants, and specialists to formulate a detailed IT audit plan outlining the scope, goals, budget, processes, and milestones.
2. Test and Assess Current Controls
Just like financial audits, technology audits also demand tests of internal controls. The primary objective is to understand if the controls in place are sufficient to mitigate risks and align with the overall company goals.
The testing phase will allow auditing teams to prioritize potential threats and weaknesses based on their findings. IT audits often follow the COBIT ISACA framework of IT controls to detect internal and external threats.
3. Audit Completion/Reporting
Once the IT audit team completes an audit, they will document their findings. Whenever specific controls fail to deliver, they will provide evidence and advise on how to resolve it. Following completion of the IT audit, the auditor will produce an in-depth report of their findings.
4. Follow Up
Finally, the IT audit report recommendations are applied, and proposed improvements are implemented. Again, organizations must undergo another testing round to ensure that IT audit resolutions work as intended.
Once the follow-up proves to be successful, the IT audit will be officially closed.
How Do Companies Use IT Audits?
Engaging in regular IT audits provides a whole host of benefits. For example, IT audits help eliminate inaccuracies and inefficiencies in IT management and overall operations. It is also critical to protecting a company’s IT infrastructure and valuable digital assets.
Financial Review and Fraud Detection
Whenever enterprises analyze their operations, workflows, and internal controls, they can quickly detect opportunities to cut costs. They can also identify irregularities that can potentially lead to financial fraud.
With IT audits, enterprises won’t be able to determine the best way to distribute resources. They also won’t know the most profitable way to run their operation without disruption.
Data Security and Risk Reduction
Regular audits expose risks related to data availability, confidentiality, as well as integrity of IT processes and the overall infrastructure. This approach provides opportunities for organizations to resolve potential threats while ensuring business continuity.
Sometimes companies might have to accept certain risks because of performance issues or budget constraints. Whenever this is the case, businesses must adapt to working in that environment with strict controls as well as know the difference between active scanning and passive scanning and agentless scanning versus agent-based scanning. Agentless network discovery can be important to consider.
IT audits also ensure sensitive data security during an active data breach. IT teams will also be ready to respond to an active security event.
IT Governance
IT governance protocols establish the structure and framework of the organization and best practices. This method helps ensure that enterprise technology protocols support business goals.
In that sense, technology audits play a critical role in maintaining compliance during daily operations while adhering to local and national rules and regulations.
IT audits also ensure that management understands the risks, controls, and overall value of their IT infrastructure. Whenever staff follows company policies and protocols, it will enhance operational efficiencies and security.
System Integrity
IT audits let management know if they are investing in the right technologies (or not). This approach ensures that the organization uses the most appropriate system to achieve business objectives. Whenever present technologies fall short, an IT auditor will recommend better alternatives.
Future Budgeting and Scaling
Businesses often leverage IT audit reports when planning for the future. With the benefit of understanding the potential of the current IT infrastructure, management can budget appropriately and plan ahead.
Most often, having an in-depth understanding of how the company uses applications and cloud resources will help businesses scale seamlessly and cost-effectively.
What Are the Potential Challenges of IT Audits?
Considering the complexities of the current threat landscape and regulatory compliance requirements, conducting IT audits is far from straightforward.
Data Management and Governance
\It is becoming more and more challenging to audit data management and governance protocols. When organizations add artificial intelligence, machine learning, and real-time monitoring, the risks associated with them also become increasingly complex.
As data powers digitally transformed enterprises, regularly reviewing how the organization manages and uses data is key. In this case, the IT audit report must highlight both risks and opportunities to make data a competitive differentiator.
Cybersecurity and Privacy
As companies operating in the cloud become mature and more sophisticated, it can be challenging to understand how different tools and technologies impact cybersecurity and privacy.
Whenever this is the case, organizations should engage an established IT auditor for help. Enterprises that engage in internal or external audits must also take necessary steps to ensure security and privacy during the different phases of the IT audit.
Infrastructure Changes and Emerging Technologies
Infrastructure changes that occur with the integration of emerging technologies pose potential challenges. This is because any transformation or innovation can come at the cost of significant complexity. For example, IT auditors may not understand how it all works together securely and effectively.
Third-Party Partners and Vendors
Cloud service providers also work with different partners and vendors across the supply chain. These third parties will have their own set of policies and protocols that may hinder a thorough investigation. Discussing these potential challenges and finding viable solutions is therefore recommended before committing to a cloud vendor.
Staffing and Skills Challenges
In the middle of the “great resignation,” businesses across industries will have a hard time attracting and retaining top tech talent, including IT auditors. Organizations can overcome this hurdle by engaging established IT auditing service providers to fill the skills gap and complete the IT audit report.
As the world becomes increasingly digitally transformed with cloud-based systems and software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications, IT audits are critical to mitigating risks, controlling costs, and enhancing efficiencies.
At the same time, these assessments also provide much-needed visibility into enterprise operations. Regular IT audits empower organizations by making sure that they have the most appropriate controls in place to optimize operations while mitigating risks.
How Faddom Can Help with IT Audits
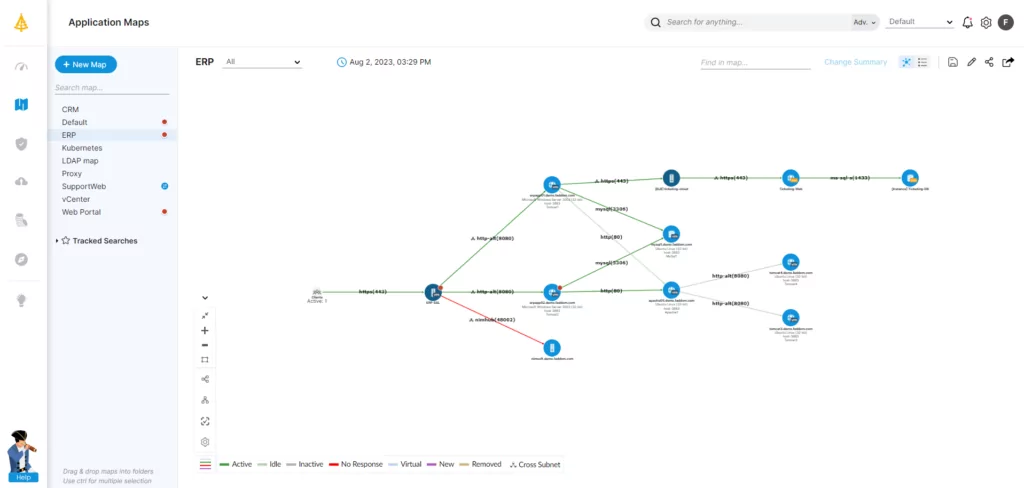
Faddom helps organizations worldwide with IT audits by mapping their entire hybrid IT environments — both in the cloud and on premise – in as little as one hour.
Learn More About IT Audits
IT Asset Management Best Practices
The ITAM market will grow 11.25% from 2022-2028. This is just one indicator showing how ITAM powers IT ops and propels business outcomes.
Read more: IT Asset Management Best Practices
Active Scanning vs. Passive Scanning in IT Environments and Data Centers
Today’s complex data centers need continuous scanning capabilities. Here are the differences between active and passive scanning.
Read more: Active Scanning vs. Passive Scanning in IT Environments and Data Centers
Agentless Scanning vs. Agent-Based Scanning in Application Discovery
Many application mapping solutions use agents for discovery, claiming that they are more accurate or affordable. But they are complex.
Read more: Agentless Scanning vs. Agent-Based Scanning in Application Discovery
The Fast-Track Guide to IT Documentation: Examples and Best Practices
Not every company gets a worthwhile return on its documentation investment. This guide shows organizations how to do it the right way.
Read more: The Fast-Track Guide to IT Documentation: Examples and Best Practices
IT Asset Discovery: The Benefits, Methods, and Process
Having a complete awareness of all assets through IT asset discovery helps to streamline operational processes and to keep IT assets secure.
Read more: IT Asset Discovery: The Benefits, Methods, and Process
The Top 12 Enterprise Architecture Tools and Software
EA is a complex discipline that needs many tools to make informed strategic decisions. Here are the common ones that form part the day-to-day toolkit.
Read more: The Top 12 Enterprise Architecture Tools and Software
See Our Additional Guides on Key Compliance Management Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of compliance management.
PCI Compliance
Authored by Exabeam
- PCI Security: 7 Steps to Becoming PCI Compliant
- Quick PCI Compliance Checklist: Be Ready for Your Next Audit
Employee Classification
Authored by Stoke
- Worker Classification: The How-To Playbook
- FLSA Classification: What Do You Need to Know?
- Employee Misclassification: It’s More Important Than What You Think
AB5
Authored by Stoke









