What Is AWS Cost Management?
AWS cost management refers to the practices, tools, and policies that organizations use to monitor, control, and optimize how much they spend on Amazon Web Services. AWS provides highly granular billing, often by the second or minute, across its vast array of cloud products.
With agile product adoption and scaling capabilities, costs can grow quickly and become unpredictable without cost controls in place. AWS cost management covers tasks from usage tracking and budgeting to optimization, forecasting, and reporting on cloud spend. Its purpose is to give organizations visibility and control over their cloud budgets.
As organizations migrate workloads to AWS, they face complex cost structures that can be challenging to understand without proper oversight. Cost management tools and strategies help technical and financial leaders understand where resources are used, identify waste, and ensure that resources are provisioned cost-effectively.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Importance and Benefits of Cost Management in AWS
Cost management in AWS ensures that cloud resources deliver maximum business value without unnecessary spend. As environments grow, visibility into usage becomes essential to prevent overspending and control total cost of ownership. There are AWS cost management tools that provide near real-time insights into resource consumption across services, regions, and departments. However, these are not the only option and many organizations use third-party tools as well.
Optimization features help identify idle or underutilized resources, such as EC2 instances during low-activity periods, allowing teams to rightsize infrastructure before costs escalate. Many tools also deliver recommendations based on historical usage patterns, making it easier to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
Proactive monitoring and alerting capabilities give teams early warnings when spend exceeds predefined thresholds. This supports departmental accountability and reduces the risk of unexpected charges.
Cost management tools also simplify the use of AWS pricing models like savings plans and reserved instances by tracking utilization and coverage, and in some cases automating purchase and renewal decisions. Automation further reduces manual oversight by continuously analyzing billing data, adjusting resource capacity, and applying optimization policies in real time.
First-Party AWS Cost Management Tools
AWS provides native cost management tools that monitor, forecast, and optimize spending. These services align with common use cases such as tracking, budgeting, purchasing, and optimization.
AWS consolidated billing, purchase order management, and credits let organizations track charges from multiple accounts in one place. Cost allocation tags and cost categories help classify spend by project, department, or workload, which is essential for accurate reporting and governance.
Budgeting tools like AWS Budgets and budget actions set predefined spending limits and trigger alerts or automated responses when thresholds are reached. Purchasing optimizations use programs such as the free tier, savings plans, reserved instances, and spot instances to lower costs based on workload patterns.
For analysis and reporting, AWS cost and usage reports, cost explorer, and the application cost profiler provide detailed historical and real-time cost data. This data supports inspections for inefficiencies, such as idle resources, and feeds into rightsizing recommendations from compute optimizer, cost explorer, or S3 intelligent tiering.
Elasticity features like EC2 auto scaling, instance scheduler, and Redshift pause and resume adjust capacity to match demand, preventing waste. Governance and control are enforced through AWS organizations, IAM policies, cost anomaly detection, and service catalog guardrails.
Forecasting capabilities in AWS Budgets and cost explorer use historical usage data to project future costs, helping teams plan spending with greater accuracy. The process relies on consistent tagging and data organization so that all cost analysis and optimization actions are based on accurate, granular usage metrics.
Third-Party AWS Cost Management Tools
Third-party AWS cost management tools go beyond the basic capabilities of AWS native tools. Here are a few popular options.
1. Faddom

Faddom provides agentless visibility into AWS and hybrid environments, helping organizations identify underutilized resources, control costs, and maintain compliance across dynamic infrastructures. It automatically discovers servers, applications, and traffic flows across AWS and on-premises systems, creating real-time dependency maps that clarify how workloads consume resources.
By understanding the full context of dependencies, Faddom enables IT and FinOps teams to rightsize workloads, detect idle instances, and prevent overspending caused by hidden or redundant assets. Its continuous mapping also supports accurate cost allocation by linking cloud expenses directly to applications and services.
Key features include:
- Agentless AWS discovery: Visualize your AWS footprint without installing agents or disrupting workloads.
- Real-time dependency mapping: Identify resource relationships and usage patterns to pinpoint inefficiencies.
- Rightsizing and optimization insights: Detect idle or oversized EC2 instances and other cloud assets to cut unnecessary costs.
- Hybrid and multicloud visibility: Consolidate on-premises and AWS infrastructure into a single cost and dependency view.
- Security and compliance alignment: Identify shadow IT and unexpected east-west traffic to ensure AWS usage remains compliant and secure.
Book a demo to get your live dependency map in under an hour!
2. CloudZero

CloudZero is an AWS cost management platform that links cloud spend to business outcomes. It allocates AWS costs, even without proper tagging, and organizes this data by team, product, feature, or microservice. This visibility enables engineering and finance teams to collaborate on optimization efforts and maintain accountability for cloud usage.
Key features include:
- CostFormation technology: Allocates AWS spend regardless of tagging quality.
- Business-aligned views: Breaks down spend by team, product, feature, microservice, or other business dimensions.
- Automated cost alerts: Sends anomaly notifications directly to responsible engineers to prevent overspending.
- Unit cost metrics: Tracks exact costs per unit of output, enabling identification of inefficient usage.
- Customizable analytics: Offers standard and custom dashboards to visualize AWS costs against business objectives.
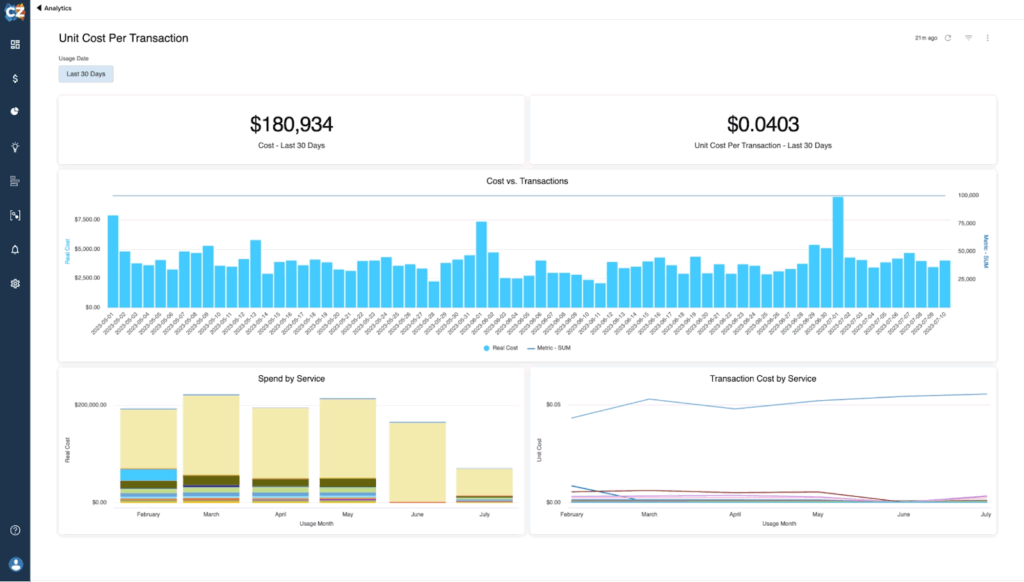
Source: CloudZero
3. Xosphere

Xosphere instance orchestrator is a Spot instance optimization platform that reduces EC2 costs by automatically shifting workloads between on-demand and Spot instances without risking downtime. It integrates natively with AWS auto scaling groups, continuously monitoring running instances to replace on-demand instances with Spot instances when capacity is available.
Key features include:
- Reserved instance prioritization: Keeps reserved instances in place, avoiding unnecessary replacement with Spot instances.
- Automatic spot diversification: Distributes Spot usage across instance families, sizes, and availability zones to reduce disruption risk.
- Connection draining: Works with ELB and ALB to gracefully terminate sessions before Spot instance shutdown.
- Container integration: Natively supports Kubernetes, ECS, and EKS for container migration before Spot termination.
- Tag-based configuration: Enables and configures optimization settings directly with AWS tags.
4. Densify

Densify is an AI-powered optimization platform for AWS and Kubernetes environments that continuously analyzes workload patterns to match applications with the right cloud resources. Its machine learning engine evaluates EC2, RDS, auto scaling groups, and EKS clusters to eliminate over- and under-provisioning, improve utilization, and reduce costs.
Key features include:
- EC2 optimization: Recommends the optimal instance size and family to avoid performance issues from under-allocation and cost waste from over-allocation.
- RDS optimization: Right-sizes database resources, defers changes for reserved instance coverage, and reduces waste.
- Auto scaling group optimization: Analyzes scaling patterns, determines ideal instance types and scaling limits, and highlights misaligned scaling policies.
- EKS cluster optimization: Assigns the right CPU, memory, and instance families for nodes, models scaling behavior, and reduces node count without impacting workloads.
- Metrics viewer: Visualizes CPU, memory, network, and disk utilization across EC2, RDS, and ASG instances to validate recommendations and track scaling behavior.
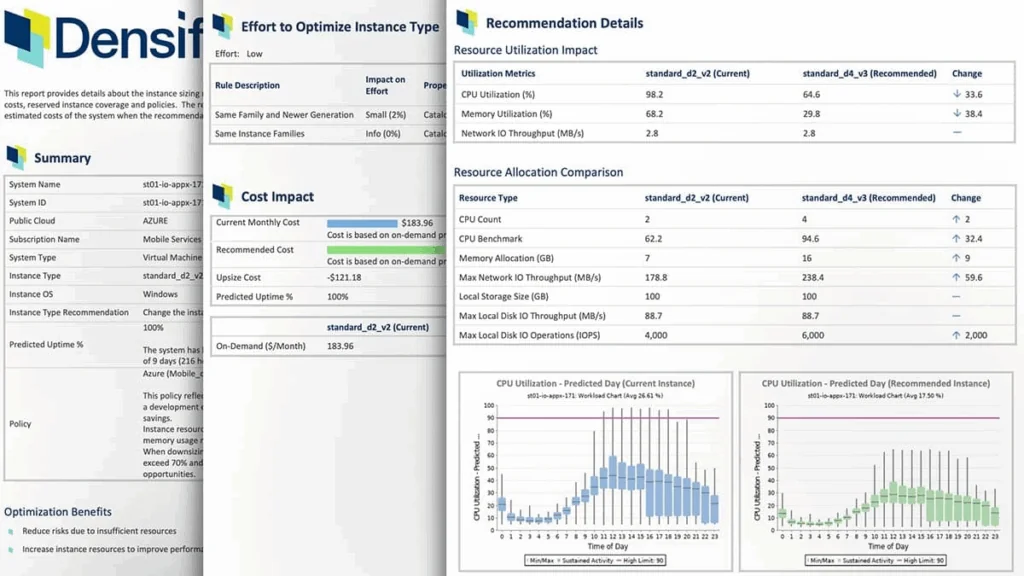
Source: Densify
5. Cloudability

Cloudability is a cloud cost management and optimization platform that provides visibility, governance, and automation for AWS environments, including Kubernetes workloads. It helps organizations track and allocate cloud spend, forecast budgets, and enforce financial accountability across teams.
Key features include:
- Cost visibility: Tracks AWS spend by service, account, project, or Kubernetes namespace, with filtering by tags and custom dimensions.
- Automated cost optimization: Executes rightsizing, pricing model arbitrage, and scheduling to reduce waste without manual intervention.
- Kubernetes cost allocation: Breaks down cluster costs by namespace, workload, or team to improve chargeback and accountability.
- Budgeting and forecasting: Uses historical data and usage trends to project future spend and set budget thresholds.
- Pricing model management: Identifies opportunities for savings plans, reserved instances, and Spot usage.
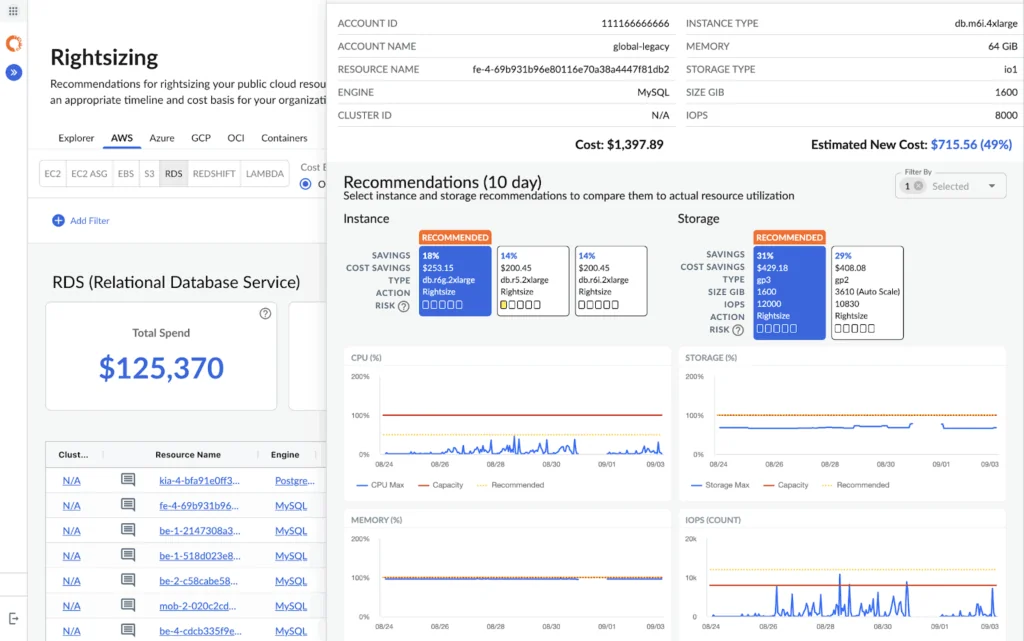
Source: Cloudability
6. CloudHealth
CloudHealth by Tanzu is an AWS management and optimization platform that helps organizations control costs, improve resource utilization, and enforce governance policies as they scale their cloud environments. It provides financial, operational, and migration planning capabilities to align AWS usage with business goals.
Key features include:
- AWS cost and resource optimization: Offers actionable rightsizing recommendations, lifecycle management for reservations and savings plans, and visibility into container resource utilization.
- Business context alignment: Maps AWS usage and cost data to business units, projects, or teams, with customizable reports and dashboards.
- Financial management: Monitors spending trends, detects anomalies, and tracks cost, usage, and performance metrics for major AWS services.
- Automated governance policies: Implements prebuilt or custom rules to maintain tagging hygiene, automate workflows, and enforce compliance.
- Policy-based actions: Triggers alerts for policy violations, authorizes user actions, or automatically executes remediation steps.
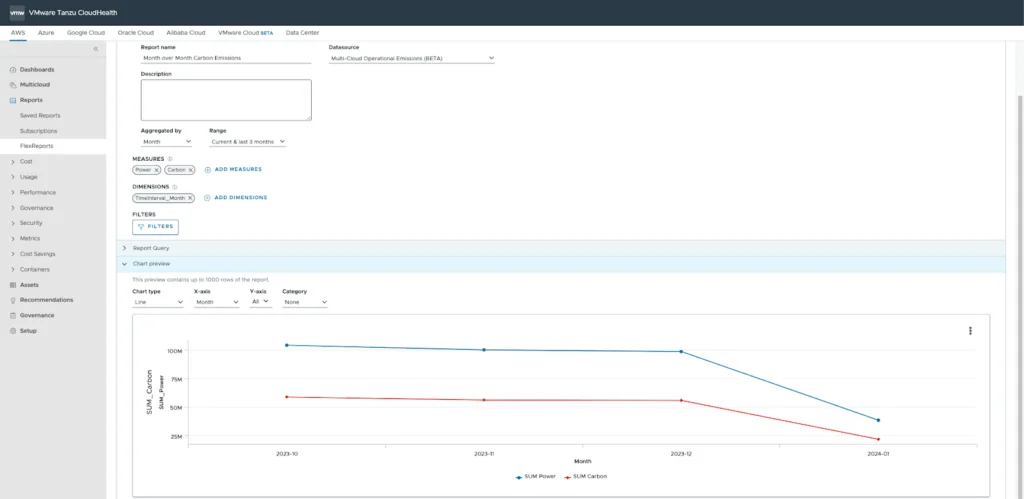
Source: VMware
7. nOps

nOps is an AWS cost optimization platform that uses AI and machine learning to automatically reduce cloud waste and maximize savings. It provides visibility into AWS, Kubernetes, GenAI, and SaaS costs and allocates spend by customer, product, cost center, or other business dimensions.
Key features include:
- Cost visibility: Tracks 100% of AWS, Kubernetes, GenAI, and SaaS spend, with allocation by customer, application, team, or cost center.
- Commitment management: Maximizes savings plans and reserved instance utilization while reducing long-term commitment risk.
- ML-driven optimization: Continuously rightsizes and scales compute resources across pricing models for maximum efficiency.
- Spot orchestration: Automates Spot usage for EKS and auto scaling groups to reduce compute costs without impacting reliability.
- Container rightsizing: Optimizes Kubernetes workloads to match CPU and memory needs.
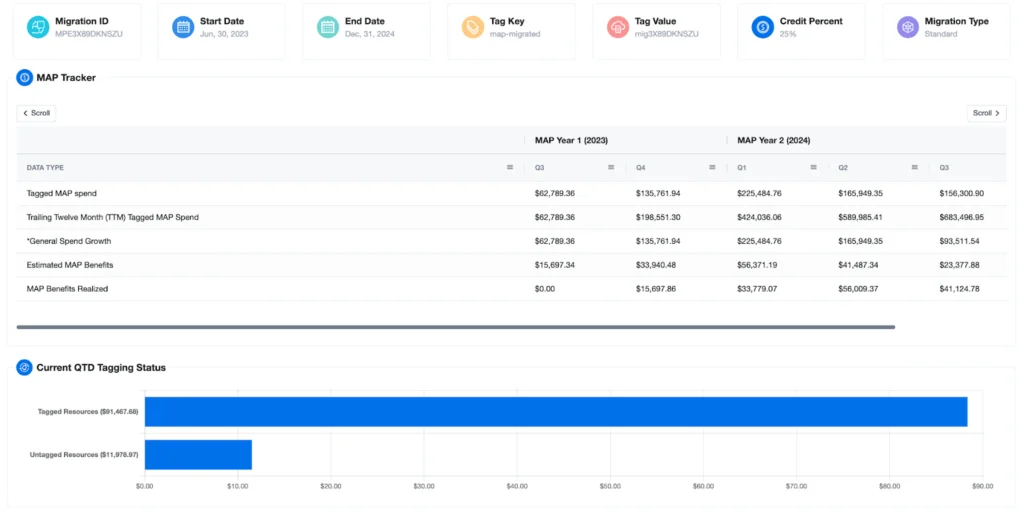
Source: nOps
Common Challenges in AWS Cost Management
Complex Billing Structures
AWS’s granular, pay-as-you-go billing model offers flexibility but leads to intricate cost breakdowns across services, regions, and accounts. Pricing varies between different services such as EC2, S3, or Lambda as well as within services, based on instance type, reserved capacity, spot pricing, and data transfer volumes.
This complexity makes it difficult for teams to predict costs accurately and attribute charges to particular business units without robust tagging and reporting. The extensive array of discounts, reservations, and marketplace subscriptions compounds this challenge. Navigating the rules behind reserved instances, savings plans, and marketplace products often requires specialized expertise.
Untracked Resources
Untracked or orphaned resources are a common culprit for unnecessary AWS expenses. When development or testing teams quickly spin up compute instances, storage volumes, or networking components without standardized tracking methods, these resources may remain active and accumulate charges long after their intended use.
This can happen due to incomplete clean-up processes, lack of tagging discipline, or lapses in monitoring for idle assets. The impact is compounded in complex environments with multiple AWS accounts and automated provisioning pipelines. Without automated resource discovery and continuous usage auditing, untracked resources can grow unnoticed.
Forecasting Uncertainty
Forecasting future AWS expenses is inherently difficult due to variable workloads, evolving application architectures, and frequent service changes. Spikes in usage from seasonal traffic, marketing campaigns, or new product launches can cause cloud costs to deviate sharply from historical trends.
Static forecasting methods struggle to keep up, leading to inaccurate budget projections and greater risk of overruns. AWS regularly introduces new pricing options, instance families, or billing models, requiring constant adjustment of forecasting systems. If usage data is not granular and current, or if business projections are not regularly reviewed against real-time cost analytics, organizations may find themselves ill-prepared for sudden increases in spend.
Aligning Finance and Engineering
One of the persistent challenges in AWS cost management is ensuring alignment between finance departments, which track spending and manage budgets, and engineering teams, which deploy and manage resources. Finance typically requires predictability and clarity, while engineering values agility and performance, sometimes at the expense of cost controls.
This disconnect can lead to finger-pointing over unexpected expenses or missed optimization opportunities. Developing a shared understanding and vocabulary around AWS usage, budgeting, and optimization is crucial.
Best Practices for AWS Cost Management
Organizations should consider the following practices to help them manage costs in AWS.
1. Use Tagging and Resource Naming Standards
Implementing clear tagging and naming conventions is foundational for effective AWS cost tracking and accountability. Tags assign metadata to resources, indicating owner, project, environment, or cost center. Standardized tagging enables precise cost allocation, budget enforcement, and informed decision-making about which teams or applications are responsible for charges.
A resource naming standard complements tagging by supporting automation and simplifying inventory management. Properly named resources make it easier to enforce policies for scheduled shutdowns, backups, and clean-up. Automated scripts and cost management tools rely on consistent naming and tagging to operate efficiently.
2. Implement Service Quotas and Permissions
Enforcing service quotas and permissions is essential for preventing runaway resource creation and the associated costs in AWS environments. Service quotas set hard or soft limits on the number of resources that can be provisioned, such as instances or network components. These constraints support budget control and prevent accidental over-provisioning.
Combining quotas with robust IAM (Identity and Access Management) permissions restricts which users or roles may provision, modify, or delete resources. By controlling access and limiting administrative privileges, organizations reduce the risk of unapproved spending. Regularly reviewing and updating permissions keeps access policies aligned with organizational changes.
3. Establish Lifecycle Policies
Establishing and enforcing lifecycle policies for resources (such as EC2 instances, EBS volumes, and S3 storage buckets) helps organizations avoid cost creep from forgotten or obsolete assets. Lifecycle policies automate the archiving, deletion, or transfer of data after defined periods or when specified criteria are met.
This reduces manual oversight and ensures that inactive resources do not continue to incur unnecessary charges. Lifecycle policies are especially important for environments supporting prototyping, short-lived workloads, or Dev/Test cycles. Automated expiration and cleanup routines remove human error and reduce overhead in ongoing cost management.
4. Auto-Scale Instead of Over-Provisioning
Auto-scaling automates the adjustment of compute and storage resources in response to real-time demand, in contrast to traditional over-provisioning for peak usage scenarios. Over-provisioning means running resources at maximum anticipated loads, resulting in idle capacity and higher costs when demand drops.
Auto-scaling solutions such as AWS auto scaling groups for EC2 help maintain performance while optimizing spend by dynamically scaling resources up or down as needed. This approach also enhances application reliability and performance. Auto-scaling can be configured with policies based on metrics like CPU utilization, network throughput, or custom business indicators.
5. Schedule Non-Production Downtime
Scheduling downtime for non-production environments like development, staging, or QA reduces costs by powering down resources outside working hours. These environments often do not need to operate 24/7, but if left unchecked, they continue to accrue charges when idle.
Automating start/stop routines through AWS Lambda, CloudWatch Events, or third-party tools helps enforce downtime schedules and maximize savings. Effective scheduling requires close coordination with team workflows to avoid disrupting development or testing activities. Regularly reviewing environment usage and adjusting schedules increases cost savings while supporting productivity.
Conclusion
Effective AWS cost management requires both financial oversight and technical governance. It is not only about cutting costs but also about ensuring that cloud resources align with business objectives and deliver measurable value. By combining clear visibility, proactive controls, and continuous optimization, organizations can strike the right balance between agility and cost efficiency. A structured approach, supported by detailed IT documentation, allows teams to forecast spend more accurately, reduce waste, and scale cloud usage sustainably as business needs evolve.








