What Are AI Security Tools?
AI security tools are software solutions that use artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect, prevent, and mitigate cyber threats. These tools analyze vast amounts of security data, identify patterns, and automate responses to incidents.
By continually learning from new data, AI security tools adapt to evolving attack tactics more quickly than traditional, rule-based systems. Their capabilities cover threat detection, vulnerability assessment, anomaly recognition, automated decision-making, and real-time response actions, enabling more efficient management of complex security environments.
Table of Contents
ToggleAI security tools are augmentations for established cybersecurity practices, not replacements. These tools work best when integrated into broader security operations, providing insights that help human analysts focus on genuinely critical threats. Their ability to scale across networks and rapidly process data makes them suited for the dynamic threat landscape.
Key Types of AI Cybersecurity Tools
AI Monitoring and Anomaly Detection
AI monitoring and anomaly detection tools continuously analyze data from systems, networks, and applications to identify behaviors that deviate from established norms. These tools apply machine learning models to baseline historical activity, enabling the detection of subtle changes that may signal insider threats, system misuse, or early-stage attacks.
Unlike static rule-based systems, they can uncover previously unknown threats by identifying unusual patterns across traffic volumes, login times, resource usage, or user actions. These tools are particularly valuable in environments with high data volume or dynamic activity, such as enterprise networks or IoT ecosystems.
Learn more in our detailed guide to AI anomaly detection
Threat Detection and Response
AI-powered threat detection tools monitor endpoints, network traffic, cloud environments, and user behaviors to identify suspicious activity and known indicators of compromise. Using supervised and unsupervised machine learning, these systems establish baselines for “normal” operation, flagging outliers such as unusual logins, lateral movement, or anomalous file access.
Rapid identification of such activities shortens the response window, limiting harm from attacks like ransomware or data exfiltration. Threat response solutions automate many aspects of incident handling, from isolating impacted systems to executing predefined playbooks. They also integrate with broader security information and event management (SIEM) or security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms.
Cloud-Native Security
Cloud-native security tools leverage AI to manage risks across complex hybrid and multi-cloud environments. These solutions monitor cloud workloads, configuration drift, access controls, and real-time events, helping security teams identify misconfigurations, detect intrusions, and minimize attack surfaces. AI-driven analysis allows these tools to quickly correlate unusual patterns or privilege escalations across dynamic cloud assets.
In addition to threat detection, these tools automate compliance checks and policy enforcement, ensuring adherence to evolving frameworks like CIS, SOC 2, or GDPR. Their ability to scale with elastic cloud infrastructure makes them essential for modern organizations shifting workloads to public cloud or adopting containerized, serverless architectures.
Full-Lifecycle AI Security Platforms
Full-lifecycle AI security platforms provide end-to-end coverage for the entire security process—from threat prevention through detection, investigation, and resolution. These platforms consolidate data from networks, endpoints, identities, and clouds, providing a unified view that helps security teams identify threats more accurately and efficiently.
Such platforms support compliance, risk management, and security operations in complex enterprise environments. Integration with existing workflows lets organizations orchestrate responses, automate remediation, and enforce security policies throughout the IT ecosystem. Full-lifecycle solutions also maintain historical context for incidents, useful for forensic analysis.
AI Monitoring, Tracking, and Anomaly Detection
1. Faddom

Faddom is an agentless application dependency mapping and AI-powered anomaly detection platform that provides IT and security teams with comprehensive visibility into their environments. By automatically mapping servers, applications, and dependencies across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid infrastructures, Faddom identifies hidden risks that traditional tools often overlook. Its AI-driven insights facilitate the detection of abnormal traffic behaviors, help prevent lateral movement, and enhance segmentation strategies before attackers can exploit vulnerabilities.
Key features include:
- Agentless and Fast Deployment: Get started quickly. Setup can be completed in under 60 minutes, and there is no need for agents or complex configurations.
- Continuous Real-Time Visibility: Enjoy automatically updated maps of applications, servers, and traffic flows.
- AI Anomaly Detection: Automatically identifies unusual traffic patterns, at-risk servers, and potential ransomware activity without relying on manual thresholds.
- Microsegmentation Support: Provides essential context for building and enforcing zero-trust policies.
- Risk Reduction Detects shadow IT, unauthorized access, and risky east-west traffic to eliminate blind spots.
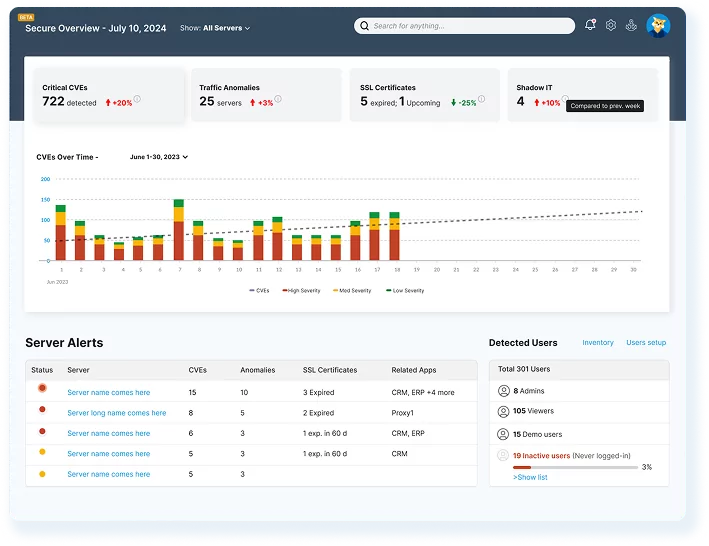
2. Microsoft Azure Anomaly Detector

Microsoft Azure Anomaly Detector is an AI-powered service that helps identify anomalies in time-series data using simple API calls. Designed for users with minimal machine learning expertise, it supports real-time and batch anomaly detection, enabling integration into existing applications and systems.
Key features:
- Univariate anomaly detection: Detects abnormal values in a single variable, such as revenue or request counts, by automatically selecting the best-fit model
- Multivariate anomaly detection: Evaluates multiple variables and interdependencies using a graph attention network to detect anomalies across systems
- Streaming detection: Analyzes incoming data points by comparing each new value against patterns learned from previous data
- Batch detection: Processes datasets to identify all anomalies within a given time range using a consistent model
- Change point detection: Identifies shifts in trends within time-series data, helping to pinpoint structural changes in metrics over time
Source: Microsoft
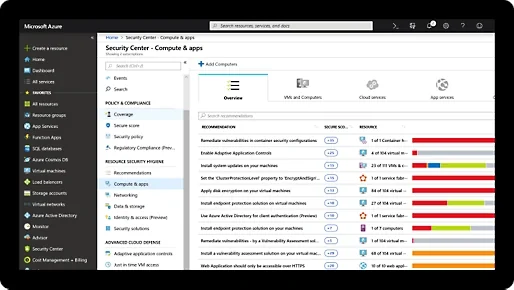
3. Dynatrace

Dynatrace provides AI-powered anomaly detection for complex environments. By leveraging continuous machine learning and predictive analytics, it detects abnormal behavior across dynamic, multicloud systems. Its deterministic AI engine, Davis, analyzes dependencies, determines root causes, prioritizes alerts, and measures customer impact.
Key features:
- AI-driven root cause analysis: Automatically identifies anomalies and traces them back to their root cause
- Alerting with Davis AI: Related anomalies are grouped into single alerts to reduce noise and avoid alert fatigue
- Multidimensional baselining: Continuously adapts thresholds using live system data, accounting for variables like time of day, seasonal trends, and usage patterns
- Dynamic environment awareness: Tailored for containerized, cloud-native systems where “normal” constantly changes
- Predictive analytics: Learns traffic and load patterns to predict future behavior
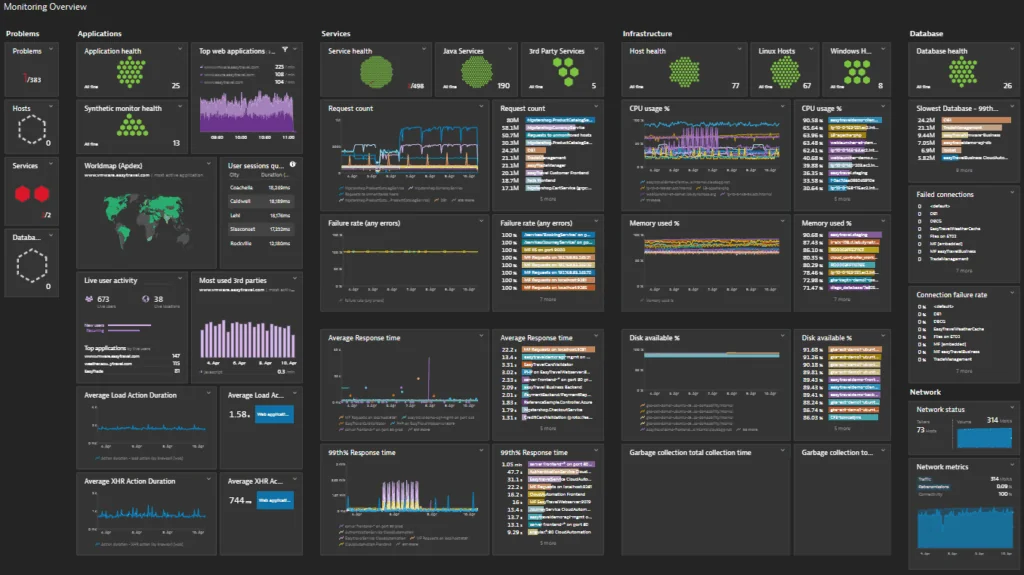
Source: Dynatrace
Threat Detection and Response
4. SentinelOne Singularity

SentinelOne Singularity is an AI-powered cybersecurity platform that delivers unified protection, detection, and response across endpoints, cloud workloads, and identities. It uses behavioral AI to stop ransomware, zero-day threats, and active attacks.
Key features include:
- Unified endpoint and cloud protection: Deploy a single agent to secure servers, workstations, and cloud workloads
- Autonomous threat prevention: Block malware and reduce the attack surface with on-device AI
- Behavioral AI detection: Identify zero-days and ransomware using static and behavioral models operating across OS and cloud environments
- Natural language threat hunting: Use Purple AI to run threat hunts with simple language queries, generate summaries, and accelerate investigations
- Automated incident response: Leverage policy-based responses or use one-click remediation actions
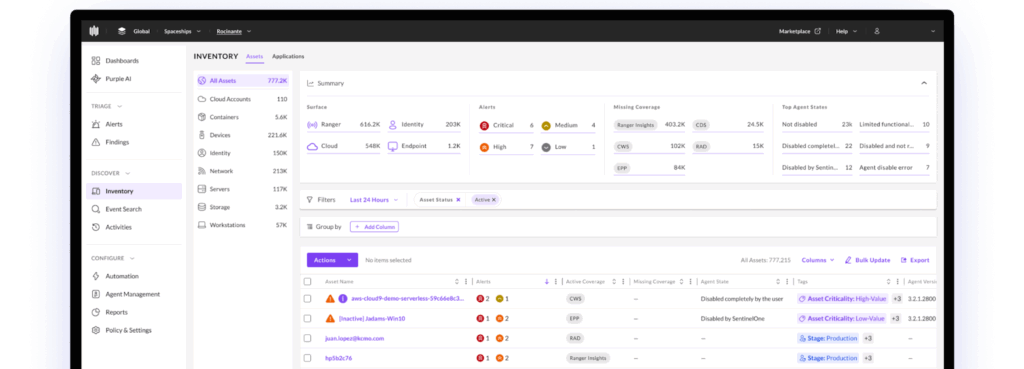
Source: SentinelOne
5. Vectra AI

Vectra AI is a network detection and response (NDR) platform that uses AI to detect and stop attackers across network, identity, cloud, and SaaS domains. By combining behavioral analytics with AI-driven triage, correlation, and prioritization, it enables visibility and response to threats that evade traditional tools.
Key features include:
- Cross-domain threat detection: Uses AI to detect attacker behaviors across data centers, remote workspaces, clouds, SaaS apps, IoT/OT environments, and identity systems
- AI analytics: Ingests, enriches, and analyzes network data to surface behaviors like lateral movement and privilege escalation
- AI signal clarity: Reduces alert noise with AI assistants that triage, correlate, and prioritize threats
- Identity threat detection: Identifies misuse of privileged accounts, credential abuse, and privilege escalation across both human and machine identities
- Cloud threat detection: Surfaces complex multi-cloud attacks across workloads and services by correlating activity across cloud roles, regions, and configurations
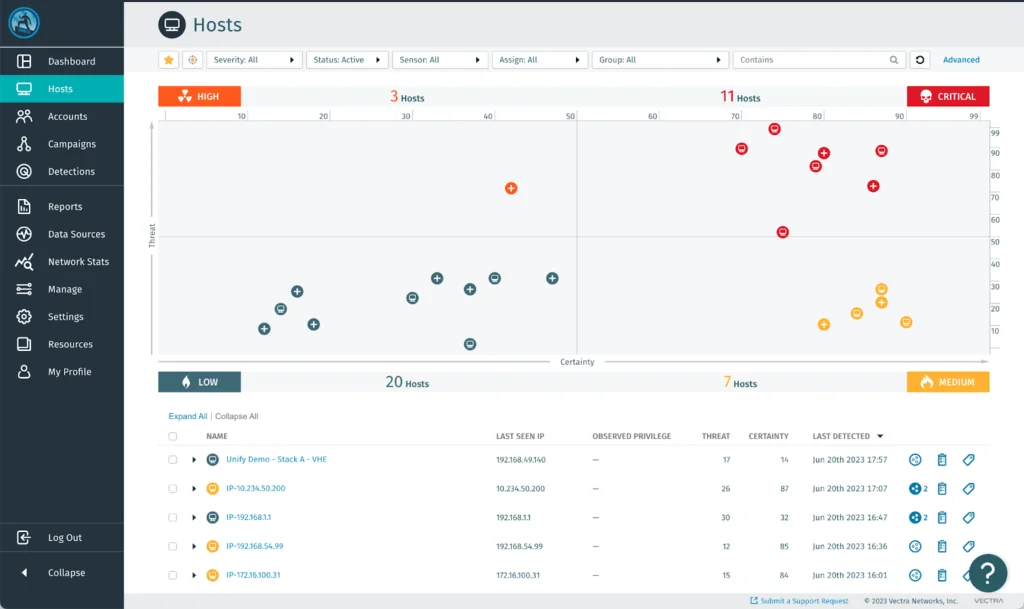
Source: Vectra AI
6. Darktrace
Darktrace / Endpoint is an AI-powered endpoint security solution that improves existing EDR systems by delivering autonomous, behavior-based detection and response across devices. It continuously learns what is “normal” for each endpoint and intervenes in real time to stop both known and novel threats.
Key features include:
- Behavior-based threat detection: Uses self-learning AI to establish a baseline of normal behavior per endpoint
- Autonomous, targeted response: Contains threats with context-aware actions, avoiding blunt isolation tactics
- Complement to existing EDR: Augments tools like Microsoft Defender for Endpoint by adding a network-based layer of visibility and defense, using the Microsoft Graph Security API
- Cyber AI Analyst™: Automates the triage and investigation process, reducing analyst workload
- Remote and hybrid coverage: Maintains visibility and protection for devices on the corporate network, remote, or in hybrid environments
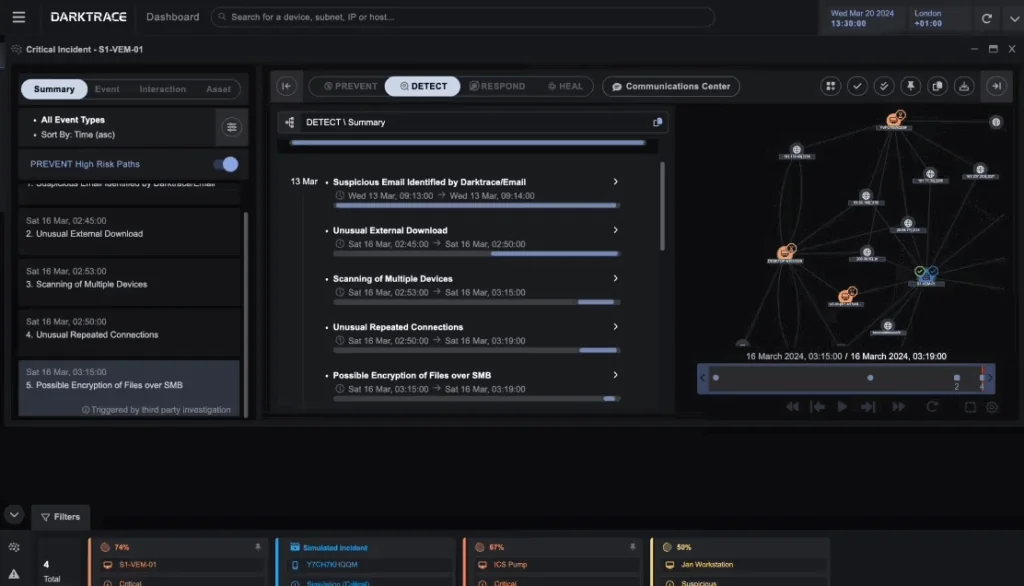
Source: Darktrace
AI-Driven Cloud-Native Security
7. Microsoft Defender for Cloud

Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP) that provides unified security across multicloud and hybrid environments. It brings together development, posture, and workload protection into a single solution, enabling organizations to manage security from code to runtime.
Key features include:
- Unified CNAPP coverage: Combines DevSecOps, cloud security posture management (CSPM), and cloud workload protection (CWPP) into one platform
- Development security (DevSecOps): Secures code pipelines by identifying misconfigurations, secrets, and risks in source code repositories like GitHub, Azure DevOps, and GitLab
- Advanced CSPM: Offers agentless posture scanning, regulatory compliance, governance workflows, and attack path analysis across multicloud environments
- Multicloud & hybrid support: Extends protection and visibility to Azure, AWS, GCP, and on-premises workloads using agent-based or agentless integrations
- Workload protection (CWPP): Delivers tailored protections for VMs, containers, databases, storage, and serverless functions through specialized Defender plans
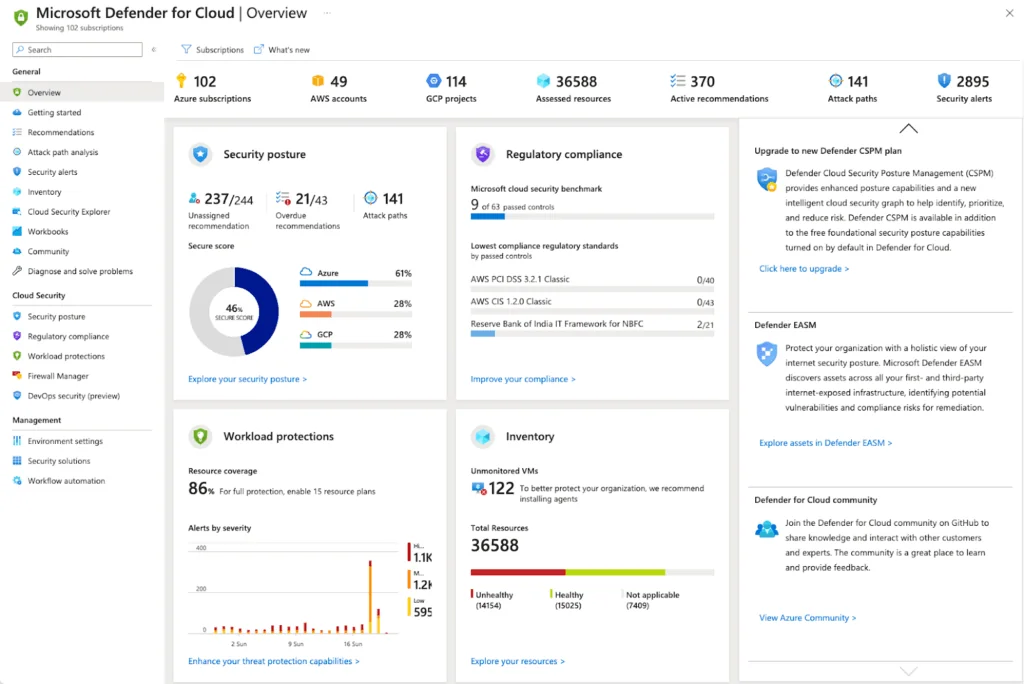
Source: Microsoft
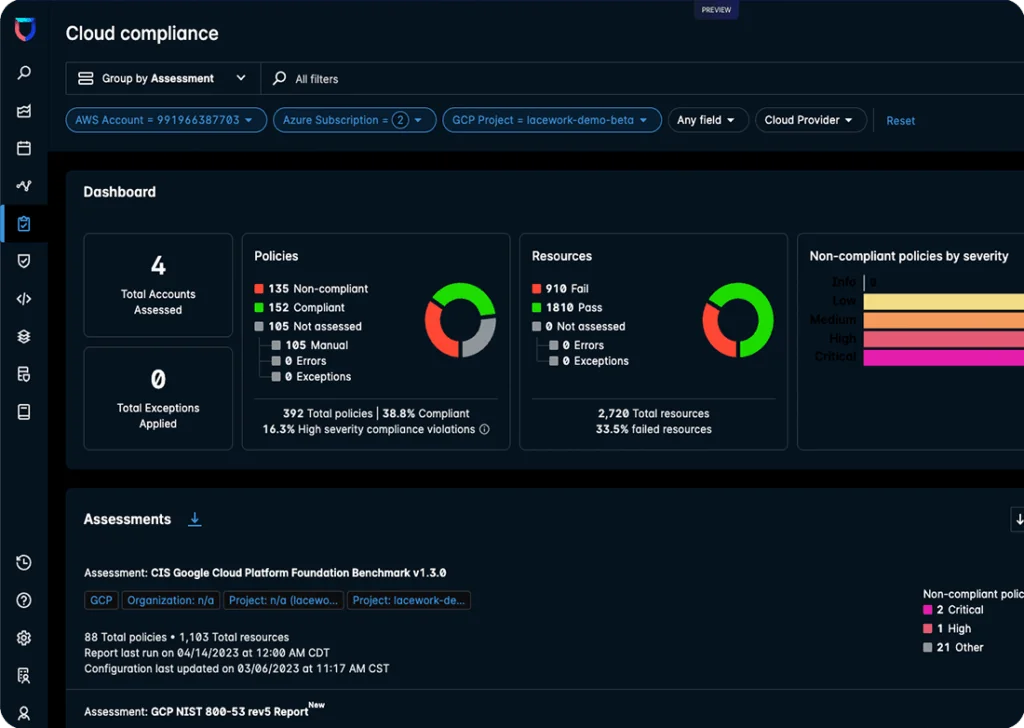
8. Prisma Cloud

Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks is a CNAPP that secures the application lifecycle. It delivers visibility, risk prioritization, and real-time protection across infrastructure, applications, identities, and data.
Key features include:
- Cloud security posture management (CSPM): Continuously evaluates cloud environments to detect misconfigurations, enforce policies, and maintain compliance
- Runtime threat detection: Blocks attacks on applications, containers, serverless functions, and hosts with defense-in-depth and in-line threat prevention
- AI-powered risk prioritization: Uses AI to detect over new attacks daily and assess blast radius to prioritize the most critical risks
- Security for AI applications (AI SPM): Secures training data, model integrity, and deployment access
- Prisma Cloud Copilot: Natural language interface that enables guided investigations and remediation actions across code, infrastructure, and runtime
Source: Palo Alto Networks
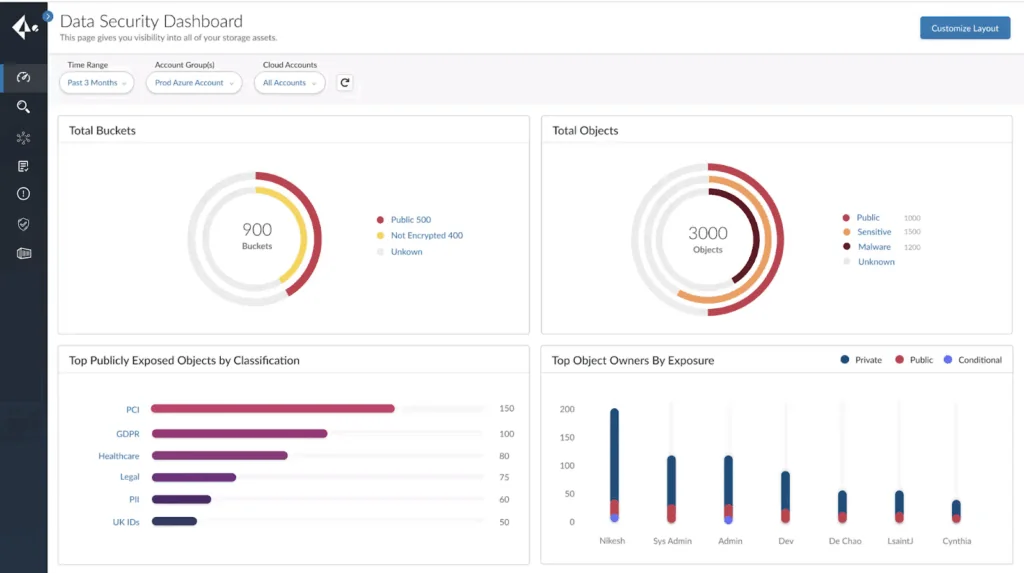
9. Lacework FortiCNAPP

Lacework FortiCNAPP is a unified CNAPP to secure applications from code to cloud with visibility, contextual intelligence, and automation. By combining Lacework’s anomaly detection and risk prioritization with Fortinet’s SOAR and threat intelligence capabilities, FortiCNAPP helps security and DevOps teams to detect threats early and remediate faster.
Key features include:
- Unified security platform: Combines CSPM, CWPP, KSPM, CIEM, IaC security, application security, and cloud detection and response
- Behavior-based threat detection: Identifies zero-day threats like compromised credentials, ransomware, and cryptojacking using machine learning
- Risk prioritization engine: Automatically correlates vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and active threat data to highlight the most critical risks and likely attack paths
- Cloud identity and entitlement management (CIEM): Provides continuous visibility into identity access across cloud providers
- Continuous compliance: Maps assets and activity to major frameworks (PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC 2, ISO 27001)
- Integrated Fortinet capabilities: Improves detection, response, and orchestration with FortiSOAR and FortiGuard integrations
Source: Fortinet
Full-Lifecycle AI Security Platforms
10. Microsoft Security Copilot & Sentinel

Microsoft Security Copilot, integrated with Microsoft Sentinel, forms a full-lifecycle AI security solution that improves threat detection, investigation, and response. Copilot uses natural language prompts to interact with security data, summarize incidents, and generate hunting queries. Sentinel acts as the primary data source, providing security telemetry from across cloud, network, and endpoint environments.
Key features include:
- Natural language interaction: Use plain language to generate KQL queries, request incident summaries, or investigate suspicious activity across Sentinel data
- Unified incident view: Integrates Microsoft Sentinel incidents with Microsoft Defender XDR for complete visibility and context across attack surfaces
- Guided investigation: Copilot suggests next steps, offers summaries, and creates reports tailored for technical or non-technical audiences
- Real-time analytics: Access near real-time alerts and incidents through plugins like SAP (Preview) for proactive threat detection
- Prompt customization: Configure default Sentinel workspaces and personalize plugins to improve prompt accuracy and workflow efficiency
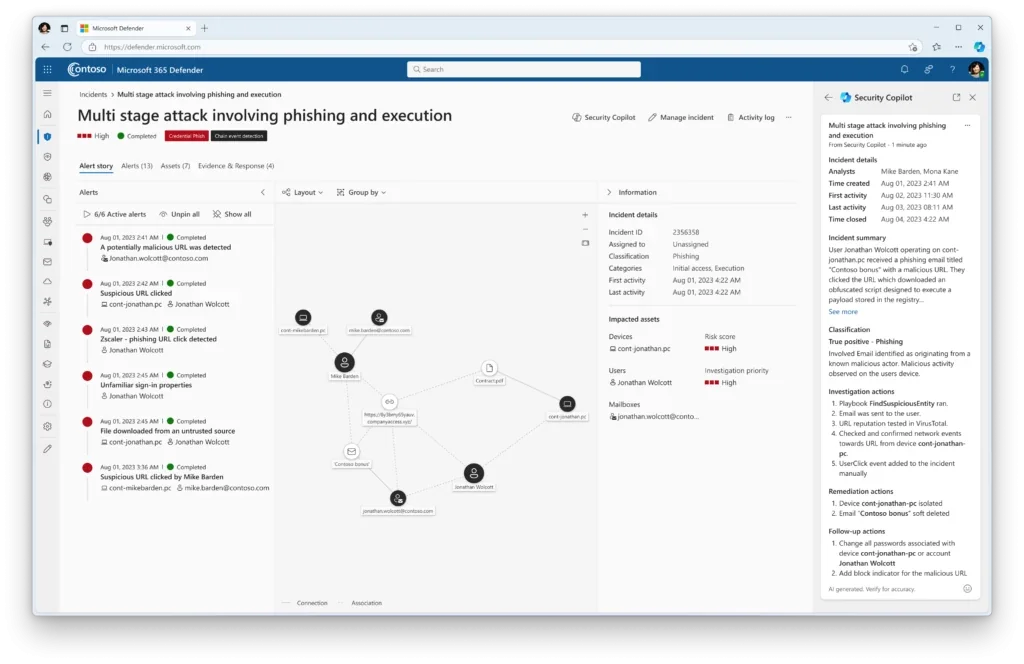
Source: Microsoft
11. Google Security Operations (SecOps)

Google Security Operations is a cloud-native, AI-powered security platform to unify threat detection, investigation, and response. Built on Google’s infrastructure, SecOps processes vast security telemetry with high speed and precision, using threat intelligence and automation to reduce manual effort and accelerate outcomes. Security teams can interact with data using natural language, automate workflows with playbooks, and gain visibility across environments.
Key features include:
- Scalable threat detection: Includes curated, continuously updated detections developed by Google’s threat research team, with support for custom detections using YARA-L language
- Natural language search with Gemini: Use AI-powered chat to search logs, explore threats, and author new detections without complex query syntax
- Security telemetry pipeline: Filter, route, redact, and normalize large volumes of security data to make it immediately actionable
- Integrated SOAR capabilities: Build and automate response playbooks across tools, including EDR, IAM, and network security platforms
- Case management and collaboration: Track incidents, document investigations, and collaborate with team members via an auto-documenting case wall
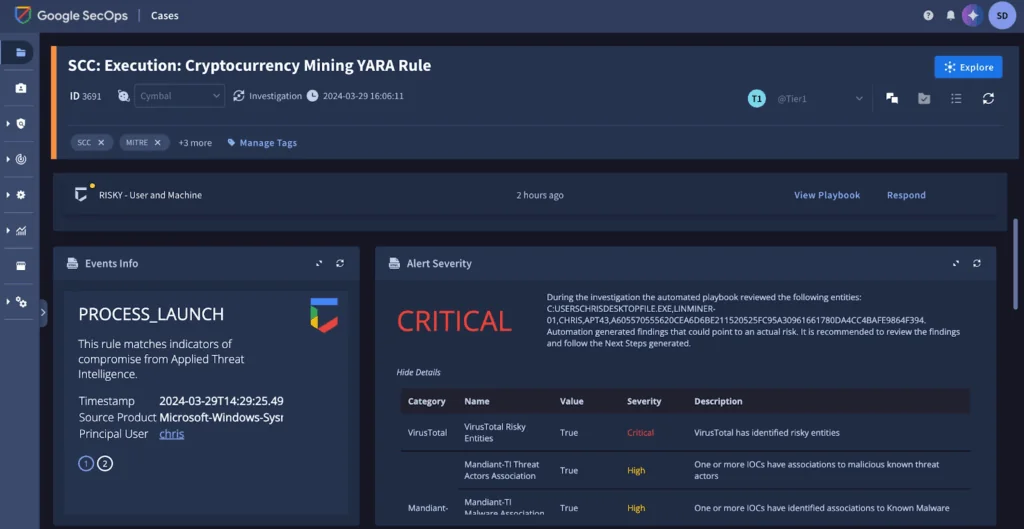
Source: Google
12. Opus Security

Opus Security is an AI-powered vulnerability management platform that helps organizations eliminate noise, focus on real risks, and drive remediation. It consolidates findings across tools and attack surfaces, prioritizes vulnerabilities based on real-world context, and automates resolution using a suite of AI agents.
Key features include:
- Unified risk view: Aggregates, normalizes, and deduplicates data from security tools across cloud, application, and infrastructure environments
- Context-rich prioritization: Goes beyond CVSS by assessing exploitability, active threats, business impact, and technical environment to focus on relevant risks
- AI-driven remediation: Uses AI agents to guide, automate, or execute vulnerability fixes, aligning with organizational policies and security SLAs
- Role-based insights: Delivers personalized views and guidance to engineers, admins, and security leads
- Adaptive workflows: Automates the remediation lifecycle with flexible workflows that fit existing team structures and toolchains
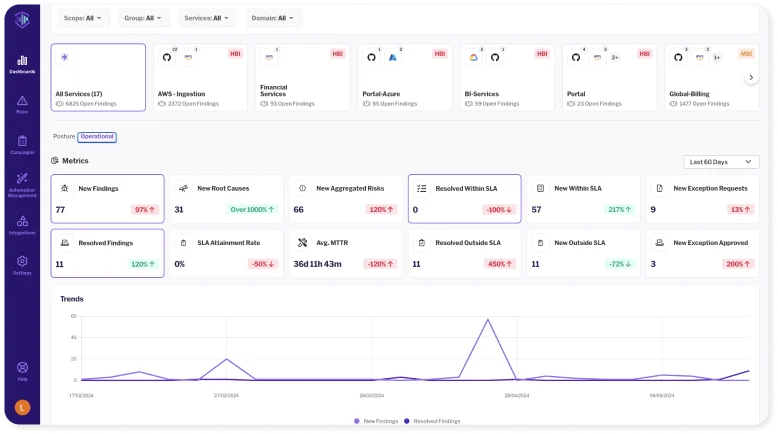
Source: Opus Security
How to Choose the Best AI Security Tool for Your Needs
Selecting the right AI security tool requires aligning its capabilities with your organization’s security maturity, risk profile, and operational constraints. With a growing number of tools offering overlapping features, the key is to prioritize based on specific use cases, integration needs, and the complexity of your digital environment.
Key considerations include:
- Security objectives and use case fit: Identify the primary function you need: threat detection, vulnerability management, fraud prevention, or cloud security. Tools optimized for a specific domain often outperform general-purpose platforms in that area.
- Integration with existing stack: Evaluate how well the tool integrates with your current SIEM, SOAR, EDR, cloud providers, and DevSecOps workflows. Tight integration minimizes disruption and improves data correlation across sources.
- Data coverage and telemetry ingestion: Consider what types of data the tool collects and analyzes—endpoint logs, cloud telemetry, network flows, identity events—and whether it supports your environment at scale.
- AI model transparency and customization: Look for tools that explain their detection logic and allow tuning or model customization. This improves trust, reduces false positives, and aligns with internal threat models or compliance needs.
- Speed and automation of response: Assess how quickly the tool can detect threats and trigger automated responses. Look for features like playbook execution, incident triage, and remediation workflows that reduce time to contain.
- Compliance and reporting support: Ensure the tool can map to relevant regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2) and provides built-in reporting or dashboards for auditors and executives.
- Vendor viability and support: Consider the maturity of the vendor, update frequency, and availability of support. A strong roadmap and responsive support team are essential for long-term reliability.
- Cost and licensing model: Understand pricing structure—whether it’s usage-based, tiered, or flat-rate—and ensure it aligns with your usage volume and growth plans.
Conclusion
AI-driven security tools are becoming essential for managing the scale, speed, and complexity of modern cyber threats. From anomaly detection to full-lifecycle platforms, they provide automation and intelligence that reduce alert fatigue, accelerate investigations, and improve response times. While no tool eliminates the need for skilled analysts, integrating AI into security operations helps teams focus on the most critical risks and stay ahead of evolving attack tactics.








