What Is AWS Application Discovery Service?
AWS Application Discovery Service (ADS) is a tool designed to help enterprises plan migration projects. It does this by collecting information about their on-premises data centers, using either an agentless scanning method or an agent you can deploy on on-premises servers and VMs. The service is mainly focused on discovering VMware virtual machines and databases.
Migrating applications and data to the cloud can be a complex process. It requires careful planning and a deep understanding of the interdependencies between applications and servers. Without this knowledge, the migration process can lead to performance issues, increased costs, and other potential setbacks.
Table of Contents
Toggle- What Is AWS Application Discovery Service?
- Key Features of AWS Application Discovery Service
- How Does the AWS Application Discovery Service Work?
- Benefits of Application Discovery Service
- Limitations of AWS Application Discovery Service
- Tutorial: Getting Started with AWS ADS Agentless Collector for VMware Environments
- Faddom: Ultimate AWS Application Discovery Alternative
AWS Application Discovery Service can help by identifying these dependencies by collecting information about your servers, applications, and data, providing a detailed view of your IT environment. This information is crucial for planning a successful migration to the cloud.
This is part of a series of articles about application migration
Key Features of AWS Application Discovery Service
Before starting a migration, AWS ADS gathers and organizes detailed information about your existing infrastructure. This enables accurate workload assessment and migration planning.
Key features include:
- Inventory collection: Captures server specifications, CPU usage, memory utilization, network activity, and storage details to provide a clear view of capacity and performance.
- Application dependency mapping: Identifies communication between servers and applications, helping uncover hidden interdependencies that could affect migration order and grouping.
- Database discovery: Detects installed databases, their versions, and usage patterns to guide cloud migration sizing and configuration.
- Integration with AWS Migration Hub: Sends discovered data directly to AWS Migration Hub, where you can track progress and manage migration projects in a central dashboard.
- Exportable data for analysis: Allows exporting raw discovery data in CSV or other formats for offline review or integration with third-party migration tools.
Secure data handling: Encrypts all collected information in transit and at rest, ensuring compliance with enterprise security policies.
How Does the AWS Application Discovery Service Work?
AWS Application Discovery Service operates by collecting configuration, utilization, and dependency data from on-premises environments and storing it in your selected AWS Migration Hub home Region. Before starting, you must set this home Region because all discovery data is stored there and linked to migration tracking in Migration Hub.
Once discovery begins, the service provides three main options for data collection:
- Agentless discovery – Deploy the Agentless Collector as an OVA file in VMware vCenter. It automatically identifies VMs and hosts, gathering static configuration data (hostnames, IP addresses, MAC addresses, disk allocations), database engine versions, and average/peak utilization metrics such as CPU, RAM, and disk I/O. This method does not capture process-level details or full network connection data.
- Agent-based discovery – Install the AWS Application Discovery Agent on each physical server or VM. This collects static configuration data, detailed time-series performance metrics, active processes, and inbound/outbound network connections. It provides the most complete dataset but requires installation per server.
- File-based import – Import environment details directly into Migration Hub without deploying collectors or agents. The analysis quality depends on the provided dataset.
Application Discovery Service can also integrate with third-party AWS Partner Network discovery tools. These tools can import environment data into Migration Hub through the public API, enabling you to group servers into applications and track migrations.
For VMware workloads, both Agentless Collector and Discovery Agent can be used together—Agentless for broad coverage, and agents for deeper inspection of specific servers. For database workloads, the Agentless Collector can inventory and measure performance for Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL without installing an agent on each host.
Collected data can be viewed in Migration Hub, exported to CSV, or analyzed with AWS services such as Amazon Athena and QuickSight. Performance metrics can also be fed into cost models to estimate AWS infrastructure costs and identify migration priorities.
Benefits of Application Discovery Service
Here are some of the key benefits of Amazon ADS:
- Visibility over application portfolios: The service collects detailed configuration and usage data from servers, databases, and applications across your IT environment. This includes details like server hostnames, IP addresses, operating system details, and more.
- Migration planning: Amazon ADS provides detailed information about applications and their dependencies, and also offers data connectors to popular migration planning tools such as AWS Migration Hub, TSO Logic, RISC Networks, and others. You can export the collected data directly to these tools to improve migration planning.
- Centralized management and tracking: All your discovery data can be accessed and managed from a single location, the AWS Management Console. This makes it easier to track the progress of your discovery efforts. You can monitor the status of your data collection, view summary reports, and drill down to detailed data on specific applications.
- Integration with AWS services: Amazon ADS seamlessly integrates with other AWS services. For example, you can export discovered data to Amazon Athena and Amazon QuickSight for further analysis and visualization.
Limitations of AWS Application Discovery Service
Complexity in Setup and Use
Setting up and utilizing AWS Application Discovery Service can present certain complexities, particularly for organizations with extensive or particularly unique IT environments. The initial configuration may require a detailed understanding of both the current IT infrastructure and the specific capabilities of AWS ADS.
In some cases, choosing between agentless and agent-based discovery methods can complicate the setup further, as each has its own prerequisites and limitations. Additionally, integrating the discovery data with other AWS services or third-party tools for migration planning may require additional expertise in API management and data handling.
Performance Impact
The use of AWS Application Discovery Service, especially when deploying the agent-based method, can lead to a performance overhead on the servers being analyzed. The agents continuously collect and transmit data, which can consume significant CPU, memory, and network bandwidth, potentially affecting the performance of the server and the applications running on it. Organizations must carefully plan the deployment of these agents, possibly scheduling operations during off-peak hours to minimize impact on business operations.
Limited to AWS
One notable limitation of AWS Application Discovery Service is its inherent design to facilitate migrations primarily to AWS. This focus can be a constraint for organizations seeking flexibility in choosing their cloud service providers. Businesses might find themselves needing additional tools or processes to adapt the insights from AWS ADS for use with other clouds, which could complicate multi-cloud strategies and potentially increase overall migration costs.
Tutorial: Getting Started with AWS ADS Agentless Collector for VMware Environments
This tutorial will show you how to use the ADS Agentless Collector to gain visibility over an on-premises VMware environment and prepare it for cloud migration.
Create an IAM User for the Agentless Collector
The first step in utilizing the AWS Application Discovery Service is to create an Identity and Access Management (IAM) user for the agentless collector. An IAM user is an entity that you create in AWS to represent the person or application that uses it to interact with AWS.
To create an IAM user, navigate to the Migration Hub in the AWS Management console and select a Region. Then, create an IAM user and set the DMSCollectorPolicy.
For the Agentless Collector, you need to attach the DiscoveryConnector policy to the user. Review the user details and then create the user. Remember to download the Access key ID and Secret access key, as you will need these later.
Download the Agentless Collector
With the IAM user in place, the next step is to download the agentless collector. The Agentless Collector is a virtual appliance that you can deploy on your VMware environment. It collects configuration, usage, and behavior data from your server and sends it to the AWS Application Discovery Service.
To download the agentless collector, navigate to vCenter. You need to be a VMware administrator to do this. Choose the target directory for the collector download. Follow the instructions provided to download the connector to your local machine. The connector is an OVA file that you can deploy on your VMware environment.
You can download the OVA file here.
Deploy the Agentless Collector
To deploy the collector, you will need administrator access to vCenter.
In the vCenter UI, select File from the menu, then Deploy OVF Template. Browse to the location where you saved the OVA file and select it. Follow the prompts to deploy the agentless collector.
Access the Agentless Collector Console
The Application Discovery Service Agentless Collector console allows you to configure the collector and start the data collection process.
To access this console, enter the collector’s IP address in your web browser’s address bar. When first accessing the collector, you’ll be given the option to Get Started. After that, you’ll have to select Log in.
Configure Agentless Collector
Configuring the collector involves setting up the network settings and testing the connectivity to the AWS Application Discovery Service.
In the Agentless Collector console, navigate to Configure Agentless Collector. Provide the Collector name in the relevant field (note that the name can include spaces but not special characters). You will be asked to provide the Access key ID and Secret access key for the IAM user that you created earlier. This allows the agentless collector to communicate with the AWS Application Discovery Service.
You will also need to set up an Agentless collector password with 8-64 characters. Re-enter the password to complete the verification process.
Next, you’ll need to read and accept the license agreement under Other Settings. You can also specify settings such as automatic updates. When finished, select Save configurations.
Set Up the Agentless Collector Data Collection Modules
The data collection modules determine the type of data that the agentless collector collects from your server.
In the Agentless Collector console, go to Data collection and select the relevant VMware machines. Currently, only VMware machines from analytics and database servers are supported.
The collector collects data at regular intervals and sends it to the AWS Application Discovery Service. You can view the status of the data collection process in the console.
View the Collected Data
After the data collection process is complete, you can view the collected data in the AWS Management Console. This data provides insights into your server’s configuration, usage, and behavior, which can help you plan your migration to AWS.
In the AWS Management Console, navigate to the Migration Hub and select Servers under the Discover tab. You can view details about the data discovered by the vCenter collector by selecting the relevant server hostname under Server info. This will display more details about the server, including the IP address and performance metrics.
You can also view data from the analytics and database collection module via the AWS Database Migration Service console. Under the Discover tab, select Inventory and then Analyze inventories. You can then view the results of the data analysis under the Schemas tab.
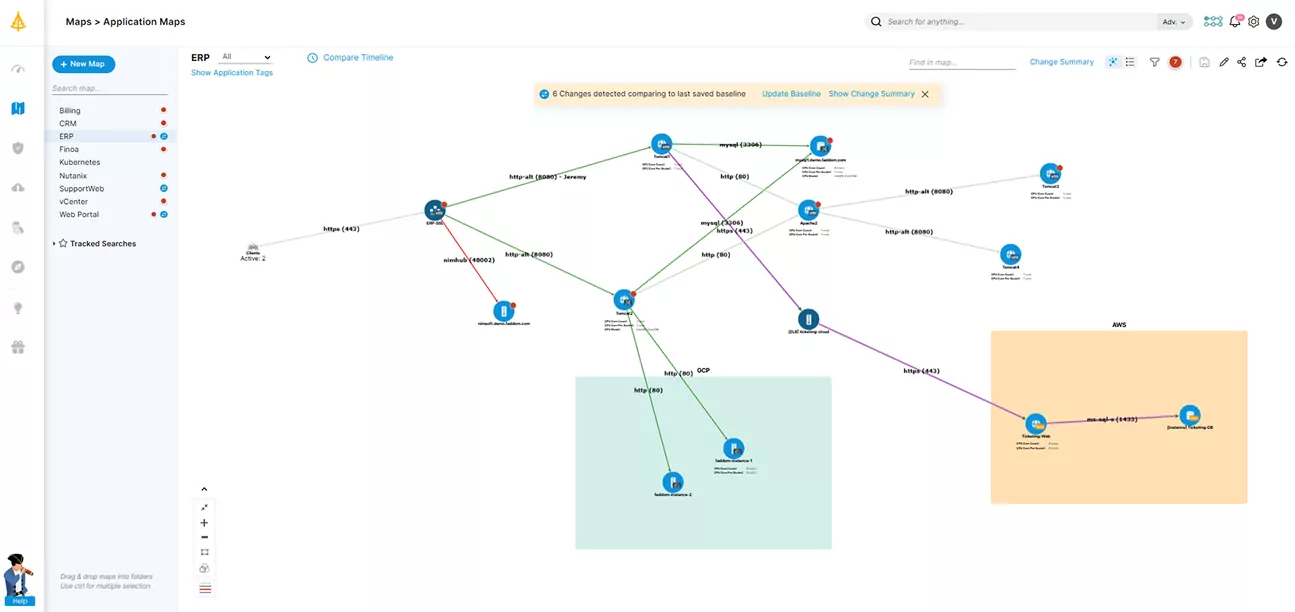
Faddom: Ultimate AWS Application Discovery Alternative
Faddom is a lightweight alternative to AWS Application Discovery. It can map assets AWS Application Discovery does not, including Microsoft Hyper-v, KVM, Nutanix, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Kubernetes, Radware, Kemp, A10, F5, and Citrix.
It is agentless, does not require credentials, and is cost-effective. It can map your entire environment in real-time, updating 24/7. Only one person can map an entire organization in under an hour.
Learn more about Faddom for application mapping or start a free trial to the right!