What Is CMDB Software?
CMDB (configuration management database) software solutions act as a central repository for tracking all IT assets, such as hardware and software, and documenting the complex relationships and dependencies between them. They provide a single source of truth for an organization’s IT infrastructure, enabling better support for IT service management (ITSM) processes like incident management, change management, and problem management.
By providing a clear map of IT components and their connections, CMDB software helps organizations understand their environment, manage risks, ensure compliance, and improve overall IT stability and efficiency.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey functions of CMDB software include:
- Centralized IT asset tracking: Stores detailed information about all IT components, including hardware, software, licenses, and network devices.
- Relationship mapping: Documents the connections and interdependencies between different IT assets, showing how they relate to business services.
- Impact analysis: Helps determine the potential business impact of changes or failures by visualizing how different assets are connected.
- Support for ITSM processes: Provides the foundational data for key IT processes.
- Risk and compliance management: Enhances security by providing visibility into all interactions and ensuring compliance with regulations and internal policies.
- Asset lifecycle management: Supports tracking assets from procurement to disposal, including managing warranty and license information.
Key Functions of CMDB Software
Centralized IT Asset Tracking
CMDB software excels at tracking all IT assets in one place. It adds structure and context to information usually dispersed across different teams, spreadsheets, or platforms. By automatically or manually populating inventory records, it enables IT professionals to understand what assets exist, where they are located, and their current status.
This centralized approach is vital in large, complex environments where manual tracking is error-prone. With up-to-date records, organizations can quickly locate devices or software installations, identify unused resources, and plan for upgrades or replacements. Asset tracking also provides historical data, making it easier to audit changes, troubleshoot issues, or analyze usage trends over time.
Relationship Mapping
Another key feature of CMDB software is mapping the relationships between configuration items. It identifies how servers, applications, databases, and other devices are interconnected, forming a topology of the IT environment. Understanding these dependencies is essential for troubleshooting and change management.
By visualizing relationships, IT teams can anticipate how the failure or modification of a single asset might impact others. This capability is particularly relevant during system upgrades or migration efforts, as it helps avoid unintended service disruptions. CMDBs also enable automated impact assessments, allowing faster and more reliable decision-making.
Impact Analysis
Impact analysis is a critical safety feature in any effective CMDB. It allows IT teams to predict how changes, from updates to hardware replacements, may ripple through the IT environment. By modeling asset dependencies and their configurations, the CMDB reduces the risk of service interruptions and costly downtime.
When a proposed change needs review, the CMDB can automatically highlight affected assets and services. This foresight leads to better planning, improved scheduling, and fewer surprises during deployment. As a result, impact analysis improves overall business continuity and supports more robust change management.
Support for ITSM Processes
CMDB software is foundational for IT Service Management (ITSM) frameworks like ITIL. It supports critical ITSM processes, such as incident, problem, and change management, by providing accurate, up-to-date insights into assets and configurations. By linking incidents or changes to specific CIs, teams can accelerate root cause analysis and resolution.
Additionally, integrating the CMDB with help desk or ticketing systems simplifies workflows, reduces manual data entry, and ensures that IT support actions are informed by real-world, real-time data. This integration supports more effective service delivery and compliance with audit or regulatory requirements.
Risk and Compliance Management
Effective risk and compliance management depend on a clear and current picture of IT assets and their configurations. CMDB software provides this visibility, enabling organizations to spot potential vulnerabilities and enforce adherence to internal policies or external regulations. With an up-to-date CMDB, compliance audits become simpler and more transparent.
The software can flag non-compliant assets, outdated software, or unauthorized changes, allowing IT teams to address issues proactively. Automated reporting features also help organizations demonstrate compliance to auditors or regulatory bodies, minimizing the risk of penalties while maintaining trust with stakeholders.
Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset lifecycle management tracks the journey of every CI from procurement to retirement. A CMDB manages key phases such as acquisition, deployment, maintenance, upgrades, and decommissioning. With a clear record, organizations can optimize costs, schedule timely maintenance, and reduce wastage.
Lifecycle management also enables better planning for asset replacement and capacity expansion. By recording warranty details, lease dates, and performance history, the CMDB helps IT teams make informed investment decisions and ensure the ongoing health of their infrastructure.
Benefits of Using CMDB Software
CMDB software delivers strategic value by improving visibility, control, and coordination across the IT environment. It strengthens operational efficiency and supports decision-making across IT and business functions:
- Improved visibility and transparency: Centralizes asset data and relationships, providing a clear, real-time view of the IT infrastructure.
- Faster incident resolution: Enables quicker root cause analysis by linking incidents to affected assets and configurations.
- Better change management: Reduces risk of downtime by identifying dependencies and forecasting the impact of proposed changes.
- Enhanced compliance: Supports regulatory and internal policy adherence through accurate reporting and audit trails.
- Cost optimization: Identifies underused or redundant assets, helping control spending and eliminate unnecessary purchases.
- Simplified IT processes: Integrates with ITSM tools to automate workflows and reduce manual tasks across incident, problem, and change management.
- Improved risk management: Detects configuration drift, unauthorized changes, and vulnerabilities before they escalate into larger issues.
- Lifecycle tracking: Supports strategic planning by offering detailed insight into asset status, performance, and retirement schedules.
How CMDB Software Works
Data Discovery
The first step in any CMDB implementation is discovering all relevant assets. CMDB software uses automated discovery tools to scan networks, identify devices, and collect configuration data. This automation ensures the inventory remains accurate even as assets are added, removed, or changed.
Manual entry is also supported for items that can’t be automatically detected, such as documentation or external services. Combining automated and manual methods reduces gaps in the database. Accurate discovery is critical because downstream processes like troubleshooting, lifecycle management, and audits depend on comprehensive asset coverage.
Data Standardization
Once data is collected, the CMDB must standardize information to ensure consistency. This involves normalizing naming conventions, categorizing assets appropriately, and validating data quality. Without standardization, reports become unreliable, and automated processes can break.
Data standardization occurs continuously, especially as new assets are discovered or existing ones change. Many CMDB tools support rules and templates to simplify this task. Consistent data not only improves internal reliability but also supports integrations with other IT management platforms that may require data in structured formats.
Relationship Building
Building accurate relationships among configuration items is foundational to a functional CMDB. The software links hardware, applications, networks, and services based on data from discovery tools and manual input. These relationships are visualized through dependency maps or graphs, helping IT professionals understand and analyze the full context of their infrastructure.
Relationship building isn’t a one-time process. As assets or configurations change, the CMDB must update dependencies to remain accurate. Failure to maintain updated relationships can compromise impact analysis, change management, and incident response, making this an ongoing operational priority.
Data Access
To be valuable, a CMDB must make its data easily accessible to authorized users, applications, and processes. Modern solutions include powerful search, filtering, and reporting features, enabling teams to find and exploit relevant information without delay. Integration with ITSM and monitoring tools brings CMDB insights to workflows where they are most needed.
Role-based permissions and audit logs ensure sensitive data is protected and accessed only by those with need. Some CMDBs offer APIs for programmatic access, enabling automation and advanced reporting. Ease of access is key; if users can’t quickly retrieve needed data, the CMDB’s value declines, making usability and integration critical evaluation criteria.
Related content: Read our guide to CMDB tools

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better leverage CMDB software:
-
Build a governance framework early: Establish ownership for data quality, CI lifecycle policies, and update accountability before CMDB rollout. Without governance, CMDBs become unreliable quickly due to drift and duplication.
-
Segment the CMDB into domains: Divide CIs by logical domains like infrastructure, applications, cloud services, and business services to simplify access controls, reduce data clutter, and support domain-specific reporting.
-
Start with high-value CIs: Don’t aim for full coverage immediately. Focus on CIs that are most critical to business operations and incident response first. Expand scope as maturity grows.
-
Use tagging and metadata for context: Add business-relevant tags (like owner, SLA tier, or criticality) to each CI. These enrich search, automate workflows, and help prioritize incidents and changes effectively.
-
Combine with real-time monitoring: Integrate monitoring tools to reflect CI status in real time. This helps operations teams correlate alerts with CI relationships and perform faster root cause analysis.
Notable CMDB Software Solutions
1. Faddom

Faddom is an agentless application dependency mapping platform that helps organizations populate and maintain an accurate CMDB across hybrid and multicloud environments. Through continuous discovery of real-time dependencies, servers, and business applications, Faddom removes the need for manual data collection and keeps configuration records consistently reliable for ITSM, audits, and change management.
Key features include:
- Agentless discovery: Automatically map IT assets and dependencies in under 60 minutes without installing agents or opening ports
- Real-time updates: Continuously refresh dependency data to keep the CMDB accurate and free of configuration drift
Hybrid and multicloud visibility: Discover and map assets across data centers, virtual environments, and cloud platforms - ServiceNow integration: Sync dependency maps and asset data directly into ServiceNow CMDB to strengthen ITSM processes
- Accurate impact analysis: Provide trusted upstream and downstream relationships for safer changes and faster incident resolution
Book a demo to see how Faddom can keep your CMDB complete and always up-to-date!
2. SolarWinds Service Desk

SolarWinds Service Desk is a cloud-based IT service management (ITSM) platform that integrates a configuration management database to improve operational visibility and efficiency. Designed with AI capabilities, it helps IT teams simplify workflows, accelerate incident resolution, and better align IT services with business needs.
Key features include:
- Incident management: Automatically identifies solutions, monitors ticket sentiment, and assigns tickets based on rules to speed up resolution.
- Integrated CMDB: Visualizes relationships between infrastructure and applications, helping teams understand dependencies and assess the impact of changes.
- IT asset management: Tracks hardware and software assets to support compliance, optimization, and lifecycle planning.
- Change management: Provides structured workflows to reduce risk during updates, deployments, or infrastructure changes.
- Live collaboration tools: Supports real-time communication through web, email, Teams, Slack, and mobile apps for seamless incident handling.
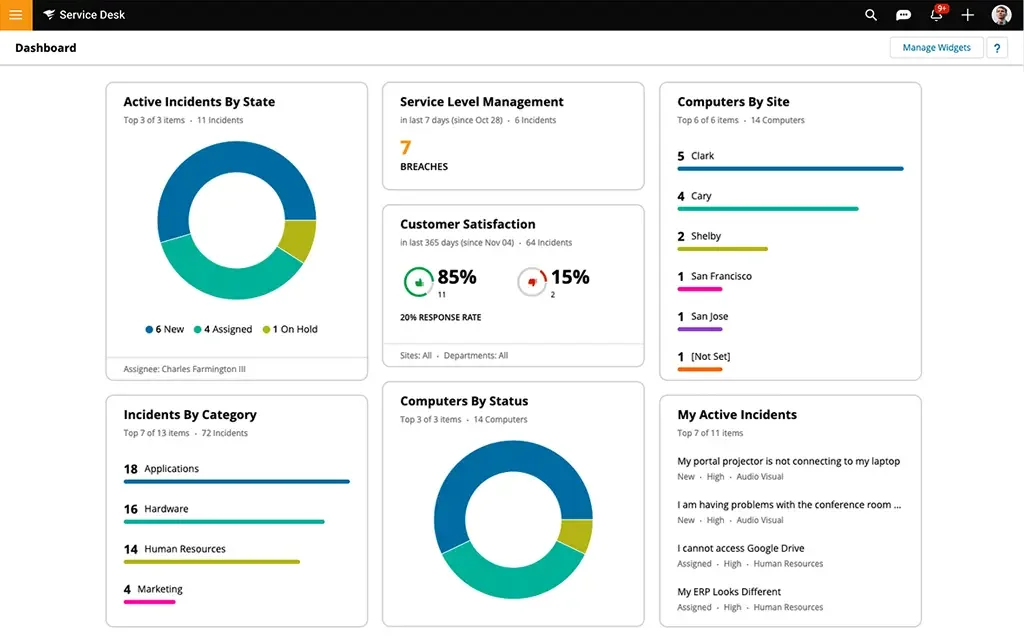
Source: SolarWinds
3. Freshservice CMDB

Freshservice CMDB is an automated configuration management database that gives IT teams visibility into their infrastructure, dependencies, and configurations. It combines discovery, inventory updates, and visualizations to help organizations manage IT operations more intelligently.
Key features include:
- Automated discovery: Scans the IT environment, including hardware, software, cloud, and legacy systems, to maintain a continuously updated CMDB.
- Dependency mapping: Visualizes upstream and downstream relationships between configuration items to help assess the impact of changes and prevent service disruptions.
- Inventory management: Maintains a clean, complete inventory of all IT assets, simplifying compliance audits and reducing security risks.
- Visibility: Offers full-stack visibility through detailed topology maps, dashboards, and enriched asset data for smarter decision-making.
- Compliance and audit support: Simplifies regulatory reporting with one-click audit-ready data, helping to reduce the risk of fines and ensure policy adherence.
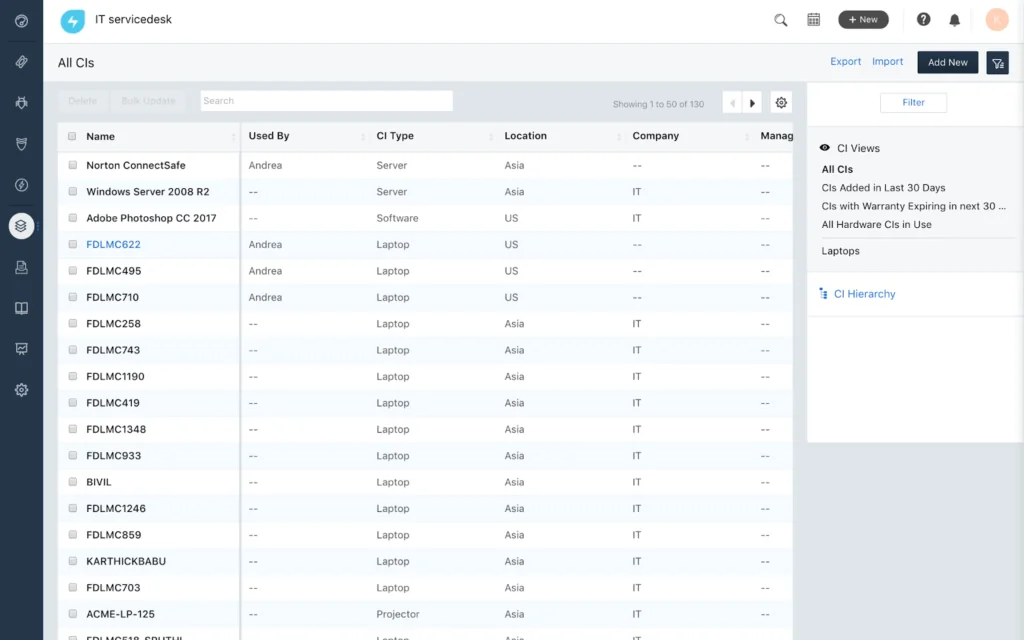
Source: Freshservice
4. ServiceNow CMDB

ServiceNow CMDB is an enterprise-grade configuration management database that serves as a unified system of record for all configuration items (CIs) across the IT landscape. It centralizes and curates data from multiple sources, offering insights into the relationships and statuses of IT assets.
Key features include:
- CMDB workspace: A centralized interface for exploring, validating, and managing CI data, helping ensure accuracy and insight across the organization.
- Service graph connectors: Standardize and automate the integration of external data from various IT systems to populate the CMDB reliably.
- Data acquisition tools: Pulls data from multiple sources to build and refresh a complete, real-time view of the IT environment.
- Visualization and reporting: Provides visual maps that show technical and business relationships between CIs, supporting impact analysis and decision-making.
- Trusted data curation: Continuously evaluates and improves data quality to support audit-readiness and reliable AI outcomes.

Source: ServiceNow
5. i-doit

The i-doit Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized platform designed to manage, document, and analyze components of an organization’s IT infrastructure. Built according to ITIL standards, it provides a structured and compliant foundation for IT service management by capturing data on assets and their relationships.
Key features include:
- Centralized IT asset management: Records and manages all IT components in one place, offering visibility into infrastructure and configurations.
- Status overview: Provides up-to-date information on asset conditions and relationships to support daily operations and planning.
- Support for ITSM processes: Integrates with key IT service management workflows, including incident, change, problem, and release management.
- ITIL compliance: Delivers a CMDB structure aligned with ITIL best practices, ensuring compatibility with standard ITSM frameworks.
- Impact analysis and change management: Uses current and historical data to analyze the impact of proposed changes, helping reduce service risks.
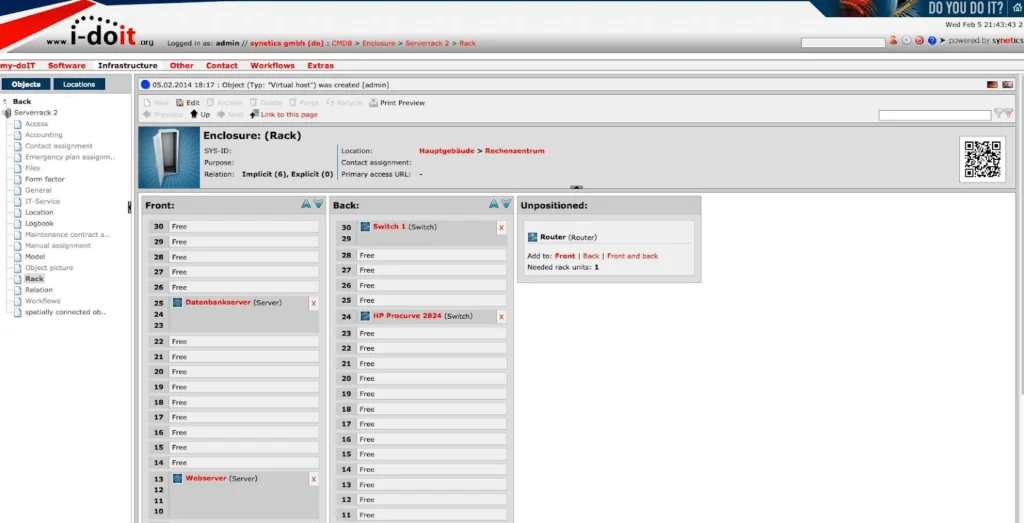
Source: i-doit
Conclusion
A well-implemented CMDB provides organizations with the visibility and control needed to manage increasingly complex IT infrastructure. It enables proactive planning, reduces risks tied to changes or failures, and supports compliance with internal and external standards. By aligning IT assets with business services, a CMDB ensures that technology decisions are better informed, incidents are resolved faster, and IT operations contribute more directly to organizational goals.