What Is a CMDB?
An enterprise Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a central IT repository that tracks and documents all hardware, software, and service assets (Configuration Items, or CIs) and their relationships, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s IT infrastructure.
Key enterprise benefits include enhanced IT decision-making, improved incident and change management, better IT service management (ITSM) and compliance, and support for digital transformation by mapping dependencies and improving asset visibility across hybrid cloud environments.
Table of Contents
ToggleCMDBs offer enterprises the following capabilities:
- Enhanced visibility and control: Provides a single, consolidated view of the entire IT infrastructure, breaking down silos and improving control over assets and configurations.
- Improved ITIL processes: A CMDB is a foundational element of the ITIL framework, enabling effective IT service management (ITSM).
- Incident management: Quickly identifying impacted services to diagnose and resolve issues faster.
- Change management: Assessing the potential impact of changes on other CIs and preventing disruptions.
- Problem management: Analyzing recurring issues by understanding the underlying IT components.
- Informed decision-making: Offers data-driven insights for strategic planning, resource allocation, and budgeting related to IT assets.
- Support for digital transformation: Automates asset discovery in cloud environments, providing critical data for cloud migration strategies and managing transient cloud-native tools.
- Compliance and governance: Supports regulatory compliance by providing accurate, complete records of IT assets and their configurations, essential for auditing and data governance.
- Asset lifecycle management: Helps track assets from their procurement and deployment to their maintenance and retirement, optimizing their value.
Why a CMDB Is Essential for Enterprises
Enhanced Visibility and Control
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) provides a centralized inventory of all IT assets, including hardware, software, networks, and their interdependencies. This visibility allows IT teams to see precisely what assets exist in their environment, where they are located, and how they interact with each other. With this level of detail, it becomes easier to diagnose issues, plan maintenance, and optimize resource use.
Enhanced control comes from the ability to manage asset information in a single authoritative source. Enterprises gain the capacity to track the state and changes of each component, preventing configuration drift and ensuring compliance with internal standards. Having accurate, up-to-date data in the CMDB reduces the risk of accidental service disruptions.
Improved ITIL Processes
A CMDB forms the backbone for many ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) processes by providing the reliable data that these frameworks require. For example, ITIL processes such as incident, change, and problem management all benefit from the comprehensive view that a CMDB offers.
Beyond supporting core ITIL processes, a well-maintained CMDB standardizes the information flow across different teams and tools in the enterprise. This interoperability is critical for executing standardized procedures, automating repetitive tasks, and maintaining data quality, all key tenets of ITIL.
Incident Management
When incidents arise, quick and accurate response is critical for enterprise IT. A CMDB dramatically accelerates incident management by mapping incidents directly to affected assets, helping support teams quickly identify root causes. Knowing the relationships between configuration items (CIs) means support staff don’t waste time searching for the affected systems, and can immediately begin remediation based on real system data.
The CMDB provides historical context for every configuration item involved in the incident. Support analysts can review recent changes, dependencies, and previous incidents involving the same asset, allowing them to make informed decisions faster. This context leads to shorter mean time to resolution (MTTR) and reduces the risk of recurring incidents.
Change Management
Enterprise change management processes are complex and can introduce significant risk if not controlled. A CMDB supports change management by documenting the entire IT landscape, including dependencies and potential impact zones. When a change request is submitted, IT teams use CMDB data to accurately assess the scope and risks before implementation, reducing the likelihood of unintended side effects or outages.
The CMDB also enables detailed change tracking by recording what modifications were made, when, and by whom. This audit trail not only simplifies post-change reviews but also aids in root cause analysis if problems arise.
Problem Management
Problem management focuses on identifying and eliminating the underlying causes of incidents. A CMDB aids this process by providing a historical view of assets, configurations, and their change records. Analysts can trace recurring issues back to specific configuration items or patterns, making it easier to identify trends and systemic problems in the IT environment.
Additionally, the structured data in a CMDB makes knowledge sharing and collaboration more effective. When a root cause is documented, the information becomes available for future reference, preventing the same issue from resurfacing unnoticed.
Informed Decision-Making
Enterprises operate IT environments that are both complex and business-critical, making decisions around upgrades, migrations, and investments high-stakes. A CMDB provides the data foundation needed to inform these choices. By consolidating configuration and relationship details into a single source of truth, it enables leaders to evaluate the impact of technology initiatives with confidence.
Beyond immediate operations, CMDB data supports long-term strategy and governance. Enterprises can analyze usage trends, align IT spending with business priorities, and identify opportunities to optimize or consolidate resources. This structured information allows CIOs and IT managers to forecast future needs, allocate budgets effectively, and plan roadmaps that balance stability with innovation.
Support for Digital Transformation
Digital transformation initiatives demand agility, scalability, and a clear understanding of complex IT ecosystems. A CMDB provides the foundational data required to map dependencies and align IT assets with new business services. Enterprises can confidently launch, migrate, or decommission services with reduced risk, knowing asset relationships and potential impact areas are visible and understood.
CMDB-driven visibility enables enterprises to automate repetitive tasks and orchestration workflows. As digital initiatives often involve rapid change, automation backed by accurate configuration data ensures compliance and reduces manual intervention.
Compliance and Governance
Maintaining regulatory compliance is a major concern for most enterprises, especially those in regulated industries such as finance and healthcare. A CMDB streamlines audit processes by providing a holistic and up-to-date view of all IT assets, their configurations, and historical changes. This transparency allows organizations to quickly demonstrate compliance with internal and external standards.
Governance practices are also improved through the use of a CMDB, as it centralizes policy enforcement across the IT landscape. Enterprises can automate compliance checks and ensure that only authorized changes are made to critical systems. The resulting audit trails and reports not only support regulatory requirements but also strengthen internal security and risk management postures.
Asset Lifecycle Management
Tracking asset lifecycles is critical for ensuring optimal utilization and timely maintenance or replacement. A CMDB consolidates the lifecycle status of every asset, from procurement through deployment, operation, and retirement. This view enables IT teams to schedule timely upgrades and decommissions, minimizing the costs and risks associated with aging infrastructure.
Additionally, effective asset lifecycle management powered by a CMDB improves budget forecasting and planning. By knowing exactly what assets are in use, where they are located, and what stage of the lifecycle they’re in, enterprises prevent over-purchasing and optimize asset allocation. This precision enhances both financial efficiency and operational readiness.
Notable CMDB Solutions for Enterprise
1. Faddom

Keep your CMDB accurate and complete with Faddom. Faddom automatically discovers, maps, and maintains real-time visibility into servers, business applications, and dependencies across hybrid and multicloud environments. It ensures that your configuration data is consistently updated, aligned with reality, and free from blind spots or manual errors. By reducing effort and providing a single source of truth, Faddom enhances IT operations and governance.
Key features include:
- Agentless discovery: Map all assets and dependencies in under 60 minutes without installing agents.
Continuous dependency mapping: Keep CMDB records automatically synchronized with live infrastructure data. - Integration with ServiceNow: Enrich ServiceNow CMDB with accurate configuration and relationship details for improved ITSM and change management.
- Change management visibility: Identify upstream and downstream impacts before implementing changes.
- Incident resolution: Trace dependencies instantly to accelerate root cause analysis.
- Hybrid and multicloud coverage: Consolidate on-premises, virtual, and cloud environments into a unified view.
Discover how Faddom can elevate your CMDB accuracy and automation!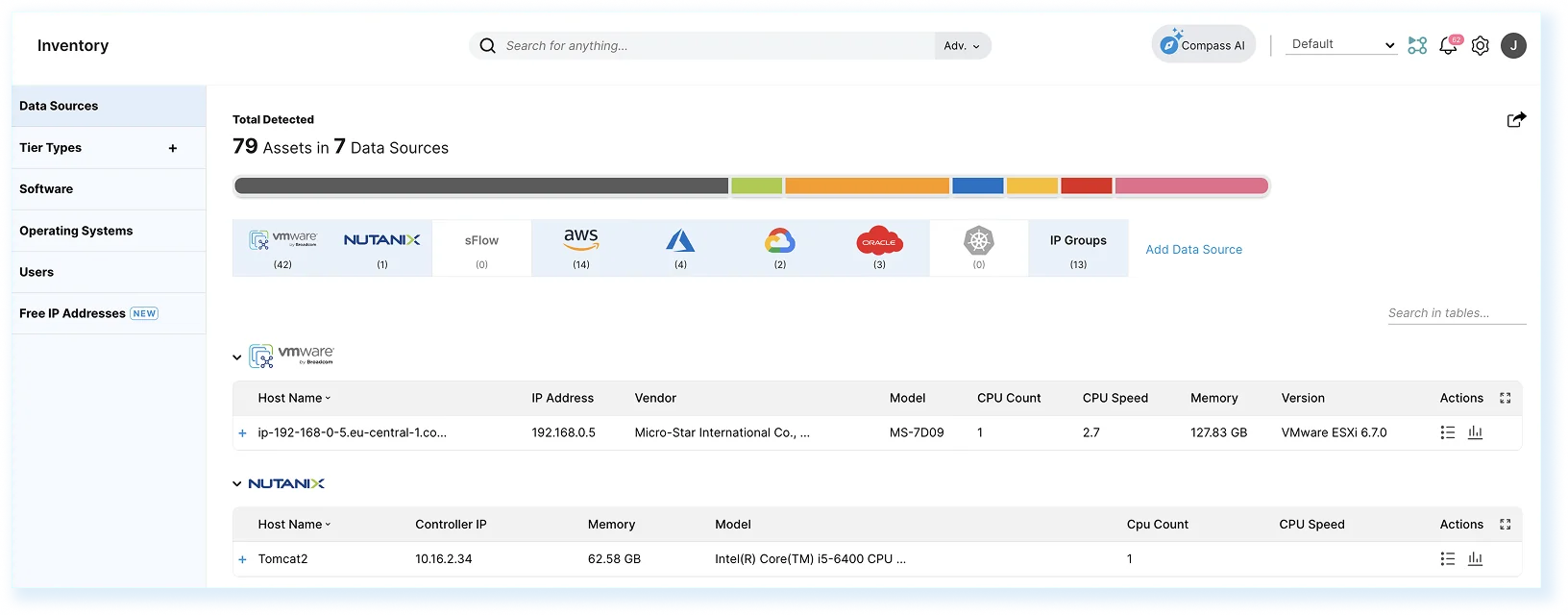
2. ServiceNow CMDB

The ServiceNow Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a cloud-based, centralized system of record for managing the configuration data of IT environments. Designed to work with other ServiceNow applications, it helps enterprises consolidate, validate, and maintain accurate data about IT assets and their relationships.
General features include:
- Single data model: Uses a consistent, predefined schema shared across all ServiceNow applications for seamless integration and immediate usability
- Discovery integration: Works with ServiceNow ITOM Discovery to automatically identify and update infrastructure and service data
- Automated service mapping: Maps technical and business services to infrastructure for context-aware incident and change management
- Data quality controls: Includes dashboards, data certification, duplicate prevention, and automated remediation to maintain data accuracy
- Third-party data ingestion: Supports connectors and ETL tools for importing data from external systems with integrity check.
Enterprise features include:
- Support for hybrid and cloud environments: Visibility into platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Kubernetes, and serverless services
- Identification and reconciliation engine (IRE): Normalizes data from multiple sources and prevents CI duplication
- Service graph connectors: Certified integrations for clean, consistent third-party data ingestion, governed by ServiceNow standards
- Customizable data certification workflows: Enables scheduled or on-demand verification of CI data by responsible owners
- Health dashboards with industry benchmarks: Measures CMDB completeness, correctness, and compliance, with benchmarking across peer organizations
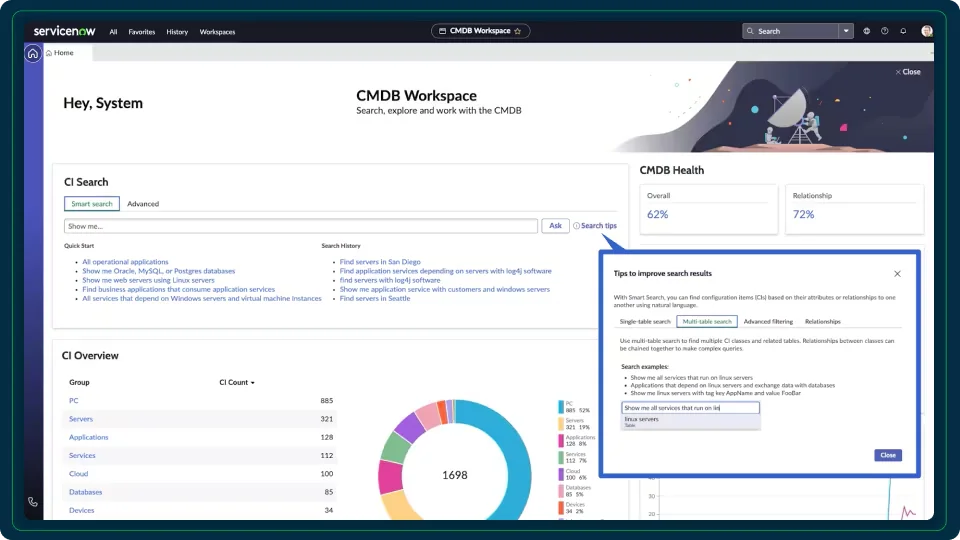
Source: ServiceNow
3. BMC Helix CMDB

BMC Helix Configuration Management Database is an enterprise solution that unifies data from disparate sources to create a complete view of IT assets and their relationships. Designed to support both day-to-day operations and long-term strategy, it enables organizations to understand how infrastructure connects to business services and their consumers.
General features include:
- Adaptable data model: Standards-based model that can be extended or customized to meet specific organizational needs
- Data quality engine: Built-in normalization, deduplication, and reconciliation to ensure clean, trusted data
- Visualization tools: CMDB Explorer provides in-context views of CIs, including impact simulations and dependency mapping
- Integrated discovery support: Comes pre-integrated with BMC Helix Discovery for automatic population of infrastructure data
- Integration options: Supports Java, C, SOAP, and REST APIs to connect with external systems and applications.
Enterprise features include:
- Service-centric architecture: Maps infrastructure to business services to understand the impact of outages on consumers
- CMDB health indicators: Built-in KPIs provide real-time insights into data completeness, consistency, and accuracy
- Configuration management: Enables robust governance through configuration tracking and relationship management
- Support for hybrid environments: Consolidates physical, virtual, and cloud infrastructure into a unified view
- Strategic decision support: Provides a single reference point to assess risk, plan changes, and align IT services with business goals

Source: BMC
4. Cloudaware CMDB

Cloudaware CMDB is a unified configuration management database for multi-cloud and hybrid environments. It consolidates data across public cloud platforms, on-premise infrastructure, and user devices to create a centralized, trusted source of configuration item (CI) data.
General features include:
- Unified asset inventory: Consolidates CIs across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, VMware, Kubernetes, and on-premise environments
- Discovery engine: Supports over 3,000 cloud services with automatic discovery via APIs, network scans, and SNMP
- Software asset management: Auto-discovers software and builds a centralized catalog with SBOM support
- Multi-layer change tracking: Detects and logs changes across cloud services, operating systems, and infrastructure layers
- Visualization & reporting: Offers dashboards and reports for compliance, cost usage, service ownership, and infrastructure health
Enterprise features include:
- Multi-cloud governance: Enables centralized visibility and control across global DevOps environments
- Automated compliance monitoring: Out-of-the-box support for PCI, HIPAA, NIST, and ISO standards without additional integration
- Change management with scoring: Assigns risk scores to changes and blocks non-conforming changes automatically
- Service catalog integration: Links CIs with service catalog entries to improve ownership tracking and governance
- Cost optimization: Provides asset-level cost and usage reporting to support rightsizing and budgeting
Source: Cloudaware
5. Device42

Device42 provides an automated configuration management database that delivers visibility across IT environments. By capturing and mapping assets across cloud, virtual, and physical infrastructure, it helps eliminate blind spots and manual updates. The platform serves as a foundation for IT operations, helping teams make decisions and accelerate incident response.
General features include:
- Automated discovery: Continuously captures CIs across legacy, virtual, and cloud environments with minimal manual input
- Asset inventory: Tracks physical hardware, software, cloud services, network devices, and end-user systems in one platform
- Interactive dashboards: Delivers configurable reporting and visualizations, including roll-up summaries and dependency views
- Dependency mapping: Maps relationships between applications, services, and infrastructure for root cause and impact analysis
- Preconfigured CI models: Includes ready-to-use templates for faster onboarding and reduced setup effort
Enterprise features include:
- Topology views: Visual resource maps help understand complex interdependencies and change impact
- Audit-ready inventory: Maintains accurate, up-to-date asset records to simplify compliance and governance
- Hybrid environment support: Provides unified visibility from mainframes and on-premise servers to containers and cloud services
- Security and risk reduction: Helps predict and prevent outages with complete context for infrastructure and service layers
- Data enrichment and normalization: Enhances discovery output with contextual details to improve data quality and usability

Source: Device42
Related content: Read our guide to CMDB tools
Conclusion
A CMDB is indispensable for enterprises seeking to gain control over sprawling, hybrid IT environments. It consolidates asset data, maps dependencies, and provides the insights needed for efficient operations, effective risk management, and informed strategic planning. By embedding CMDB capabilities and accurate IT documentation into IT processes, enterprises can improve resilience, reduce costs, and ensure their technology infrastructure consistently supports business objectives.