What Is Ivanti?
Ivanti’s main competitors include large technology companies like Microsoft, ServiceNow, and IBM, as well as specialized IT management and security providers such as Faddom, ManageEngine, NinjaOne, and BMC. The specific competitors vary depending on the Ivanti product or market segment being considered, such as IT service management (ITSM), endpoint security, or digital employee experience (DEX).
Ivanti is an IT software company specializing in solutions for unified endpoint management, IT asset management, and security. Its platform integrates various IT functions, allowing organizations to automate routine tasks, secure devices, manage endpoint configurations, and maintain compliance.
Ivanti’s suite supports desktops, servers, mobile devices, and cloud environments, giving IT teams centralized visibility and control across diverse infrastructures. Core modules include patch management, service management, device discovery, and remote support, all aimed at reducing operational overhead and improving IT responsiveness.
The platform caters to medium and large enterprises seeking consolidated IT operations. Ivanti is frequently chosen for its ability to blend service management and security capabilities, reducing the risk of security incidents. Its tools are used across sectors such as healthcare, education, finance, and government.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Ivanti Limitations
While Ivanti offers strong capabilities for endpoint management and IT operations, several limitations can affect its usability, performance, and adoption, especially in large or complex environments. Below are the main challenges reported by users on the G2 platform:
- User interface complexity: The interface is often described as cluttered and unintuitive, making it difficult to quickly access essential tools or navigate features efficiently.
- Performance issues at scale: Users managing a large number of devices may experience slowness or lag, particularly during patching or security updates.
- Limited dashboard customization: Current dashboard features in Ivanti Neurons lack flexibility, with limited customization options. Improvements are said to be on the roadmap but are not yet available.
- Steep learning curve: The platform requires significant time to learn and configure. Training is often necessary for IT staff to use it effectively, particularly for those new to UEM solutions.
- Automation reliability: Some automation processes are prone to errors, leading to frequent manual interventions.
- Complex setup and configuration: The initial setup can be complicated, requiring deep technical knowledge and extended time to implement properly.
- Licensing limitations: Licensing for Ivanti Neurons and Endpoint Manager (EPM) is handled separately, which can be a commercial barrier for organizations looking to consolidate tools.
- Overkill for small organizations: Smaller companies may find Ivanti’s feature set excessive for their needs, both in scope and cost.
- Delayed support response: Support responsiveness varies, with some users needing to go through intermediaries to reach the actual support team.
- Unclear feature parity between versions: There’s confusion around the differences in capabilities between Neurons EPM and the on-premise EPM, making planning and decision-making more difficult.
Notable Ivanti Alternatives and Competitors
1. Faddom

Faddom is an agentless application dependency mapping platform that provides IT teams with real-time insights into how servers and business applications interact in hybrid and multicloud environments. It helps organizations minimize operational risks, speed up troubleshooting, and maintain stable IT operations by providing always-up-to-date dependency information.
- Agentless mapping: Maps applications, servers, and traffic flows in under 60 minutes without agents or network changes.
- Lightweight and easy to adopt: Delivers clear visibility without long deployments or complex configuration.
- Real-time dependency visibility: Shows how systems connect and depend on each other to support faster incident resolution and safer change planning.
- Shadow IT discovery: Identifies unknown services, unmanaged assets, and unexpected communication paths across the environment.
- Operational stability: Reveals upstream and downstream impacts to prevent service outages during updates, patches, and infrastructure changes.
- Zabbix integration: Enhances monitoring alerts by adding full application context so teams understand not only what failed but what it affects.
Want to see it in action? Book a demo with our experts!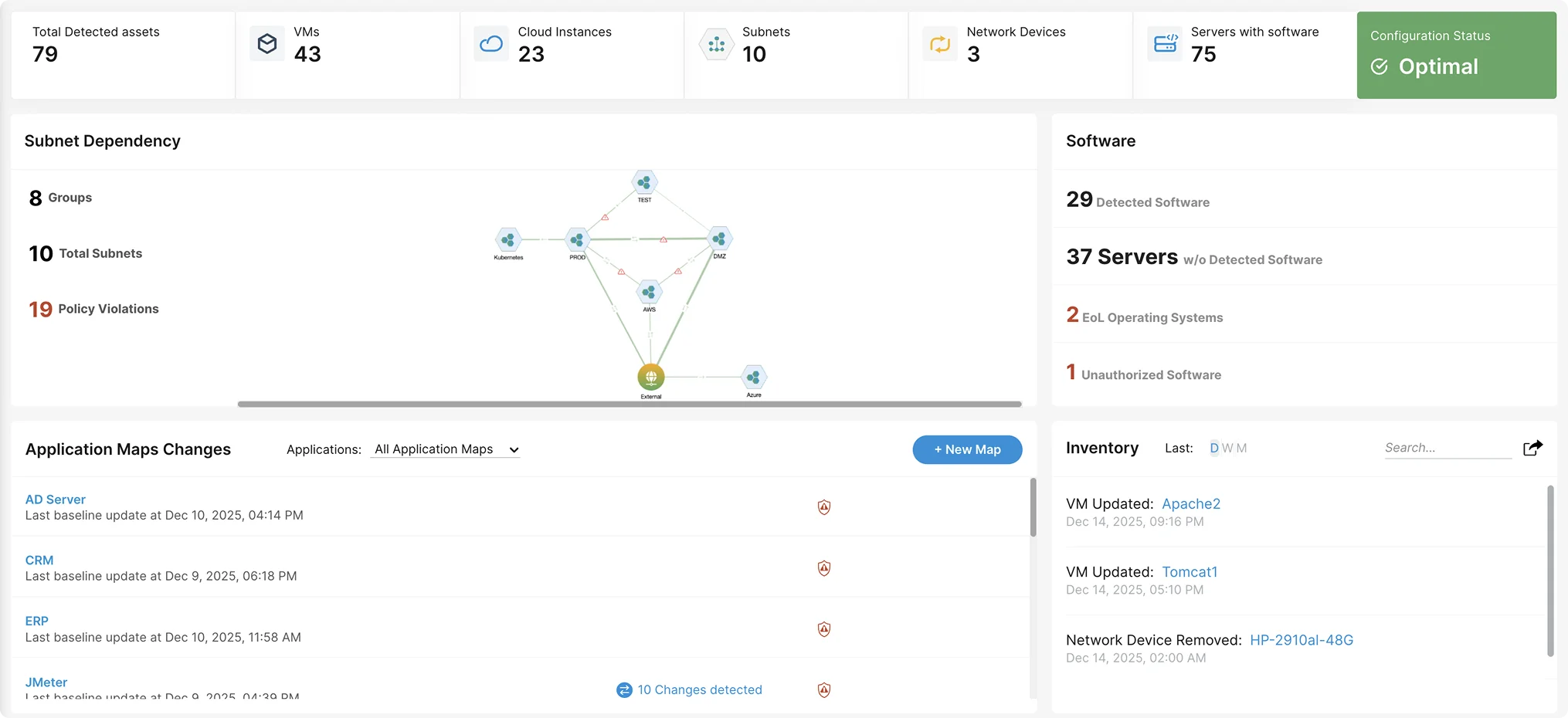
2. ServiceNow

ServiceNow is an alternative to Ivanti, offering IT service management (ITSM) solutions built on its AI-driven platform. It centralizes IT operations by unifying workflows, data, and systems into a single cloud-based environment. Organizations use ServiceNow to automate incident resolution, change management, and deliver IT services at scale.
Key features include:
- Automated IT processes: Uses AI and cloud capabilities to automate incident, problem, and change management.
- Unified platform: Operates on a single data model, integrating tools, workflows, and services.
- AI agents and analytics: Provides recommendations, performance tracking, and autonomous task execution.
- 24/7 employee support: Delivers a mobile-friendly service portal with AI search and virtual agents for self-service.
- Scalable and secure: Built for enterprise environments with high demands for reliability and compliance.
Source: ServiceNow
3. BMC Helix ITSM

BMC Helix ITSM is the cloud-based evolution of Remedy, applying predictive capabilities to automate classification, routing, and resolution of incidents while supporting multi-cloud environments. By integrating with DevOps tools and offering containerized deployment, it helps IT teams achieve greater efficiency and agility.
Key features include:
- Predictive service management: Automates classification, assignment, and routing of incidents with AI and machine learning.
- Multi-cloud support: Brokers incidents, changes, and releases across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Integrated DevOps tools: Connects with Jira and other agile platforms for seamless change and release management.
- Knowledge management: Delivers curated knowledge with lifecycle management, AI-driven recommendations, and KCS support.
- Change and release management: Reduces failed changes and costs with automated impact analysis, collision detection, and traceability.
Source: BMC
4. Microsoft Intune

Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution for hybrid and remote work environments. It enables organizations to manage and secure devices, apps, and user access across platforms such as Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and Linux. Its compliance features help protect organizational data on both company-owned and personal devices.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Supports Windows, macOS, iOS/iPadOS, Android, Linux, and virtual endpoints, covering both corporate and personal devices.
- App management: Deploys, updates, and removes applications, including Microsoft 365 apps, Win32, and line-of-business apps, with policies for securing app data.
- Policy automation: Enables centralized creation and deployment of compliance, configuration, and security policies that apply to devices over the internet.
- Self-service tools: Provides a Company Portal app and web interface for password resets, app installs, and group enrollments.
- Security integration: Connects with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and partner services to enforce compliance, analyze threats, and automate remediation.
Source: Microsoft
5. NinjaOne ITSM

NinjaOne ITSM combines IT service management with unified endpoint management (UEM) in a single cloud-based platform. It enables IT teams to simplify ticketing, documentation, remote access, and device management within one workflow. It gives visibility into endpoints and allows direct support for users anywhere without VPNs or heavy infrastructure.
Key features include:
- Incident and problem management: Accepts, prioritizes, and routes tickets with automation to meet SLAs and improve agent productivity.
- On-ticket remediation: Resolves endpoint issues directly from tickets through remote access, script deployment, and app or OS actions.
- Centralized device management: Monitors and secures endpoints globally from a single platform without VPN requirements.
- Workflow automation: Uses customizable rules, templates, and triggers for ticket creation and response to reduce manual workload.
- Automated device management: Handles onboarding, monitoring, patching, backup, and software deployment at scale.
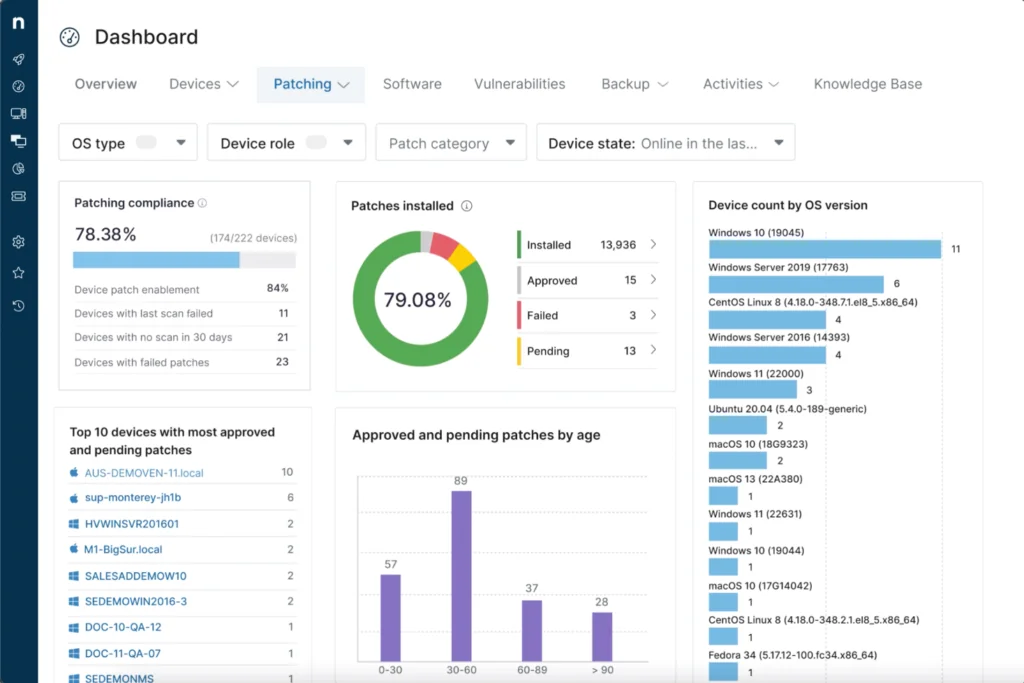
Source: NinjaOne
6. ManageEngine Service Desk Plus

ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus is an AI-driven IT and enterprise service management platform that integrates ITSM, IT asset management, and CMDB capabilities. It is ITIL-certified for 14 practices and supports departments beyond IT, including HR, facilities, and finance. With GenAI features, it automates triage, ticket resolution, and knowledge discovery.
Key features include:
- AI-enhanced service management: Uses predictive intelligence for ticket triage, routing, and sentiment analysis.
- Virtual support agents: Provides text and voice-based assistance through Zia, the platform’s AI-powered agent.
- GenAI capabilities: Integrates with ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot for knowledge discovery, response generation, and request summarization.
- Enterprise service management: Supports multi-instance models with process and data segregation across IT and non-IT departments.
- Low-code customization: Allows creation of custom modules, forms, configurations, and reports without complex coding.
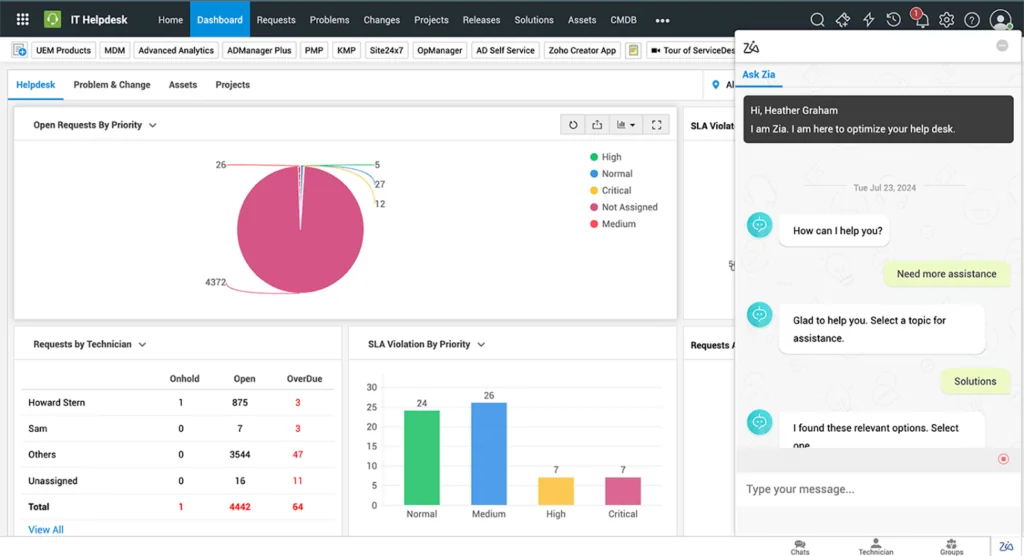
Source: ManageEngine
7. JumpCloud

JumpCloud is an open directory platform that unifies identity, device, and access management in a single cloud-based solution. It enables organizations to simplify IT operations while implementing zero trust security across users, devices, and applications. It supports Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android, centralizing device management and SaaS administration.
Key features include:
- Unified identity management: Provides one identity for all resources with single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Cross-platform device management: Manages and secures Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS devices with policy enforcement, patching, and remote troubleshooting.
- SaaS management: Monitors application usage, eliminates shadow IT, and simplifies provisioning and license optimization.
- JumpCloud Go™ authentication: Offers passwordless login using biometrics or device trust.
- Zero-trust controls: Enforces conditional access, trusted device policies, and continuous authentication across all environments.

Source: JumpCloud
8. SysAid

SysAid is an AI-based IT service management platform that combines ITSM, asset management, and automation in a single solution. It uses AI agents to monitor assets, detect issues, and trigger fixes proactively. It offers asset visibility, ITIL-aligned workflows, and reporting to help organizations simplify operations and make data-driven decisions.
Key features include:
- AI-powered automation: Uses AI agents to monitor assets, detect issues, and initiate automated fixes before users are affected.
- Asset management: Discovers and manages hardware, software, cloud, and IoT assets with embedded asset data in tickets.
- Custom dashboards and reporting: Provides insights into IT performance, KPIs, and trends for decision-making.
- End-to-end workflow automation: Simplifies incident, change, request, and approval processes with AI-driven efficiency.
- Self-service portal: Offers employees a centralized interface for ticket submission, progress tracking, and knowledge base access.
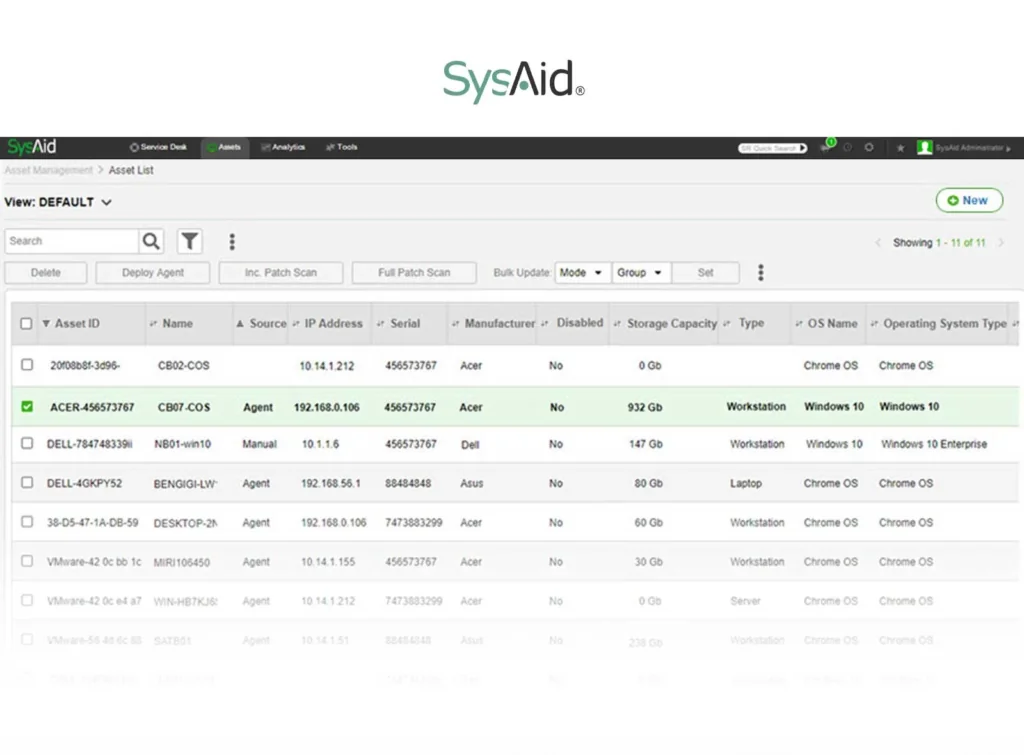
Source: SysAid
Learn more in our detailed guide to Ivanti Asset Management (coming soon)
Conclusion
When evaluating alternatives to Ivanti, organizations should consider their specific needs in areas such as endpoint management, IT service delivery, automation, and compliance. Factors like ease of deployment, scalability, support quality, and integration capabilities often play a key role in determining the right fit. Choosing the right solution depends on aligning technical requirements with business goals, ensuring that the platform can adapt to evolving IT environments without adding unnecessary complexity.






