What Is ManageEngine?
ManageEngine is a suite of IT management software developed by Zoho Corporation to help organizations simplify IT operations. It covers network monitoring, help desk ticketing, endpoint management, identity and access management, and application performance monitoring.
The platform’s modular approach allows IT departments to select only the tools they need, integrating various IT service management (ITSM) components into a unified environment. Its focus on mid-market and enterprise clients has made it a notable choice for organizations looking to centralize IT administration.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe product offerings provide cloud-based and on-premises options. ManageEngine’s solutions often appeal to organizations seeking cost-effective alternatives to more complex ITSM suites. With its broad feature set, ManageEngine simplifies visibility and control over critical IT operations. However, its breadth sometimes comes at the expense of depth and scalability.
This is part of a series of articles about ManageEngine applications manager
Key ManageEngine Limitations
While ManageEngine offers an IT management suite, there are some notable limitations that users should consider when evaluating the platform for their needs. These limitations are taken from the G2 platform:
-
- Cost structure: The licensing is based on the number of technicians rather than end users, which may not align with the needs of some organizations.
-
- Outdated user interface: The user interface can appear old-fashioned and may be less intuitive compared to more modern IT management tools, particularly for new users.
-
- Slow network scans: Asset network scans can sometimes take a considerable amount of time, which may slow down IT operations.
-
- Automation challenges: The platform’s scripting capabilities can be complex and challenging to use for automation.
-
- Limited software integration: Adding software packages that are not pre-included in ManageEngine can be a slow process, requiring approval before they can be integrated into the platform.
-
- Customization constraints: While the platform offers customization options, it has limitations. The console cannot be fully modified according to end-user requirements and customization features can be difficult to deploy.
-
- Lack of custom reports: Some users find it difficult to generate customized reports directly within ManageEngine, often requiring external tools like Analytics Plus for tailored reporting.
-
- Poor support for basic issues: The level-zero support for end users has been criticized for being unresponsive.
Notable ManageEngine Alternatives
In light of the above limitations, many organizations are seeking alternatives to ManageEngine. Here are some popular options.
1. Faddom
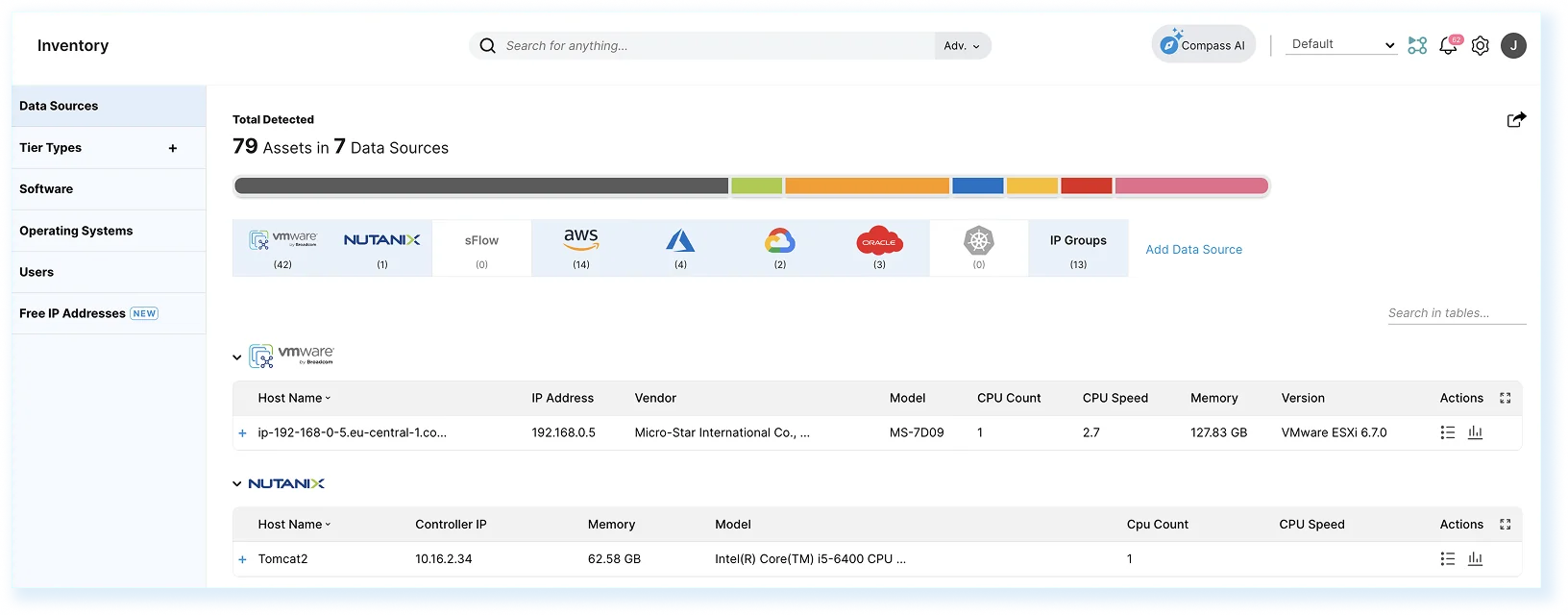
Faddom is an agentless application dependency mapping platform that gives IT teams a complete, real-time view of their on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. It automatically discovers servers, business applications, and dependencies to eliminate blind spots, uncover shadow IT, and strengthen segmentation. Designed for speed and simplicity, Faddom deploys in under 60 minutes without agents or active scans, runs with minimal resources, and delivers continuously updated topology maps that support change management, migration projects, security, and performance optimization.
-
- Agentless & Fast Deployment: Install and start mapping your infrastructure in less than an hour without agents or complex configurations.
-
- Real-Time Visibility: Continuously updated maps of servers, business applications, and traffic flows for accurate documentation and faster troubleshooting.
-
- Change Management: Assess risks before changes, track impacts afterward, and reduce downtime.
-
- Segmentation & Security: Identify risky east-west traffic and shadow IT to strengthen defenses.
-
- Performance & Optimization: Detect and resolve application and network bottlenecks before they affect users.
-
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: Lighthouse AI highlights unusual traffic behavior, from security threats to outages, without manual thresholds.
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: Lighthouse AI highlights unusual traffic behavior, from security threats to outages, without manual thresholds.
2. ServiceNow IT Service Management
ServiceNow ITSM is an enterprise-level platform to help organizations deliver resilient IT services. It aims to simplify operations by automating IT processes with AI and machine learning. ServiceNow consolidates service instances on a single system, making it easier for IT teams to manage and resolve issues.
Key features include:
-
- Consolidated IT services: Integrates multiple IT services into a unified system for easier management.
-
- AI and automation: Uses AI and machine learning to automate processes and improve efficiency.
-
- Performance analytics: Provides insights to anticipate trends and optimize resource allocation.
-
- Incident management: Routing and collaboration tools help resolve issues faster.
-
- CMDB (configuration management database): Tracks IT service dependencies and relationships for better continuity.
Source: ServiceNow
3. Jira Service Management
Jira Service Management is a service management platform that enables teams to deliver seamless service experiences. It brings together Dev, IT, and business teams on a single platform, allowing them to collaborate and resolve issues faster.
Key features include:
-
- AI-powered automation: Predicts issues and automates resolutions, turning insights into actionable steps.
-
- SLA management: Ensures timely response and resolution through service level agreements.
-
- Chat integration: Enables communication with support teams for faster resolutions.
-
- Self-service portal: Provides an interface for end-users to resolve issues independently.
-
- Assets management: Tracks and manages assets, linking them to service requests.
Source: Atlassian
4. Freshservice by Freshworks
Freshservice by Freshworks is an IT service management platform to simplify and accelerate service delivery for IT and business teams. It combines ITSM tools with AI to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights.
Key features include:
-
- Freddy AI: An AI assistant that supports self-service for employees, supports IT agents, and provides insights for leaders.
-
- IT service management: Automates workflows, provides analytics, and boosts service desk performance to improve IT efficiency.
-
- IT asset management: Tracks hardware, software, and cloud tools with an auto-updating CMDB.
-
- Omnichannel support: Lets employees request help through any channel, alerting agents for faster response and resolution.
-
- IT operations management: Offers visibility into IT operations with alerts for quicker issue resolution.
Source: Freshworks
5. SolarWinds Service Desk
SolarWinds Service Desk is a cloud-based ITSM platform to improve productivity and accelerate issue resolution. It simplifies IT operations, aiming to improve service delivery and user experience.
Key features include:
-
- AI-powered incident management: Automates ticket assignment, monitors ticket sentiment, and assists agents by providing suggested solutions.
-
- Multi-channel support: Allows users to engage with support teams via web, email, Teams, Slack, or mobile app.
-
- IT asset management: Enhances visibility and compliance with tracking and management of hardware and software assets.
-
- Configuration management database (CMDB): Tracks and understands the relationships between infrastructure components and business applications.
-
- Change management: Implements structured processes to reduce risk and improve the stability of IT changes.
Source: SolarWinds
6. SysAid
SysAid is an IT service management platform to improve productivity and service delivery. With agentic service management, it uses generative AI to automate tasks, reduce manual work, and help IT teams to deliver faster support. The platform supports ITSM functions like incident management, service request fulfillment, and change management.
Key features include:
-
- Agentic AI: Automates ITSM tasks, cutting mean time to resolution (MTTR).
-
- Incident management: Uses AI to automatically detect, route, and resolve incidents, supporting issue resolution with SLA awareness.
-
- Service request fulfillment: AI-powered routing and tracking of service requests help deliver quicker resolutions.
-
- Problem management: Detects recurring issues, suggests fixes, and helps prevent them from happening again by analyzing ticket patterns.
-
- Change management: Predicts risks and automates low-risk approvals, reducing surprises during rollouts.
Source: SysAid
7. LogicMonitor
LogicMonitor is a network monitoring platform to give enterprises visibility into their network infrastructure. By monitoring the health and performance of network devices, it helps IT teams detect and resolve issues quickly, ensuring network operation. It has out-of-the-box integrations for brands like Cisco, Juniper, and Meraki.
Key features include:
-
- Auto-discovery of network devices: Automatically discovers network devices, including firewalls, routers, switches, and wireless devices.
-
- Unified network visibility: Provides insights into network performance and health through integrated network logs, metrics, and alerting thresholds.
-
- Topology mapping: Auto-generated, contextual topology maps visualize the relationships between infrastructure resources, helping to pinpoint issues faster.
-
- Troubleshooting: Offers visibility into network traffic and dependencies, enabling identification and resolution of performance bottlenecks and service disruptions.
-
- Device support: Monitors a variety of devices via SNMP, API, jFlow, NetFlow, sFlow, WMI, NBAR2, and IPFIX, supporting both on-premises and cloud-based networks.
Source: LogicMonitor
8. Intermapper
Intermapper is a network monitoring solution to provide visibility into the distributed IT environment. With its mapping and monitoring capabilities, it allows IT teams to map their network, track performance, and troubleshoot issues to ensure uptime.
Key features include:
-
- Network mapping: Automatically discovers and documents all IP-enabled devices in the network, creating color-coded network maps to visualize network health and performance.
-
- Real-time alerts: Sends alerts via text, email, sound, and other channels to notify users of issues.
-
- Customizable maps: Offers icons and layout options for creating dynamic maps that suit the IT environment, including hierarchical maps for monitoring of specific areas.
-
- Export options: Allows users to export network maps to Microsoft Visio and .SVG formats for further analysis and documentation.
-
- Network traffic monitoring: Provides insights into bandwidth usage by analyzing NetFlow, sFlow, and jFlow data.
Source: Fortra
Conclusion
Choosing the right IT management platform depends on an organization’s size, complexity, and specific operational needs. While ManageEngine offers a broad suite of capabilities, alternative solutions can provide deeper functionality, improved scalability, and more modern user experiences. Evaluating these options allows IT teams to align their tools with strategic goals and support the demands of increasingly dynamic and distributed IT environments.



