What Is NinjaOne?
NinjaOne is a cloud-based IT management platform for managed service providers (MSPs) and internal IT departments. It offers a unified interface for monitoring, maintaining, and supporting endpoints, whether on-premises or remote. The platform integrates multiple capabilities, including remote monitoring and management (RMM), patch management, mobile device management (MDM), endpoint security, and backup, under a single solution.
This allows IT teams to reduce operational complexity and administrative effort while increasing responsiveness. Unlike some legacy tools that require on-premises installations and separate modules for additional features, NinjaOne is intended for the cloud. This architecture supports modern workforces and remote management scenarios.
The platform aims to reduce time-consuming manual tasks by automating asset management, alerting, scripting, and remediation. Because of its modular approach and centralized dashboard, teams can simplify their workflows and scale their operations.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey NinjaOne Products
NinjaOne RMM
NinjaOne RMM (remote monitoring and management) is the core product of the NinjaOne suite. It enables IT teams to monitor endpoints in real time, deploy software, automate patching, and respond quickly to incidents across distributed environments. With customizable alerting and automated remediation, NinjaOne RMM helps IT staff address issues before users are affected.
Its agent-based approach provides live data on device performance, resource utilization, and security status without the need for constant on-site presence. The platform’s scripting engine supports numerous languages, making automation and routine task management efficient. IT teams can use pre-built scripts or develop custom automations for their organization’s needs.
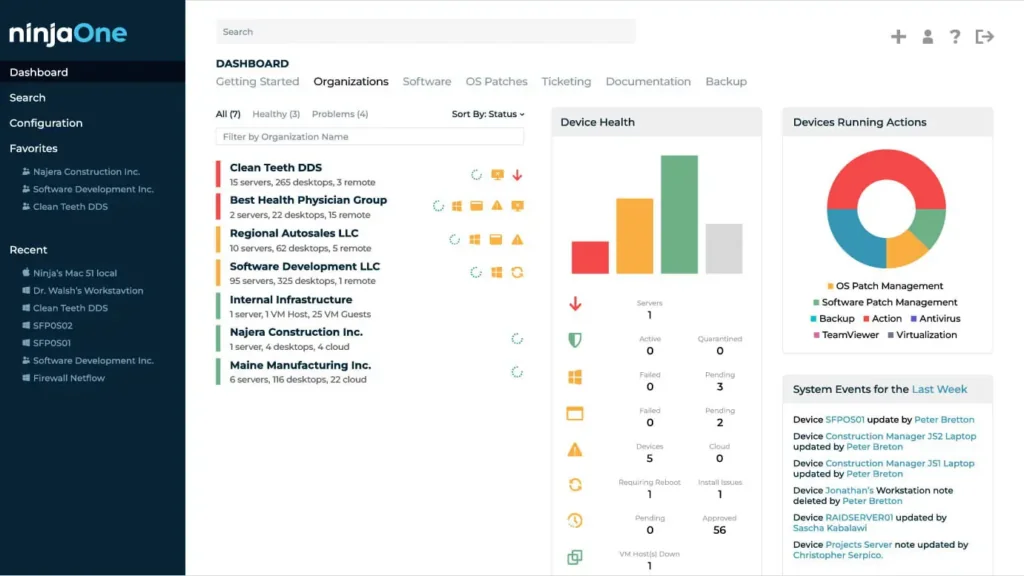
Source: NinjaOne
NinjaOne MDM
NinjaOne mobile device management (MDM) focuses on supporting a mobile workforce. With this module, IT administrators gain visibility and control over corporate-owned and BYOD (bring your own device) endpoints, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops, across platforms like iOS, Android, and Windows.
Device enrollment, configuration, policy enforcement, and security settings can be managed remotely from the NinjaOne dashboard. Although MDM is a legacy technology, its feature set includes remote wipe, lock, and location tracking, which aids in securing lost or stolen hardware.
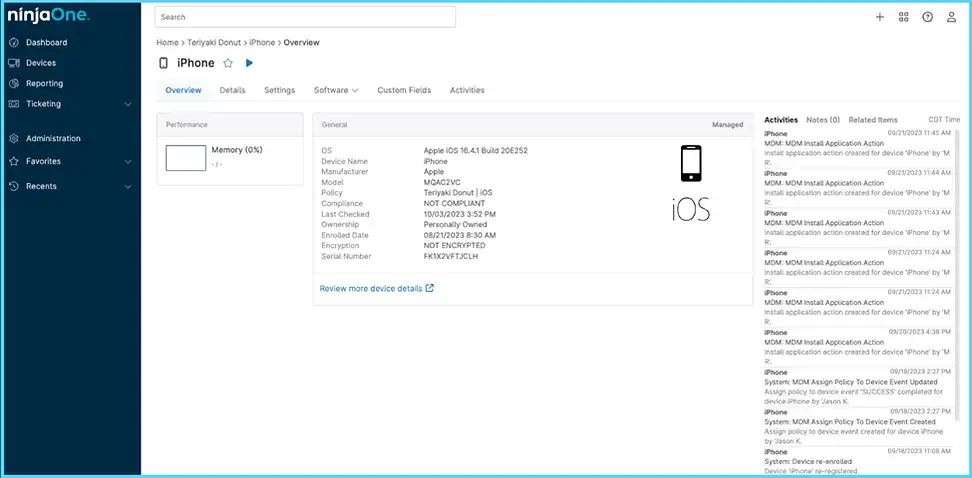
Source: NinjaOne
NinjaOne Endpoint Security
NinjaOne endpoint security integrates with the broader platform to provide defense against threats targeting endpoints. The solution includes anti-virus and anti-malware management, device encryption enforcement, and the ability to apply security patches and updates automatically.
By centralizing security controls, NinjaOne allows IT teams to manage and monitor their organization’s exposure from a single pane of glass. Security configurations can be standardized across all managed devices, ensuring that policy enforcement is consistent as devices move on and off the corporate network.
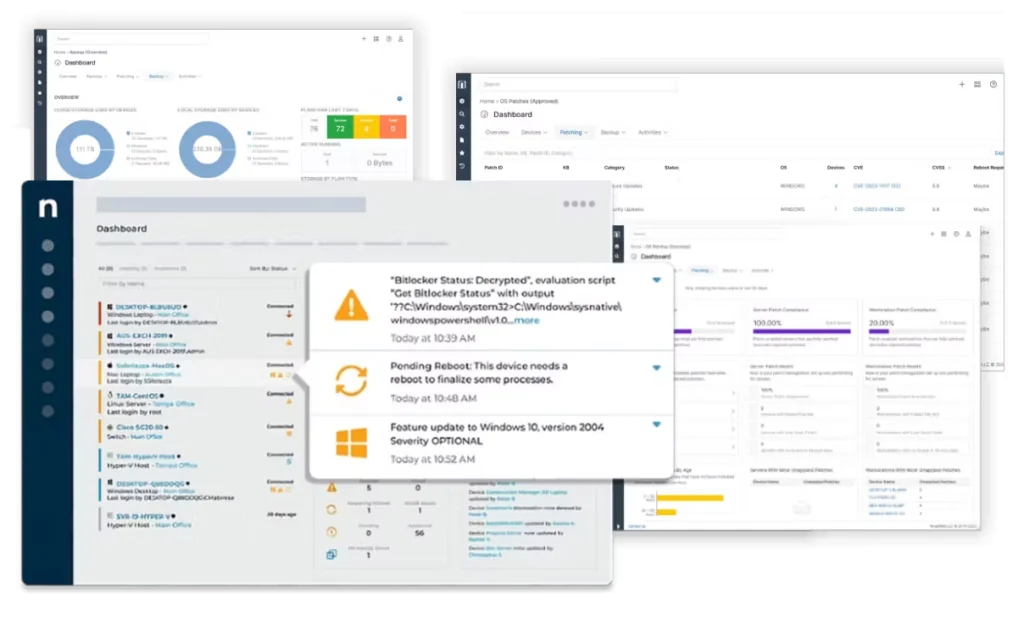
Source: NinjaOne
NinjaOne Patch Management
Patch management in NinjaOne automates the identification, deployment, and verification of software and operating system patches. The tool supports major platforms and third-party applications, allowing IT teams to control update scheduling and installation behavior. Automated patching helps organizations reduce vulnerabilities and maintain compliance without overburdening staff with manual processes.
Reporting features offer visibility into patch status, compliance rates, and deployment failures, allowing IT staff to identify gaps and remediate issues. NinjaOne Patch Management also supports custom patch approval workflows, so critical patches can be expedited while non-urgent updates are rolled out more cautiously.
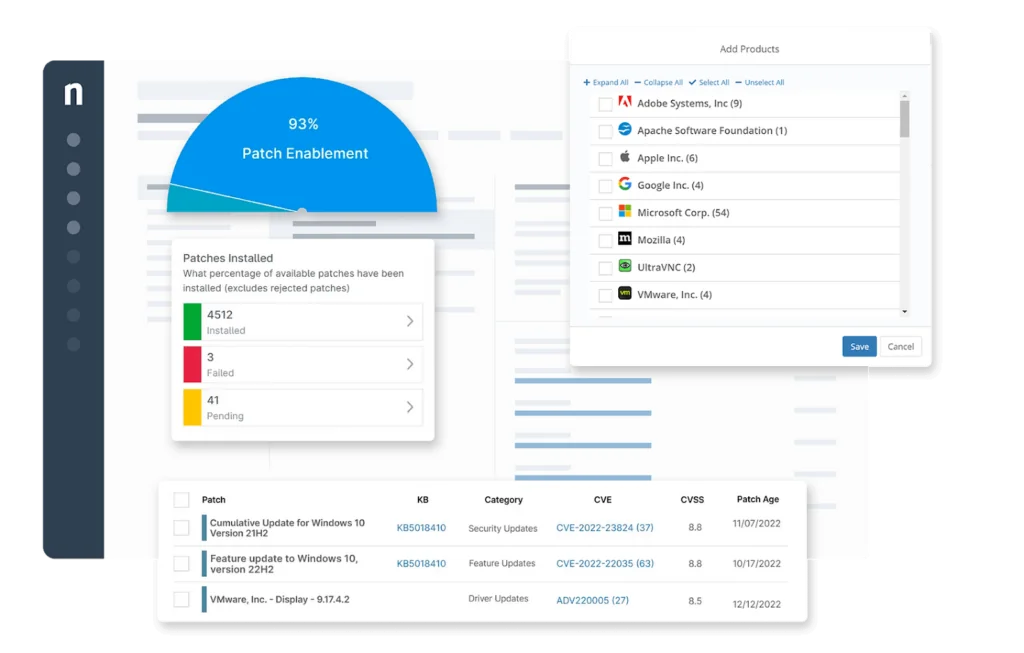
Source: NinjaOne
NinjaOne Pricing
NinjaOne uses a per-device pricing model, with costs determined by the number of endpoints under management. As organizations scale up, a tiered pricing structure provides volume discounts, lowering the per-device rate for larger deployments.
Typical pricing ranges from $2 to $4 per endpoint, with organizations managing 50 to 100 devices generally paying around $3.50 to $4 per device. On average, customers spend about $8,150 annually, though actual costs can vary between $1,500 and $19,000 depending on deployment size and selected features.
Pricing is also influenced by optional integrations with third-party tools such as TeamViewer, Splashtop, Webroot, Bitdefender, Malwarebytes, and StorageCraft. These integrations are available as add-ons and come with separate fees. However, support services are included at no extra cost.
Learn more in our detailed guide to NinjaOne pricing.
NinjaOne Limitations
While NinjaOne provides a user-friendly IT management platform, there are several areas where users have reported limitations that can affect usability and performance, especially in complex environments. These limitations were reported by users on the G2 platform:
- Limited role-based access control (RBAC): The current RBAC model lacks granularity. MSPs that co-manage environments with client IT teams often need more precise permission configurations, but cannot create fully custom roles. This forces reliance on workarounds that reduce operational clarity.
- Inefficient search functionality: The platform’s search tool can make it difficult to quickly find specific settings or features. A more responsive search capability would improve navigation and reduce wasted time.
- Basic mobile notification customization: Notification settings in the mobile app are not flexible enough to filter and prioritize alerts. Users cannot easily tailor notifications to focus on critical issues, which can lead to information overload.
- No end user knowledge base integration: There’s no built-in knowledge base for end users. Automated suggestions for articles during ticket creation or updates would empower users to self-resolve simple issues and reduce support load.
- Okta integration is minimal:
While user import from Okta is supported, deeper integration like setting NinjaOne as a fully managed app within Okta is not available. This limits single sign-on and access control capabilities. - Permissions system is hard to understand: The permissions matrix is difficult to interpret, often requiring trial and error to achieve the desired access levels. New features sometimes bypass custom permission setups, leading to unexpected access.
- Limited reporting and insight: Although reports look polished, they lack depth. For instance, patch reporting doesn’t provide actionable insight, and there’s limited ability to create detailed or compliance-focused reports.
- Basic automation capabilities: While scripts are easy to run, building cross-system automations remains largely manual. There’s no native support for complex conditional workflows across multiple modules.
- Remote access tool lacks advanced features: The built-in remote access tool works reliably but misses features like refined multi-monitor control, session logging, and file transfer queuing found in other solutions.
- Slow implementation of user feedback: Although the team is receptive to suggestions, new features and improvements are rolled out slowly. This reduces responsiveness to evolving user needs.
- Linux support is limited: Remote access to Linux GUIs like GNOME is not yet possible, and Linux-based systems are not supported for backup, limiting the platform’s reach in mixed-OS environments.
- Unreadable notification emails: Email alerts, such as those for Active Directory events, are poorly formatted and hard to scan. Critical information often appears in large, unstructured blocks of text.
- Missing key integrations: Some desired integrations, like Jira and deeper SentinelOne support, are not yet available. In particular, more automated vulnerability patching and status syncing with SentinelOne would improve efficiency.
Notable NinjaOne Alternatives
1. Faddom

Faddom is an agentless application dependency mapping (ADM) platform that provides IT, Security, and Cloud teams with real-time visibility into how business applications, servers, and infrastructure interact across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. While endpoint tools focus on device health and remediation, Faddom reveals the live behavior of the environment itself, exposing application flows, dependencies, and risk paths that remain hidden at the endpoint level. The best part? Faddom can discover your environment in less than 60 minutes!
Key Capabilities
- Real-time ADM: Automatically maps how business applications communicate across servers, networks, and environments without relying on agents or static configuration data.
- Agentless, continuous discovery: Passively observes network traffic to maintain accurate visibility as environments change, without impacting performance or requiring endpoint deployment.
- Operational impact awareness: Shows which applications and services will be affected by infrastructure changes, reducing outages caused by hidden dependencies.
- Security context beyond endpoints: Identifies unexpected connections, risky traffic paths, and exposure points that endpoint tools cannot detect on their own.
- Environment optimization insights: Highlights unused, underutilized, or overprovisioned servers based on actual traffic and dependency usage, rather than assumptions.
Fill out the form on the right to see how Faddom complements endpoint management tools!

2. Atera RMM

Atera RMM is a cloud-based remote monitoring and management platform for IT professionals and MSPs who need fast deployment and operational flexibility. It consolidates IT management functions, allowing teams to monitor, patch, automate, and remotely manage devices from a centralized dashboard.
Key features include:
- Unified remote access: Supports AnyDesk, Splashtop, TeamViewer, and ScreenConnect for secure, on-demand endpoint access
- Real-time monitoring: Provides instant visibility and alerts to track system performance and detect issues early
- Automated patch management: Ensures systems stay secure and compliant with minimal manual intervention
- IT automation and scripting: Enables scheduled tasks and custom scripts to simplify recurring maintenance
- Software and network management: Includes application deployment, network monitoring, and alert configuration
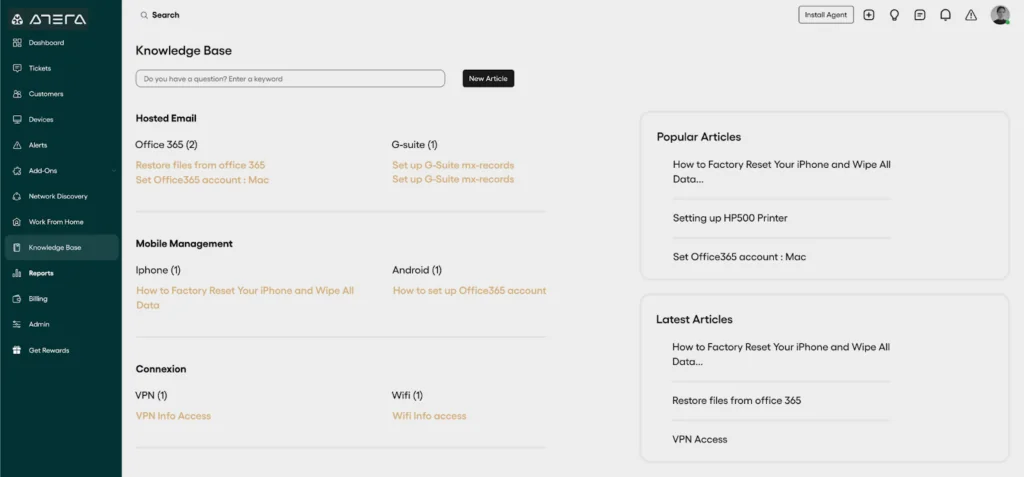
Source: Atera
3. Microsoft Intune

Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution that helps organizations manage user access, secure data, and simplify device and app administration across diverse environments. It supports hybrid and remote workforces by allowing IT teams to manage corporate and personal devices, enforce policies, and maintain security without requiring on-premises infrastructure.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Supports Windows, macOS, Linux (Ubuntu), Android, iOS, and AOSP devices, both corporate-owned and BYOD
- App lifecycle management: Enables deployment, update, protection, and removal of Microsoft 365, Win32, LOB, and third-party apps
- Policy automation: Delivers configuration, compliance, security, and Conditional Access policies to users and devices over the internet
- User self-service: Provides a customizable Company Portal for password resets, app installation, and group management
- Security integration: Works with Microsoft Defender and other mobile threat defense solutions to automate threat response and endpoint protection
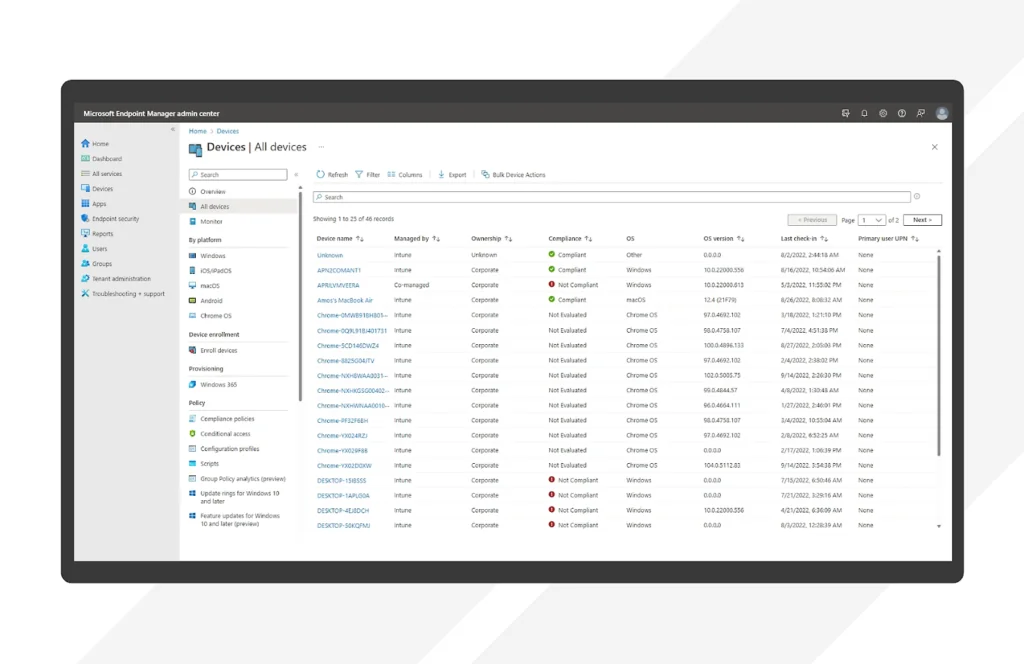
Source: Microsoft
4. ManageEngine Endpoint Central

ManageEngine Endpoint Central is a unified endpoint management and security (UEMS) platform to help organizations secure, automate, and simplify IT operations across their device landscape. It provides a centralized console to manage configurations, enforce security policies, automate patching, and monitor the digital employee experience.
Key features include:
- Automated patching: Deploy OS and third-party application updates across Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices to reduce vulnerabilities
- Threat defense: Detect, audit, and remediate endpoint threats using continuous monitoring and 75 CIS security benchmarks
- Ransomware protection: Identify root causes, enable rapid incident response, and prevent repeat attacks with layered protection mechanisms
- IT asset management: Track hardware, software, licenses, and warranties, with alerts for changes and usage patterns
- Mobile device management (MDM): Centrally manage mobile apps, content, email, and compliance policies across mobile endpoints
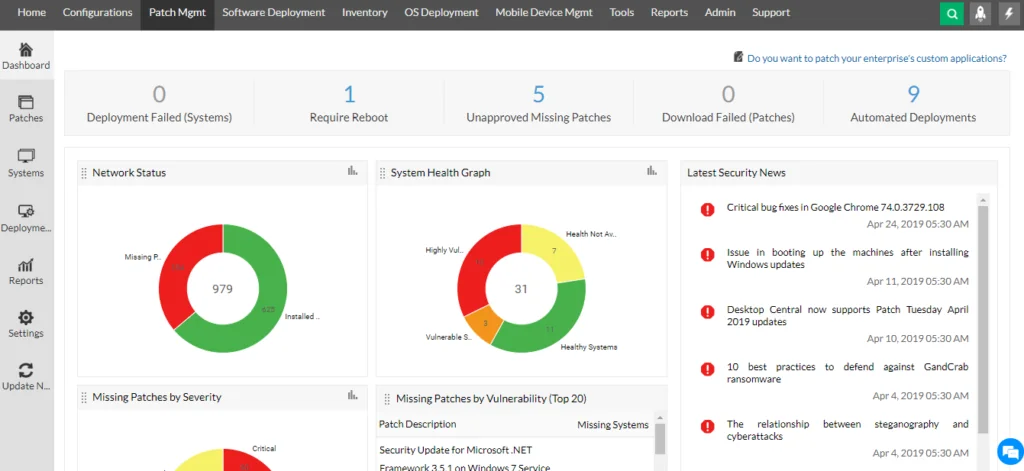
Source: ManageEngine
5. SolarWinds RMM

SolarWinds RMM is a remote monitoring and management solution to help IT teams and managed service providers (MSPs) maintain business continuity, manage distributed infrastructure, and support end users across multiple locations. It provides monitoring, security oversight, and automated alerting from a web-based interface. It helps IT teams detect issues, reduce response time, and maintain service reliability.
Key features include:
- Remote infrastructure monitoring: Track and manage VPN connections, remote endpoints, and network health across locations from a central dashboard
- Web-based admin console: Access systems, services, and diagnostics via a responsive browser interface
- End-user support tools: Remotely troubleshoot and resolve device issues, helping users transition to remote work environments
- Business continuity support: Visualize system status, gather performance data, and maintain uptime across distributed infrastructure
- Security oversight: Monitor remote access activity, enforce policies, and gain visibility into user access across the enterprise.
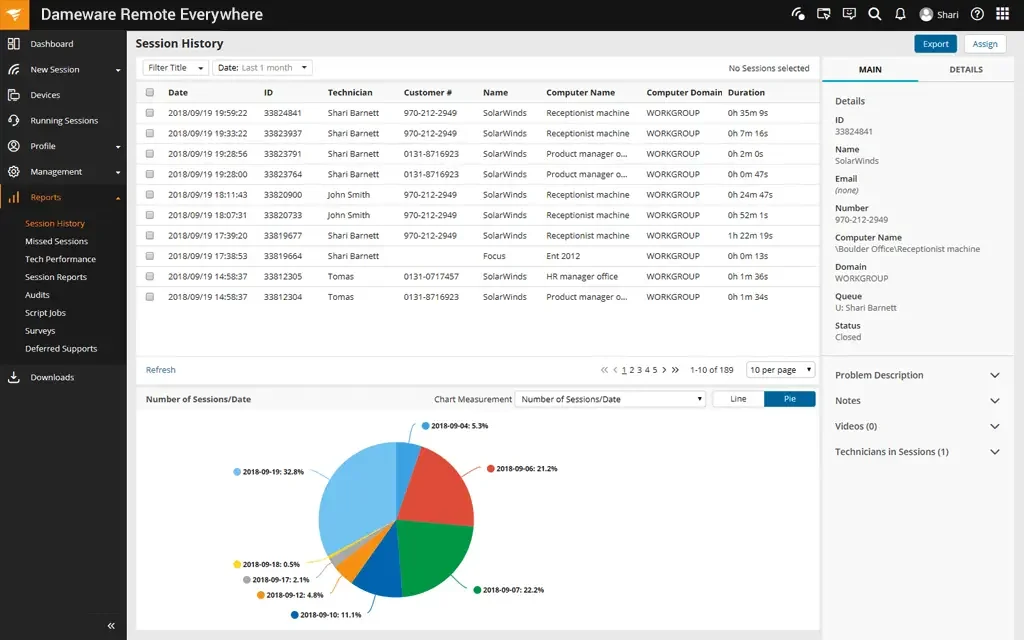
Source: SolarWinds
Learn more in our detailed guide to NinjaOne alternative
Conclusion
Centralized IT management platforms are critical for simplifying operations, maintaining security, and supporting distributed workforces. By integrating monitoring, automation, patching, and endpoint control into a unified system, IT teams can reduce complexity and improve service delivery. These solutions enable faster response times, proactive issue resolution, and better alignment with compliance requirements. As IT environments grow more diverse and remote work becomes standard, having a scalable, cloud-based platform is key to maintaining operational resilience and visibility.




