What Is Ivanti CMDB?
Ivanti CMDB (Configuration Management Database) is a centralized system for managing configuration items (CIs) across an organization’s IT environment. It provides a structured interface for viewing, editing, creating, and managing the full lifecycle of CIs such as hardware, software, and services.
Users can access the CMDB through the Ivanti CSM Desktop Client or Browser Client, enabling both detailed views and bulk operations on CI records. The interface supports filtered and searchable views, helping users locate records quickly using criteria like CI type, asset tag, hostname, or customer.
Records can be displayed in a grid for bulk actions or accessed individually for detailed updates. Through this system, organizations can maintain an accurate inventory of assets, understand dependencies, and ensure accountability by assigning ownership of each CI.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Features of Ivanti CMDB
Ivanti CMDB offers a range of features designed to simplify CI management and improve visibility into IT assets.
1. Advanced Search and Filtering
Ivanti CMDB offers multiple ways to search for configuration items. Users can perform quick searches to locate all CIs or narrow results using filters such as specific keywords, timeframes, or associated customers. Saved Searches allow frequently used queries to be stored and reused, which helps reduce manual filtering for routine tasks. These saved queries can also be used in reports and dashboards for automated monitoring.
2. CI Form and Business Object Customization
The system uses a dedicated Configuration Item Business Object that can be customized to track only the data relevant to the organization. Each CI is managed through a form that includes key fields like CI type, current status, primary user, and asset owner. The form also displays linked records, such as related events or installed software, using a dynamic arrangement section. This setup supports both structured data entry and clear visibility into associated relationships.
3. Workflow and Automation
Ivanti CMDB includes workflows to manage the lifecycle of configuration items from creation to retirement. CIs can move through various statuses using built-in processes or One-Step Actions, which automate common tasks like assigning ownership or sending notifications. Automation processes can also trigger emails and alerts based on defined rules, streamlining operational responses and reducing manual overhead.
4. Ownership and Relationship Management
Each configuration item can be assigned a primary user, such as a technician or end user, to ensure accountability and traceability. The system supports linking child records to parent CIs, enabling visibility into related components or services like installed software or system drives. This relationship mapping is reflected in the UI and helps maintain context when viewing or updating records.
5. Reporting and Dashboarding
Ivanti CMDB provides real-time dashboards to monitor key metrics, such as the number of assets by type, assets in repair, or CI events grouped by type. Reports can be generated to show up-to-date statistics across hardware, software, and vendor-based categorizations. These tools help stakeholders track trends, manage inventory, and make data-driven decisions about IT assets.
Limitations of Ivanti CMDB
While Ivanti CMDB provides configuration management features, there are several limitations that can affect usability, customization, and long-term maintenance. These limitations were reported by users on the G2 platform:
- Sparse documentation: Official documentation is limited, leaving gaps that require reliance on support desks or community forums.
- Outdated backend: The platform still uses SOAP APIs instead of REST, making integrations less straightforward. The backend feels complex and requires rework for easier configuration management.
- Steep learning curve: New users often find the system difficult to master, especially when trying to unlock its full potential.
- Disjointed modules: Some modules feel inconsistent in design and usability, as they were developed by different teams.
- Complex customization: Customizing workflows or features takes more time and effort than anticipated, delaying service improvements.
- Overengineered workflows: Simple processes often require multiple steps, making tasks slower compared to other service management tools.
- Cluttered interface: The admin and analyst views feel dated and visually crowded, reducing ease of navigation.
- Browser limitations: The web interface relies heavily on JavaScript, which breaks basic browser functions like opening multiple tabs or sending direct links. Cross-browser compatibility is also inconsistent.
- Accessibility gaps: Features such as support for visually impaired users and browser accessibility tools are not well supported.
- Long implementation times: Deployments can take years and require extensive support from partners and Ivanti itself before the system is stable.
- High complexity for non-technical staff: The broad feature set makes it overwhelming for teams without technical expertise, requiring significant training.
- Slow feature activation: The wide range of features and fields leads to delays in rolling out new configurations or service offerings.
Notable Ivanti CMDB Alternatives and Competitors
1. Faddom

Faddom is an agentless, real-time application dependency mapping platform that provides organizations with complete visibility into how business applications, servers, and infrastructure interact across hybrid and multicloud environments. By continuously mapping real dependencies, Faddom enables accurate CMDBs, safer change management, and informed infrastructure decisions without the need for manual input, agents, or disruptive scans.
Key capabilities:
- Agentless discovery: Automatically discovers servers, business applications, and communication flows without agents, credentials, or active scanning.
- Real application dependency mapping: Captures live, bidirectional dependencies based on actual traffic, not assumptions or static rules.
- Continuous CMDB enrichment: Populates and maintains accurate configuration items and relationships with continuously updated data.
- Change impact analysis: Shows upstream and downstream impact before changes are made, reducing risk and unplanned outages.
- Hybrid environment visibility: Provides a single, unified view across on-premises, cloud, multicloud and hybrid infrastructures.
- Operational clarity: Eliminates blind spots caused by undocumented connections, shadow systems, or outdated documentation.
To see how Faddom can improve CMDB accuracy, fill out the form on the right to book a demo!

2. ServiceNow CMDB

ServiceNow CMDB is designed as a single, trusted system of record for configuration items, helping organizations manage IT environments with accurate and continuously updated data. It connects systems across the enterprise, integrates with key IT sources, and provides tools for lifecycle management, automation, and risk analysis.
Key features include:
- CMDB workspace: A central interface for exploring data, monitoring activity, and ensuring accuracy of records.
- Service graph connectors: Certified integrations that bring in standardized data from external IT systems.
- Data acquisition tools: Automated population of CI records from multiple sources for a complete view.
- Visualization and reporting: Graphical mapping of business and technical relationships to show dependencies and impact.
- Trusted data curation: Continuous data quality checks to support AI-driven outcomes and compliance audits.
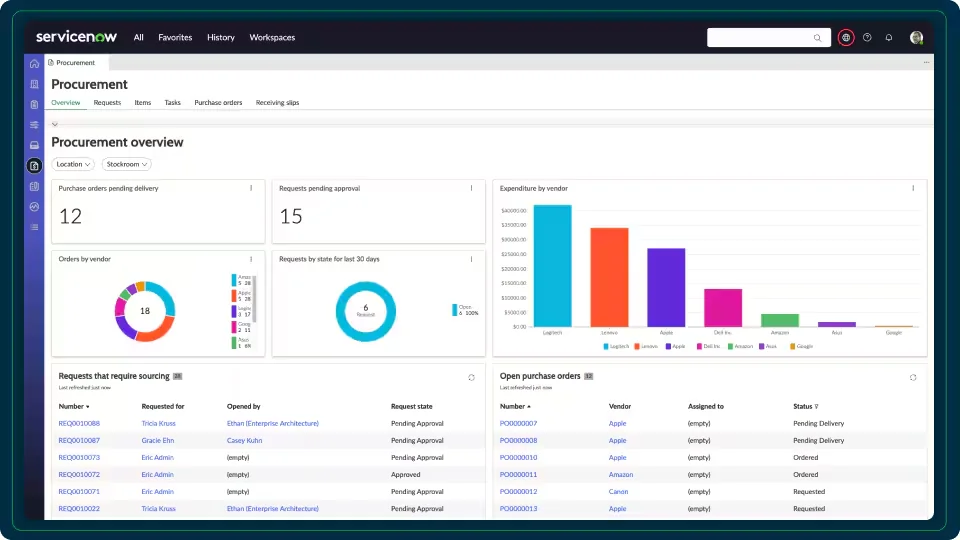
Source: ServiceNow
3. Device42 CMDB

Device42 CMDB aims to provide visibility into IT environments through automated discovery and dependency mapping. It serves as a central, authoritative source of configuration data that spans hardware, software, networks, and cloud resources.
Key features include:
- Automated discovery: Continuously captures configuration items across hybrid environments, from on-premises systems to cloud resources.
- Dependency mapping: Visualizes relationships among applications, services, and infrastructure to assess impact and accelerate root cause analysis.
- Complete inventory: Maintains up-to-date records of hardware, software, network devices, and cloud assets in a single source of truth.
- Data enrichment: Enhances discovered data with detailed attributes, ensuring accuracy for reporting and compliance.
- Configurable structures: Supports flexible reporting hierarchies and custom CI configurations to match organizational needs.
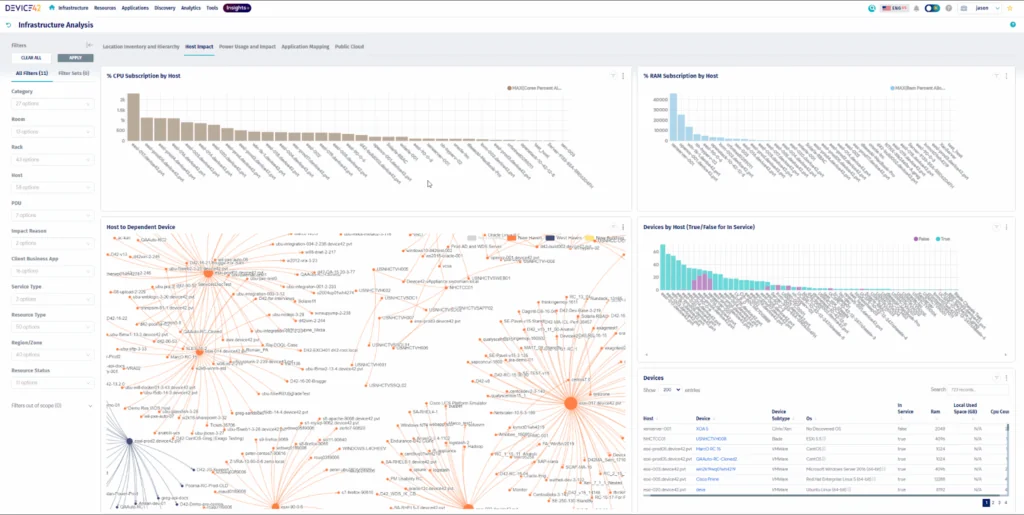
Source: Device42
4. BMC Helix CMDB

BMC Helix CMDB provides a business-aware, unified source of reference for assets and services across on-premises and cloud environments. It combines discovery, federation, and integration capabilities to automatically populate and update configuration data, ensuring accuracy at scale.
Key features include:
- Automated population: Integrates with BMC Helix Discovery, Client Management, and out-of-the-box connectors to keep CI data current.
- Data federation and integration: Combines data from multiple external sources through APIs and integration tools.
- Graphical visualization: Maps relationships and dependencies to provide context for impact analysis and troubleshooting.
- Business-aware context: Delivers KPI-driven insights for process success and data quality monitoring.
- Scalability: Maintains accurate service models for hundreds of millions of configuration items across hybrid infrastructures.
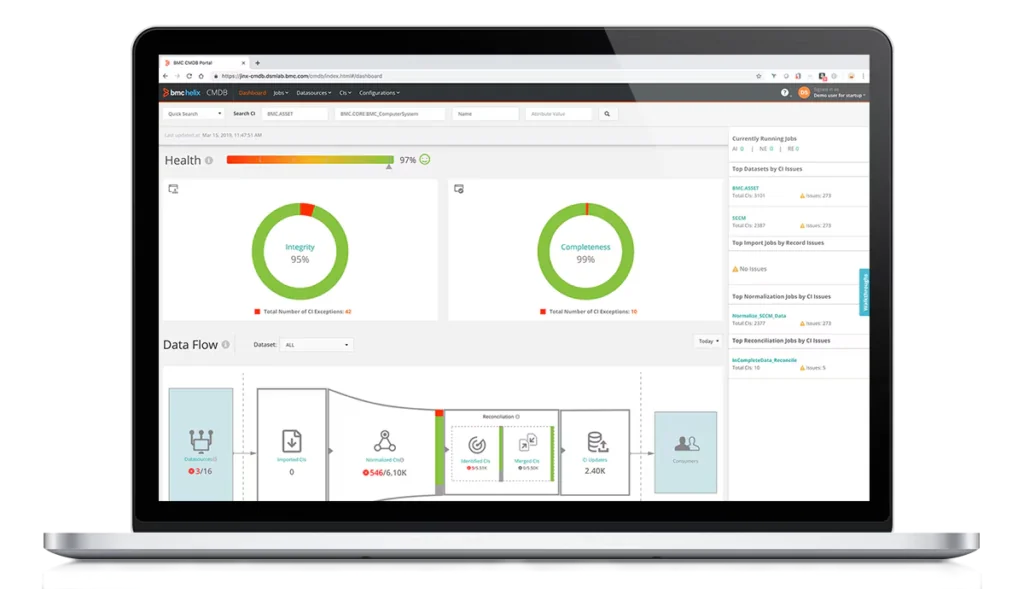
Source: BMC
5. Deepser CMDB

Deepser CMDB provides a centralized repository for physical and virtual assets in an organization, consolidating IT resources into a single, ITIL-aligned system. It allows businesses to map objects, assets, people, and processes, while linking dependencies to assess the impact of changes or failures.
Key features include:
- Customizable structure: Define classes, types, subtypes, and categories to build a CMDB hierarchy that matches organizational needs.
- Dynamic forms: Register and track assets using adaptable forms that can be tailored with drag-and-drop configuration.
- Data import: Populate the CMDB by importing spreadsheets in CSV or XML formats.
- Role-based visibility: Assign permissions to specific groups and users to control access to assets and data.
- Dependency mapping: Track relationships among assets, services, and processes to predict the impact of failures or upgrades.
Source: Deepser
Related content: Read our guide to Ivanti competitors (coming soon)
Conclusion
Ivanti CMDB provides organizations with a structured way to manage configuration items, but its complexity, integration challenges, and usability issues can limit efficiency. When selecting a CMDB solution, it’s important to balance flexibility with maintainability, ensuring that the system supports accurate data, simplified workflows, and scalable integrations. A well-implemented CMDB should act as a reliable source of truth, enabling better decision-making, reducing operational risks, and improving alignment between IT operations and business needs.






